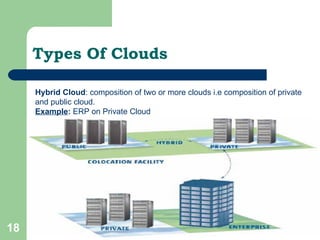
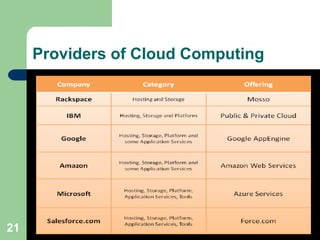
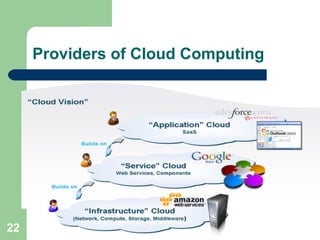
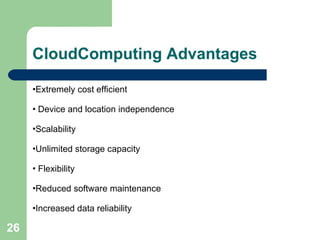
The document explains cloud computing as a model delivering hosted services over the internet, allowing users to access software and resources without needing to manage hardware. It details the benefits of cloud computing, such as reduced costs, scalability, and flexibility, as well as its different types (public, private, and hybrid clouds) and various service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS). Additionally, it outlines the risks involved and strategies for reducing IT costs through cloud solutions.