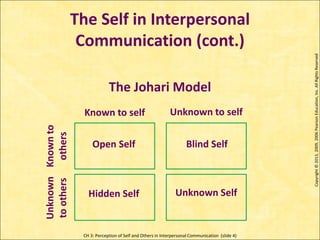
This document discusses perception of self and others in interpersonal communication. It covers how our self-concept is formed from four sources: others' images of us, social comparisons, cultural teachings, and self-evaluation. It also discusses the Johari window model of self-awareness and growing in self-awareness. Impression formation and management strategies that people use in communication are explained as well.