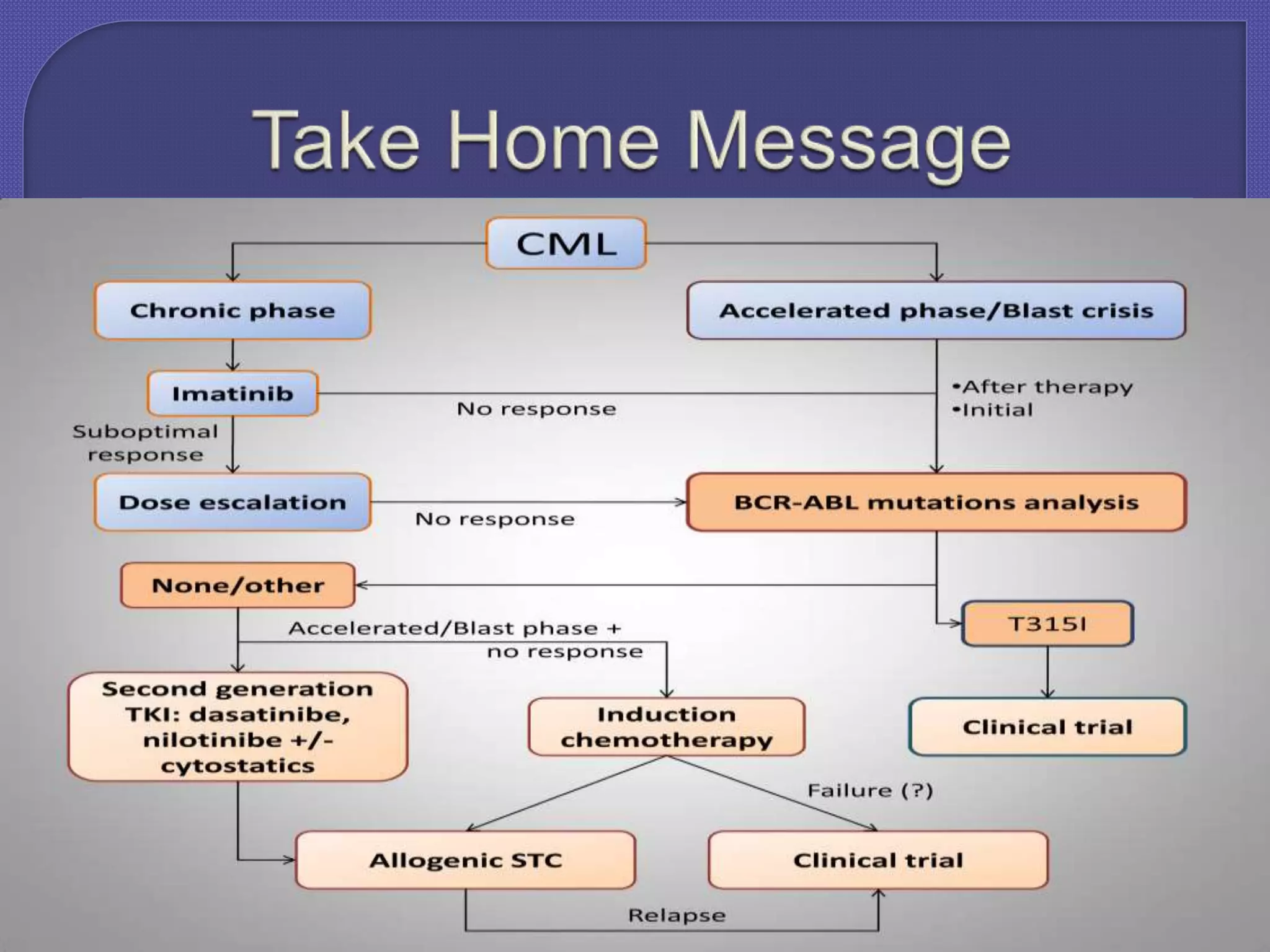
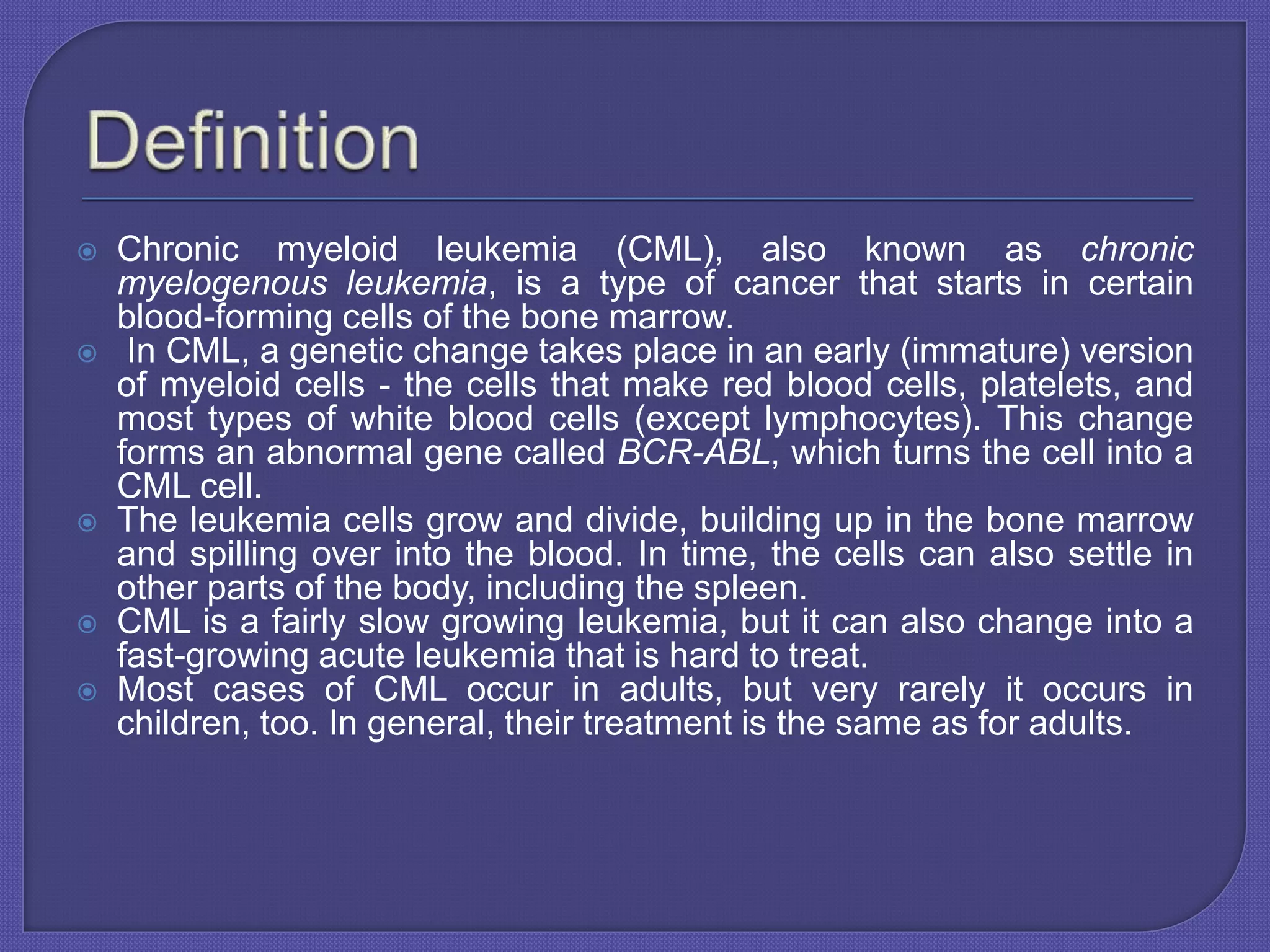
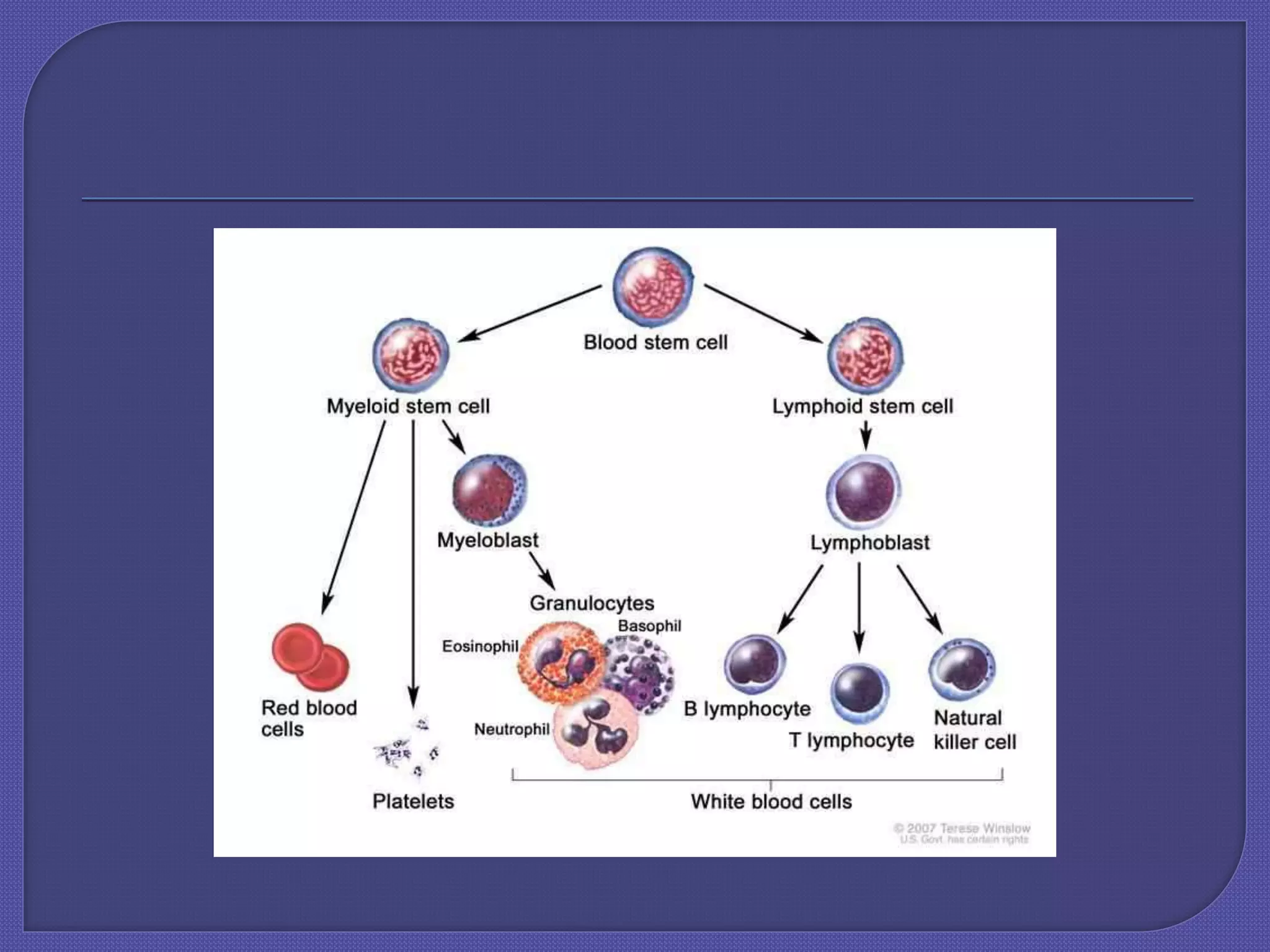
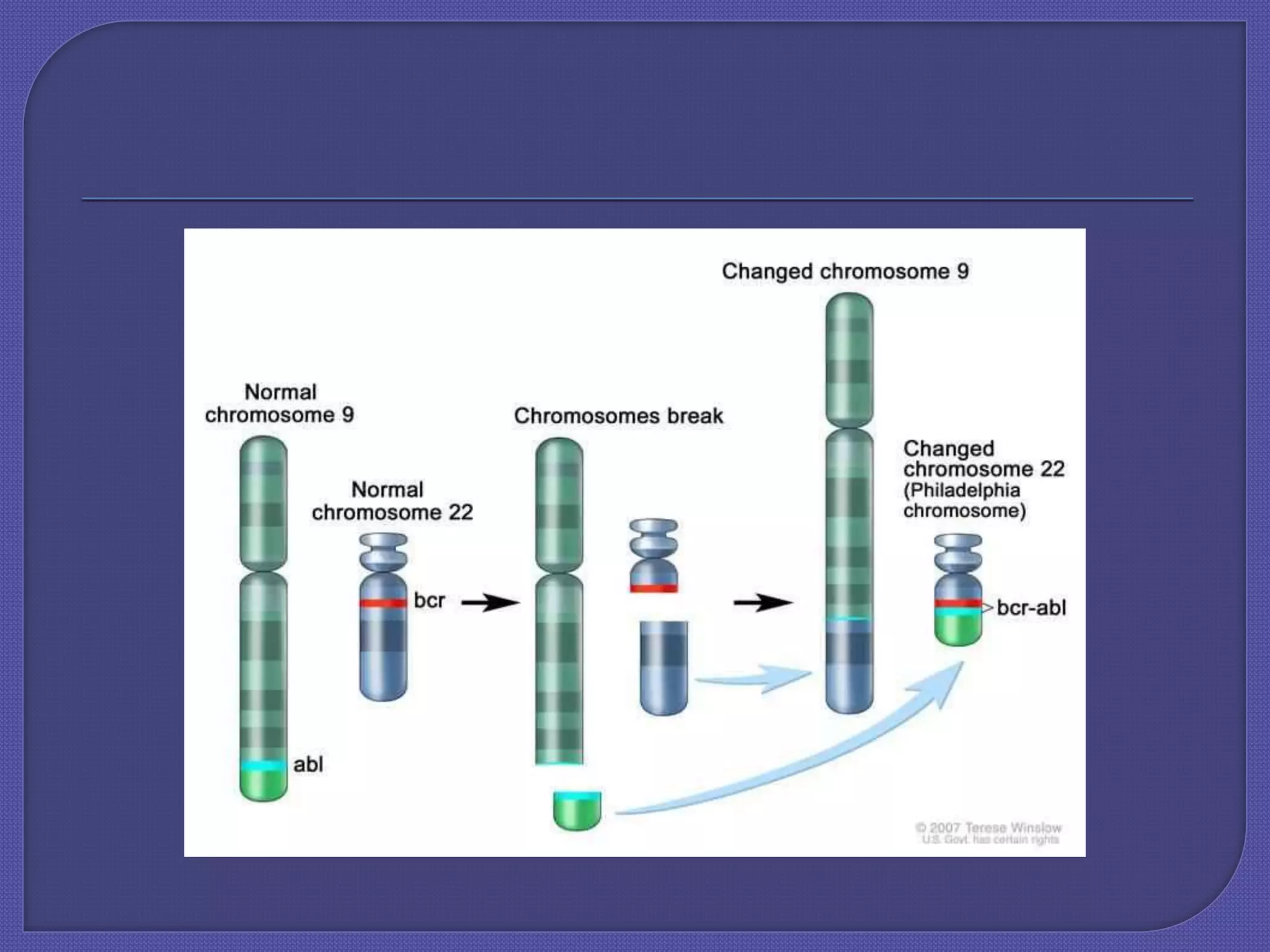
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a slow-growing cancer originating from blood-forming cells in the bone marrow, characterized by a genetic change leading to the abnormal bcr-abl gene. Diagnosis involves blood tests, and the disease progresses through phases, with treatment options including tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as imatinib, dasatinib, and others, with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation being the only proven cure. The success of treatment varies and is influenced by factors such as the phase of the disease and resistance to medications.











![Hematologic remission (normal CBC and
physical examination [ie, no
organomegaly])
Cytogenetic remission (normal
chromosome returns with 0% Ph-positive
cells)
Molecular remission (negative polymerase
chain reaction [PCR] result for BCR/ABL
mRNA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmlfinal-200525172615/75/Cml-final-16-2048.jpg)





![ A tyrosine-kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that
inhibits tyrosine kinases.
Tyrosine kinases are enzymesresponsible for the activation of many
proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated
by adding a phosphate group to the protein (phosphorylation).
TKIs are typically used as anti-cancer drugs, TKIs operate by four
different mechanisms: they can compete with adenosine
triphosphate (ATP), the phosphorylating entity, the substrate or both
or can act in an allosteric fashion, namely bind to a site outside the
active site, affecting its activity by a conformational change.[8]
Recently TKIs have been shown to deprive tyrosine kinases of
access to the Cdc37-Hsp90 molecular chaperone system on which
they depend for their cellular stability, leading to their degradation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmlfinal-200525172615/75/Cml-final-22-2048.jpg)