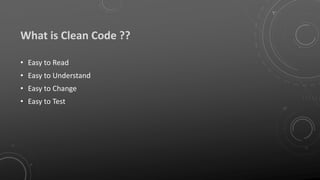
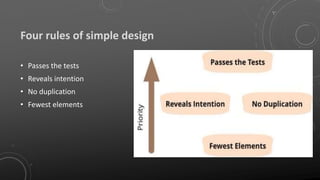
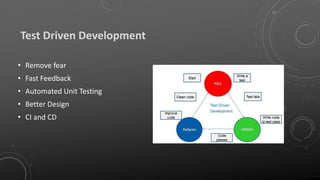
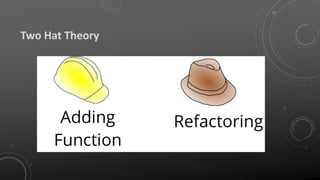
The document discusses the importance of clean code, defining its characteristics and benefits while identifying common pitfalls of bad code. It provides guidelines for maintaining readability, understandability, and changeability in code, as well as highlighting refactoring techniques to improve code quality. Additionally, it emphasizes the collaborative responsibility of development teams to ensure code cleanliness and presents the Boy Scout Rule as a guiding principle.