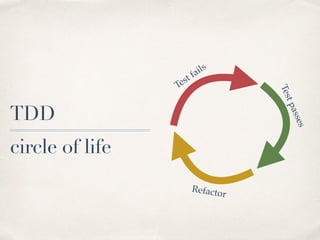
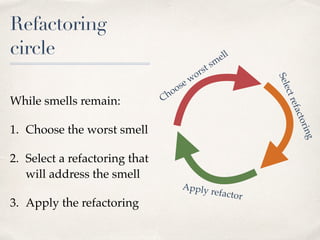
The document discusses refactoring code to improve its design. It defines refactoring as improving code design without changing its external behavior. Refactoring involves identifying "design smells" - symptoms of poor design quality like rigidity, fragility, and opacity. Common smells include long methods, large classes, primitive obsessions, and duplicate code. The document outlines different categories of smells like "bloaters", "object-orientation abusers", and "couplers" that increase coupling between classes. It advises using refactoring tools and techniques to address smells one by one in a refactoring cycle to continuously improve code quality.