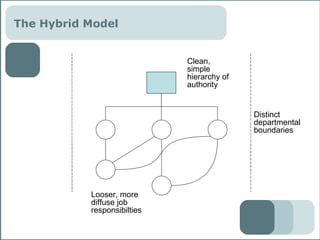
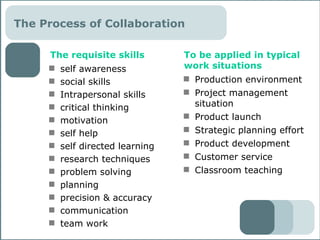
The document outlines a course on building collaborative environments in organizations. It discusses three models of collaboration with different leadership requirements: the traditional hierarchy model, the hybrid model, and the network model. It also identifies domains where these models could be explored, including production, project management, product launches, strategic planning, product development, customer service, and teaching. The document emphasizes training people and processes over technology for collaboration. It lists principles, skills, and tools for collaboration, as well as how to manage organizational change to support more collaborative work styles.