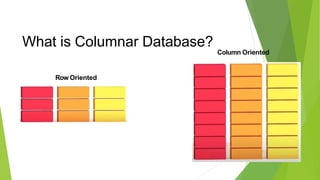
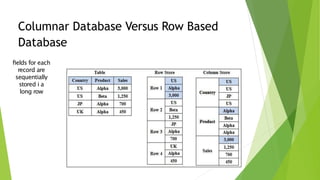
Columnar databases store data by column rather than by row. This allows for faster analytical queries on large datasets by minimizing the movement of read/write heads across disk drives. Columnar databases are well-suited for data warehousing and business intelligence tasks that require aggregating large amounts of data, while row-oriented databases are better for transactional applications that involve frequent updates to small subsets of data.