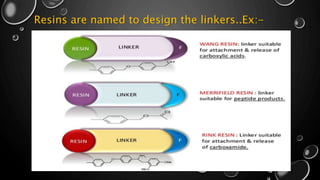
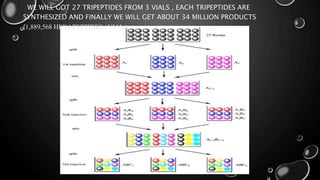
Combinatorial chemistry involves the simultaneous synthesis of large libraries of compounds under identical reaction conditions. It aims to reduce the time and cost of drug discovery by preparing many similar compounds at once rather than one at a time. Key techniques include solid phase synthesis using resin beads, and solution phase split-and-mix and parallel synthesis methods. Combinatorial libraries can contain thousands to millions of compounds and are screened to identify potential drug leads more efficiently than traditional synthesis.