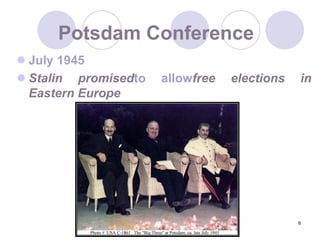
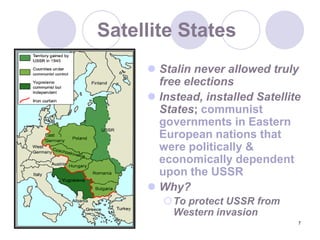
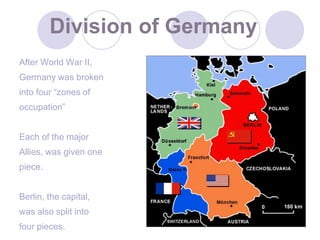
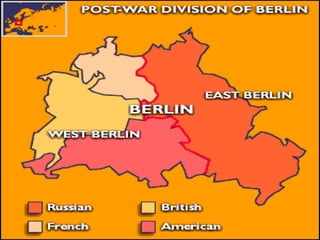
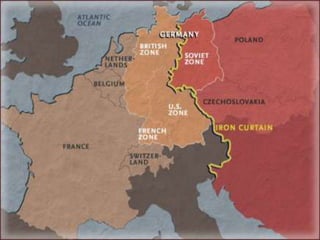
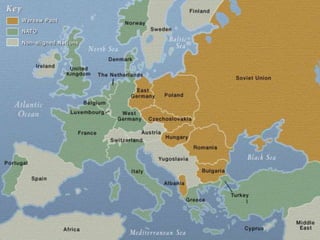
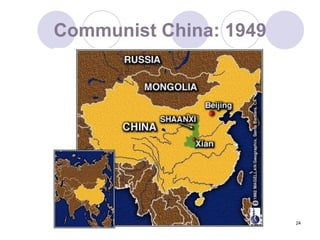
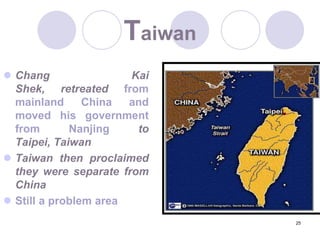
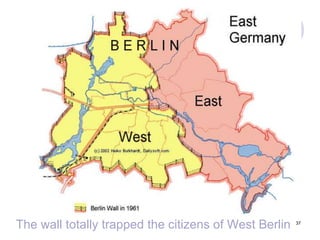
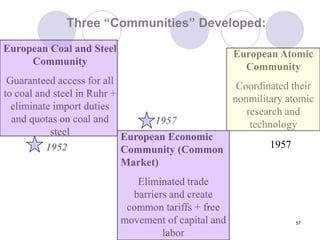
The Cold War began after World War II as tensions grew between the United States and Soviet Union. They emerged as rival superpowers with opposing political and economic ideologies of capitalism versus communism. This led to a long period of geopolitical tension and military buildup between the two nations and their respective allies that stopped short of direct armed conflict. Key events during the Cold War included the Marshall Plan and NATO helping rebuild and defend Western Europe, the division of Germany and Berlin, and escalating arms races and proxy wars. The space race and Cuban Missile Crisis heightened tensions. The Cold War ended in the late 1980s as communist governments fell in Eastern Europe and the USSR dissolved.