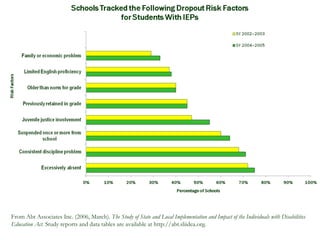
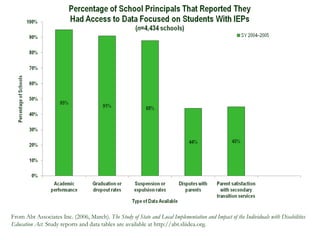
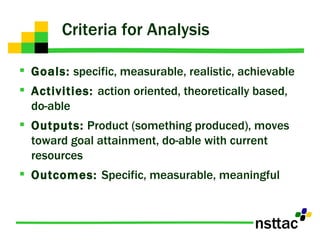
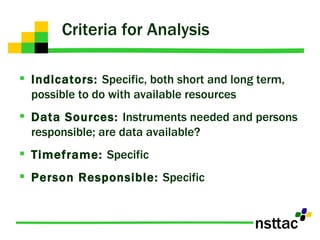
The document discusses the importance of program evaluation for transition educators and service providers. It provides examples of evaluation tools that can be used to evaluate different aspects of transition programs, including student development, interagency collaboration, family involvement, program structures, and team performance. Examples of evaluation tools include pre-post tests, questionnaires, self-assessments, and discussion questions. Criteria for effective evaluation include having specific, measurable goals and indicators to assess outcomes. Barriers to evaluation such as lack of resources or support are also addressed.