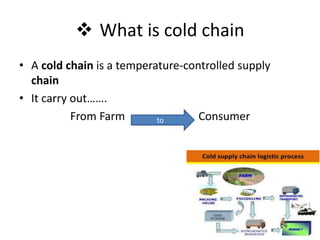
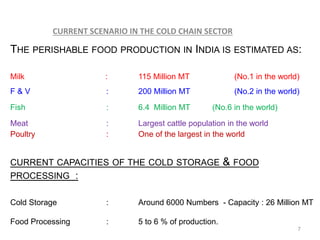
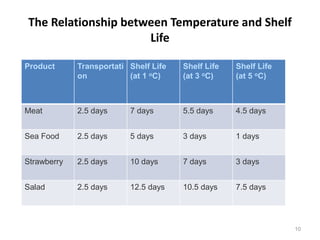
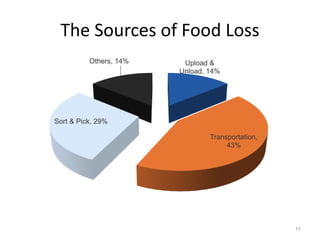
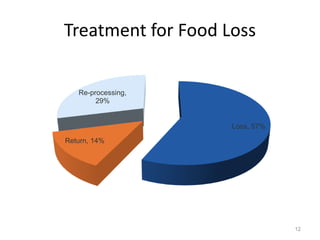
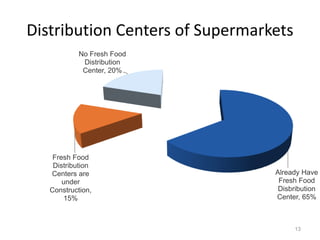
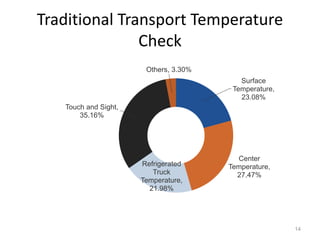
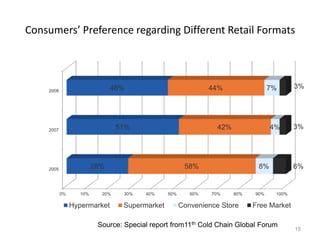
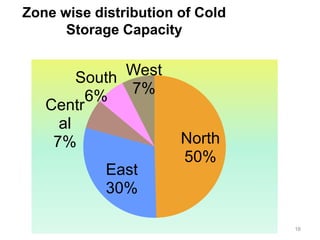
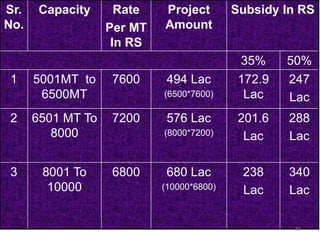
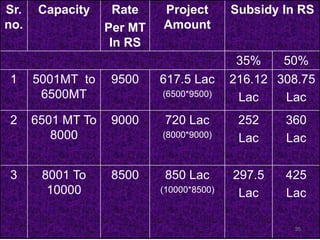
The document discusses the current status and development of cold chain management in India. It notes that while cold chains are well established for milk and dairy, they are still nascent for fruits and vegetables. This results in significant food wastage annually. Opportunities exist to improve cold storage infrastructure and modernize facilities to reduce losses. The government is taking steps like allocating funding to promote cold chain projects, but more investment is still needed to develop the sector fully.