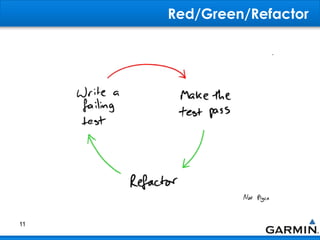
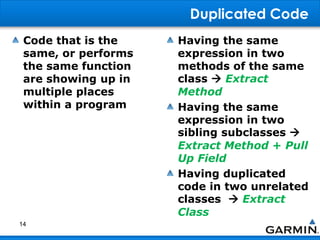
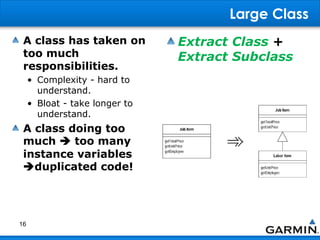
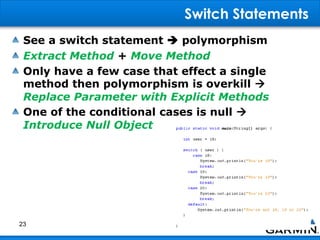
This document discusses bad smells in code that indicate refactoring may be needed. It defines refactoring as restructuring code without changing its external behavior to improve design, readability, and maintainability. Common bad smells include duplicated code, long or complex methods and classes, unused variables, primitive data types when objects could be used, and code that depends too much on other classes rather than being self-contained. The document provides examples of refactoring techniques to address each smell, such as extracting methods, replacing conditionals with polymorphism, and removing unnecessary dependencies between classes.