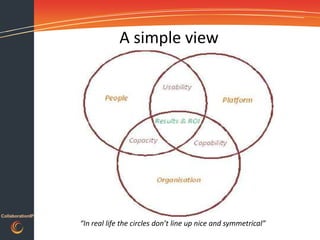
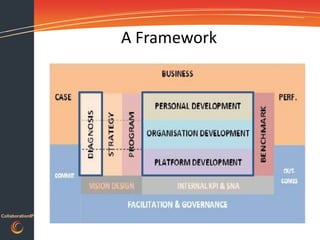
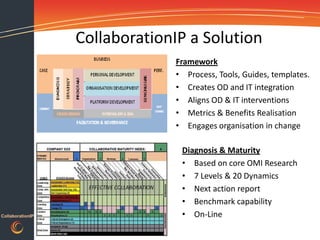
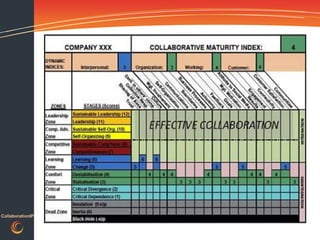
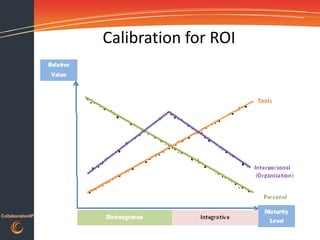
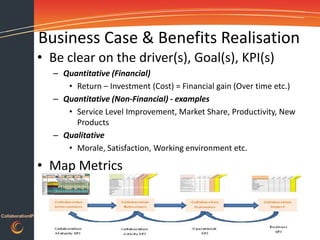
This document discusses gaining traction and results from collaboration platforms. It begins by defining collaboration and explaining why organizations consider it. Challenges to collaboration are outlined, including recognizing the human behaviors involved. How people and organizations learn and the influences on collaboration are described. A framework is presented for diagnosing an organization's collaboration maturity and designing integrated interventions across people, processes and technology to accelerate adoption of collaboration platforms and maximize return on investment.