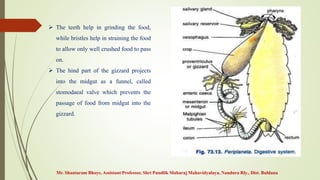
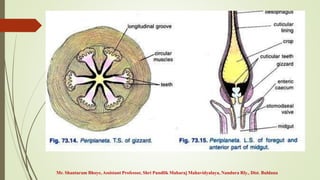
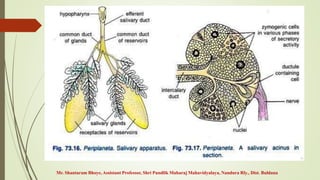
The document provides an overview of the digestive system of the cockroach, detailing its components including the alimentary canal, digestive glands, and the processes of feeding and digestion. It describes the structure and function of the foregut, midgut, and hindgut, as well as the role of salivary glands and the absorption and egestion processes. The cockroach is identified as an omnivore, with various digestive enzymes aiding in the breakdown of food.