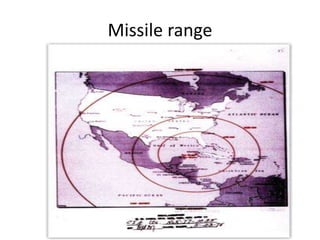
The document summarizes key events of the Cold War era Cuban Missile Crisis. In 1961, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev placed nuclear missiles in Cuba to counter U.S. threats. Three weeks later, American reconnaissance discovered the missiles. President Kennedy ordered a naval blockade of Cuba and threatened military action if Soviet ships approached. A confrontation was averted when Khrushchev agreed to remove the missiles to end the 13-day crisis, avoiding nuclear war but increasing Cold War tensions.