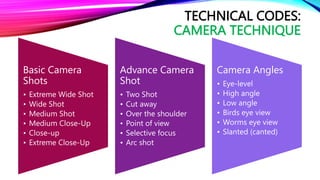
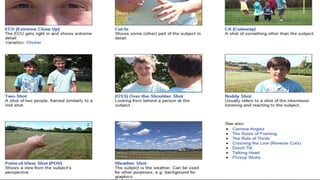
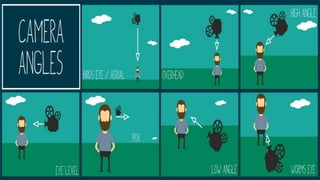
This document provides information about media and information literacy. It discusses key concepts like codes, conventions, messages, audiences, producers and stakeholders. It defines important terms and provides examples of technical codes used in media like different camera shots, angles, movements and techniques. It also discusses symbolic and written codes used to convey meaning. The document appears to be from a lesson on media and information languages that evaluates everyday media using concepts like genre, codes, conventions and messages.