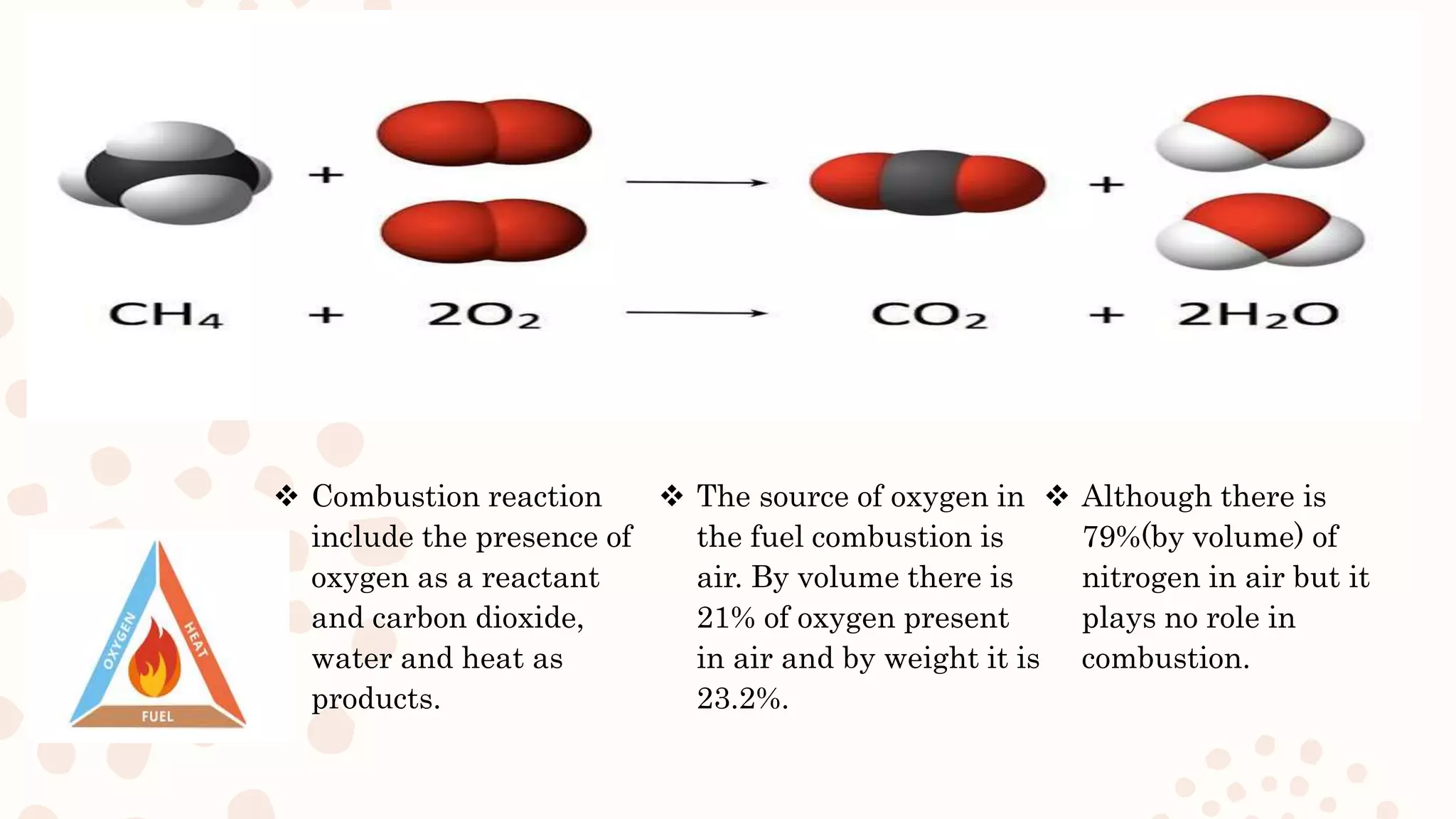
This document discusses combustion reactions of coal. It explains that combustion is a chemical reaction between a hydrocarbon and oxygen that produces carbon dioxide and water, along with the release of heat. The main combustible elements in coal are carbon, hydrogen, and small amounts of sulfur. When these elements combine with oxygen during combustion, energy is liberated. The document provides the chemical equations that describe the combustion reactions of these coal elements with oxygen, showing the reactants and products. It also discusses the role of air in providing the oxygen needed for combustion.