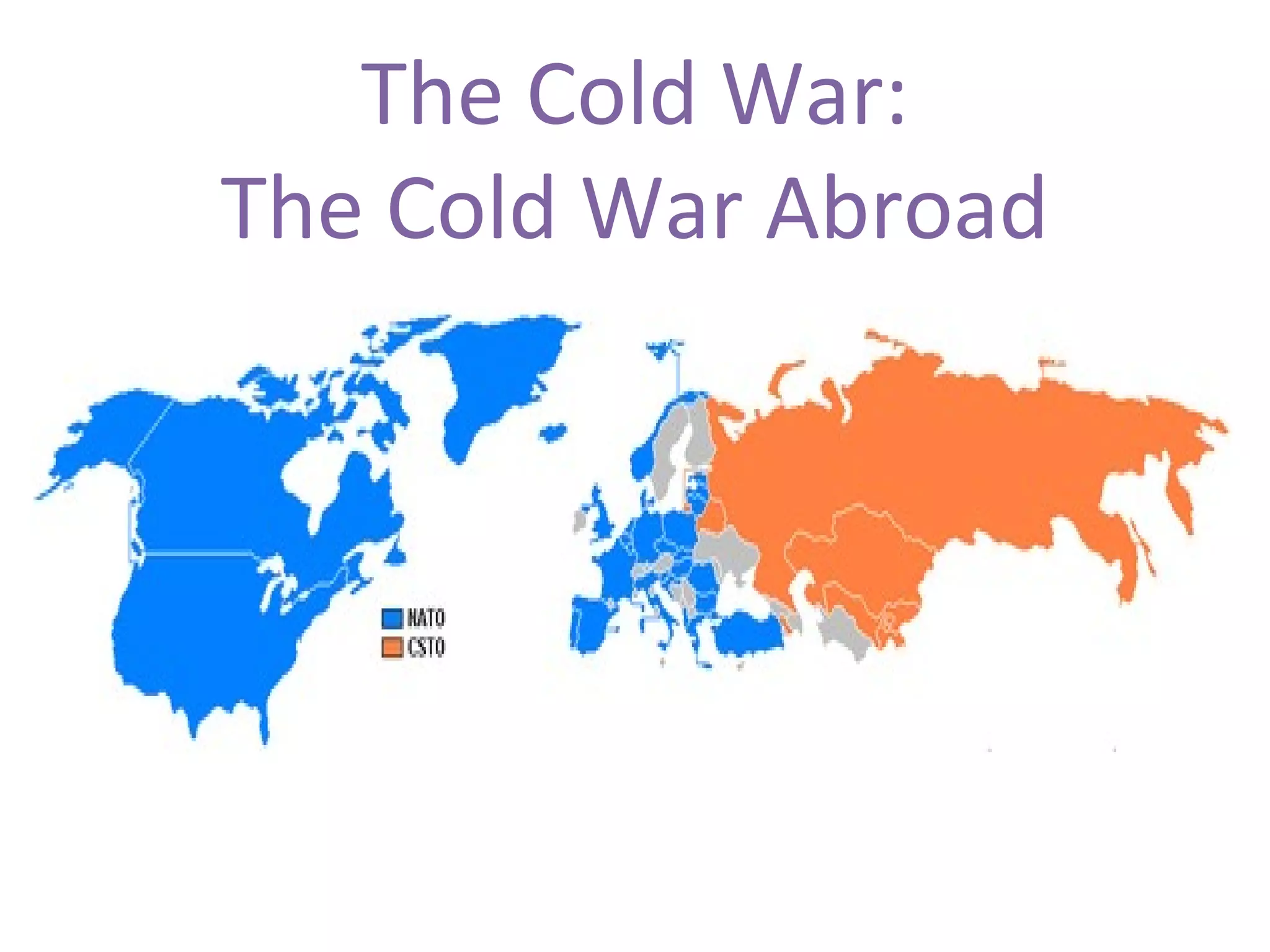
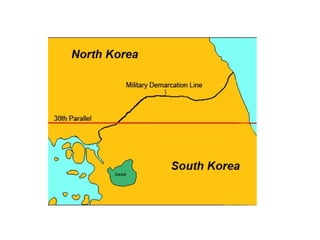
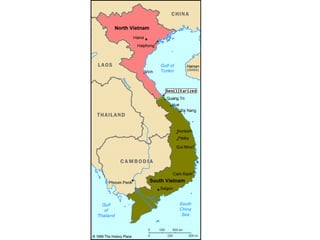
The Cold War had global impacts as the US and Soviet Union competed for influence. In Europe, the US provided economic support through the Marshall Plan to prevent countries from becoming communist. China allied with the Soviets after Mao's revolution in 1949. The Korean War in the 1950s and Vietnam War in the 1960s were proxy wars between the superpowers. Tensions escalated during the Cuban Missile Crisis, but began to thaw in the 1970s. Mikhail Gorbachev's reforms of glasnost and perestroika in the 1980s ultimately led to the collapse of Soviet communism and end of the Cold War in 1989, symbolized by the fall of the Berlin Wall.