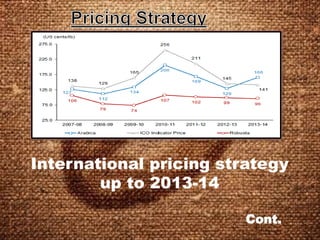
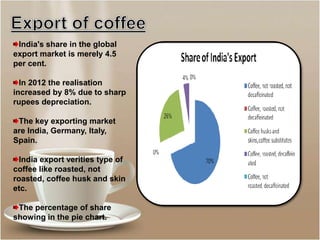
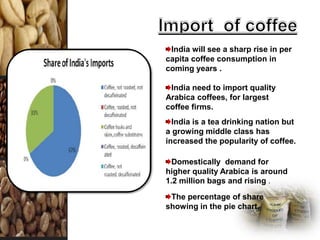
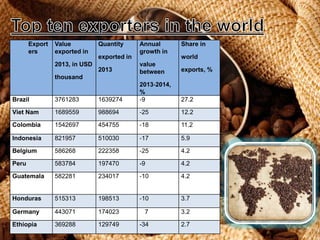
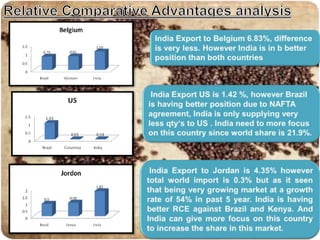
The document discusses the coffee sector in India. It notes that India is the 6th largest producer of coffee in the world. The main coffee growing states are Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Orissa, which contribute about 80% of total production. It also discusses India's exports and imports of coffee, identifying key markets. It analyzes opportunities for India to expand exports and diversify products to higher value markets. Government policies to promote the coffee sector are also summarized.