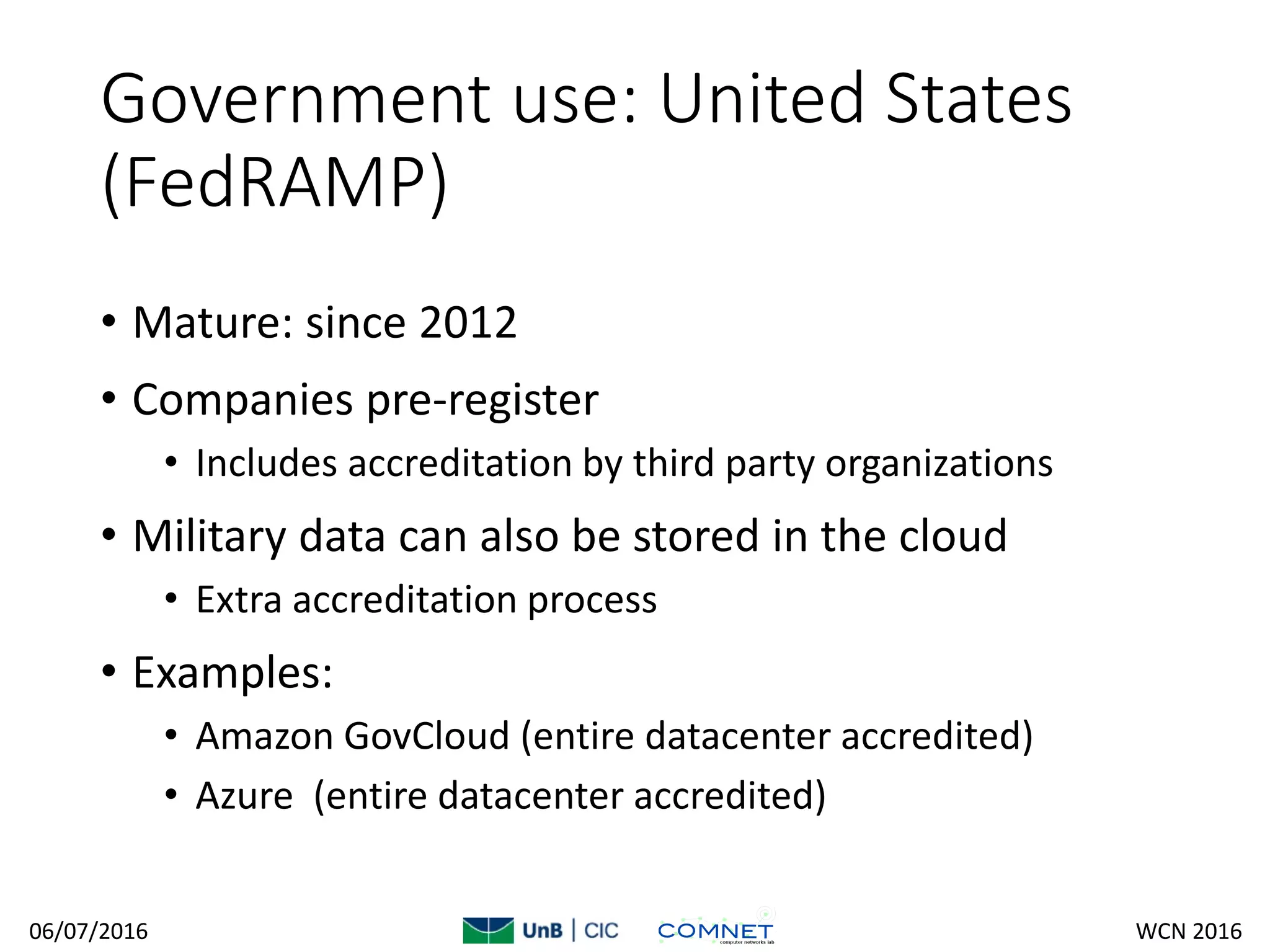
The document discusses cloud security challenges and perspectives, addressing key issues such as trust, multi-tenancy, privacy, and compliance within cloud computing. It examines the adoption of cloud services by governments in different countries, highlighting Brazil's emerging regulations, the UK's G-cloud initiative, and the US's FedRAMP program. The paper emphasizes the evolving nature of security practices in cloud environments and the necessity for robust legal and technical frameworks.