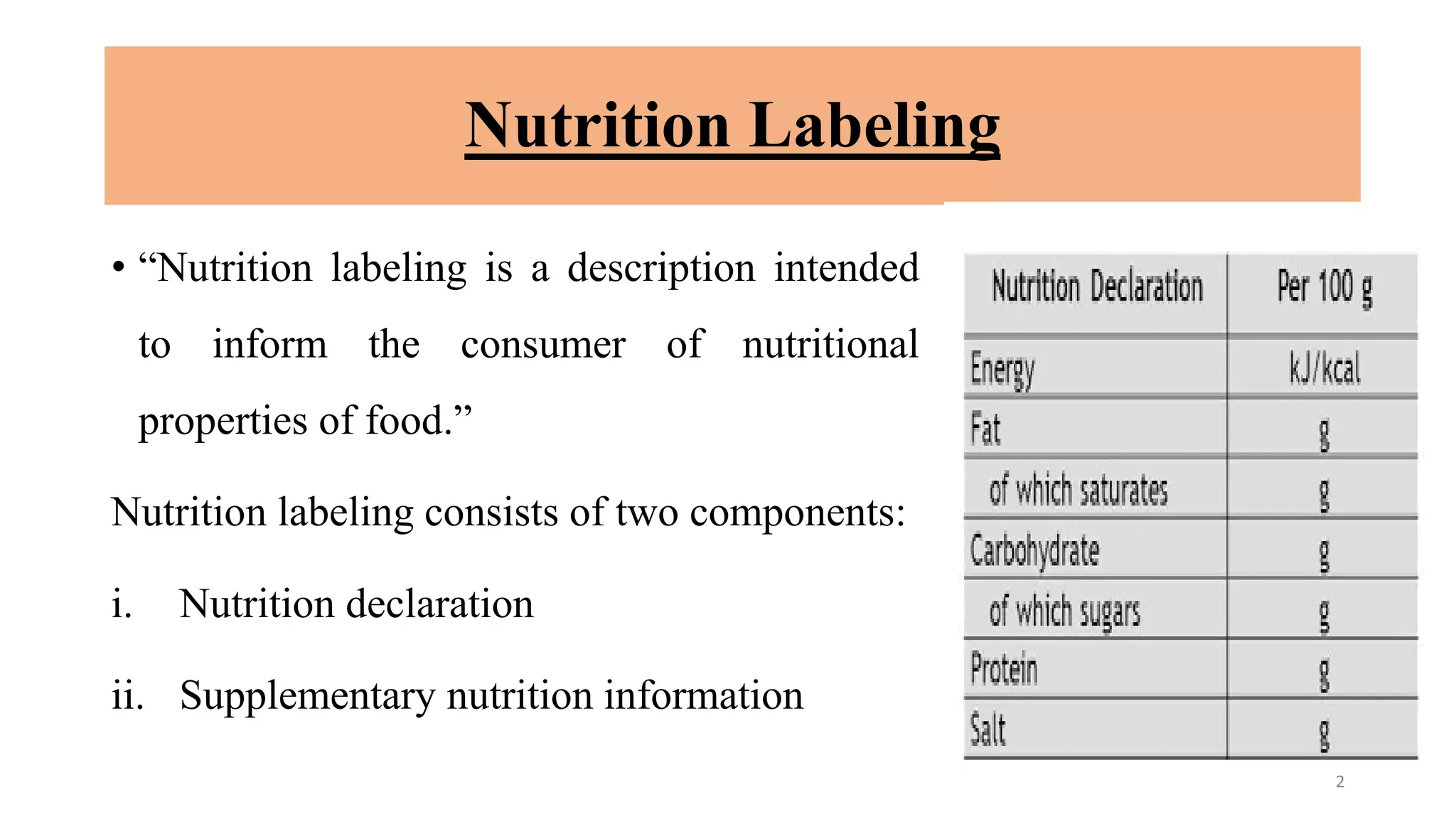
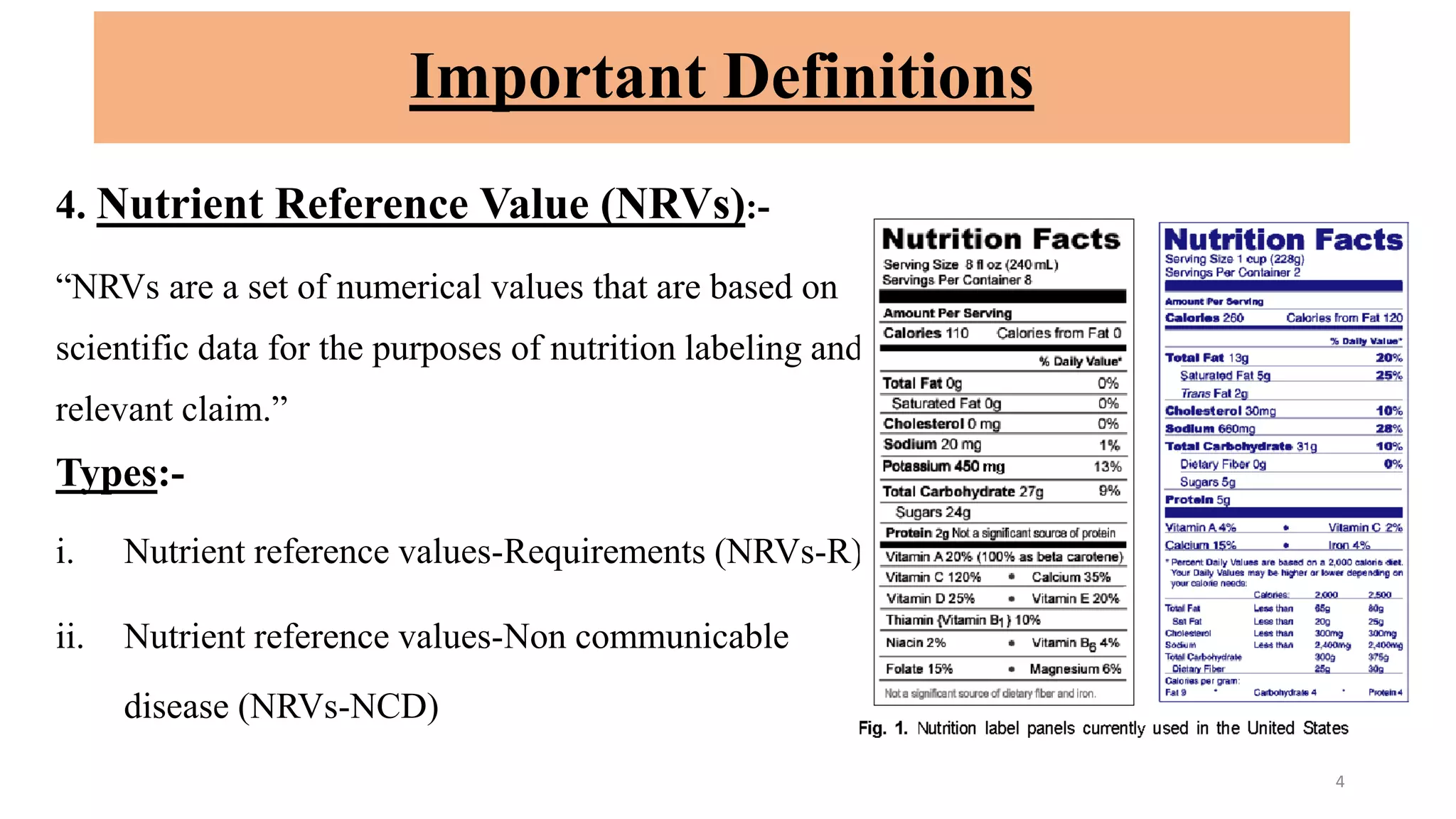
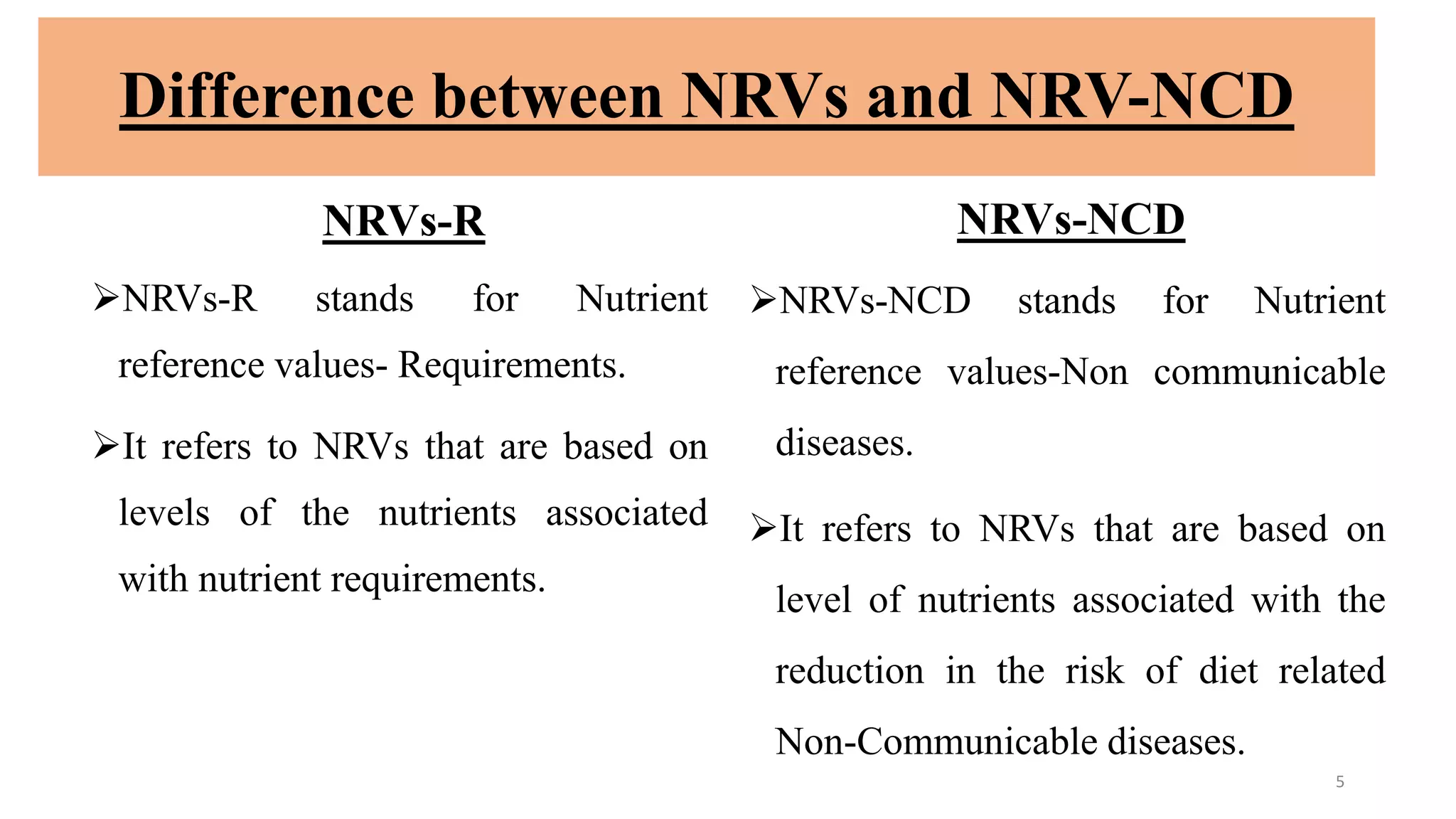
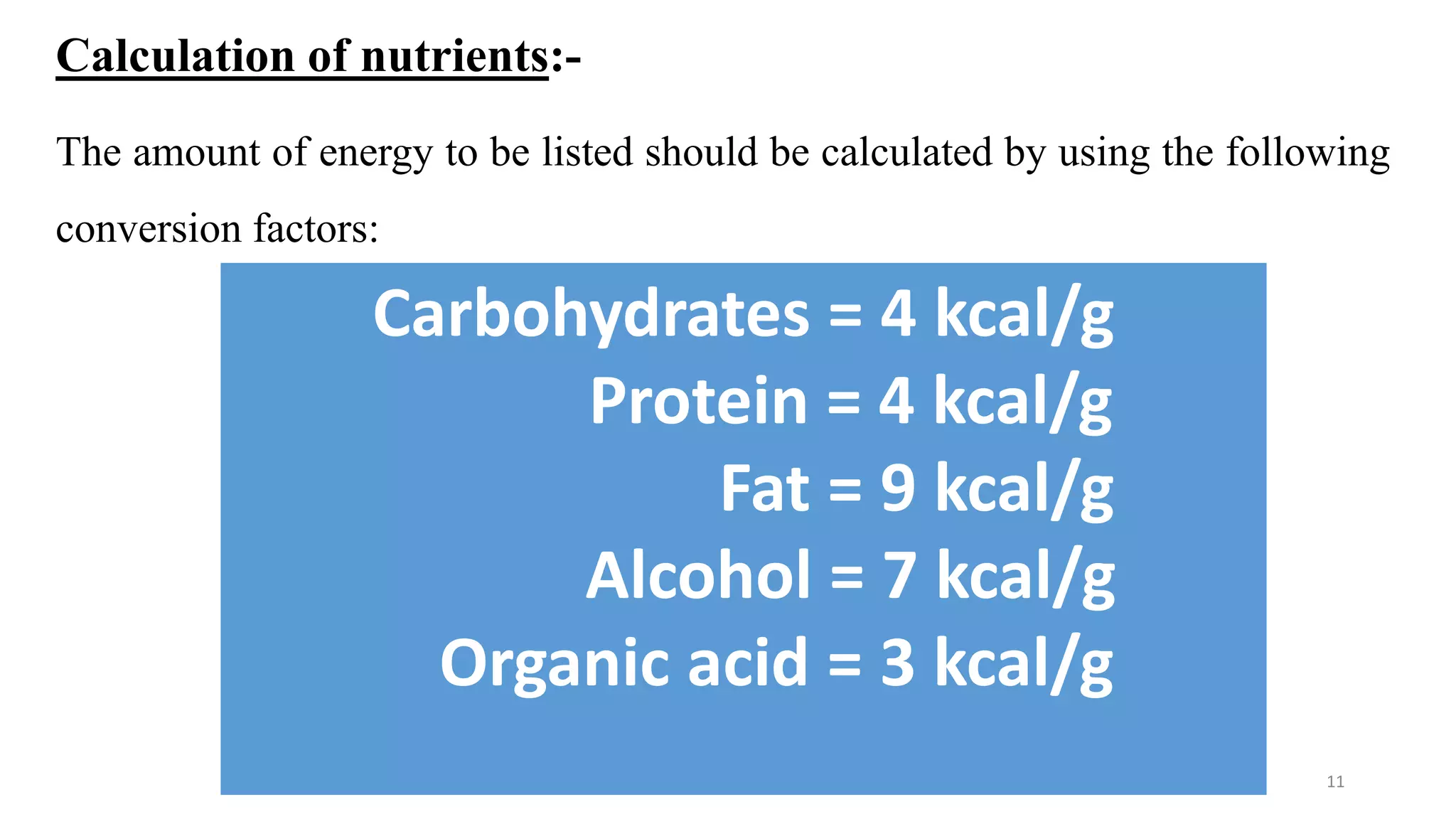
This document outlines Codex standards for nutrition and labeling. It defines key terms like nutrition declaration, nutrient reference values, and supplementary nutrition information. The standards require mandatory declaration of energy, protein, carbohydrates, fat, saturated fat, sodium, and sugars. Nutrient amounts must be calculated using specified conversion factors. Formatting guidelines are provided to enhance legibility. Supplementary nutrition information is optional but can help consumers interpret the declaration, especially for target populations with low literacy or nutrition knowledge.