This document discusses cognitive radio in 5G networks. It begins with describing the evolution of mobile standards from 1G to 4G. It then introduces the concepts of 5G and cognitive radio. The key points are:
- 5G will provide very high data rates up to 1 Gbps and connect many more devices.
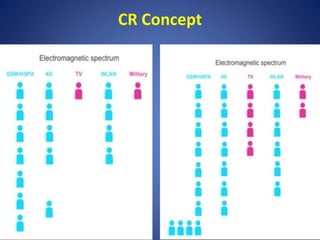
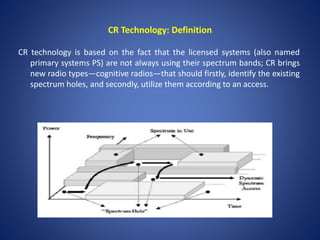
- Cognitive radio can improve spectrum efficiency by allowing unlicensed users to access licensed spectrum holes.
- The document proposes a cognitive radio based 5G network that can integrate various wireless technologies and help manage network complexity using cognitive radio's abilities.