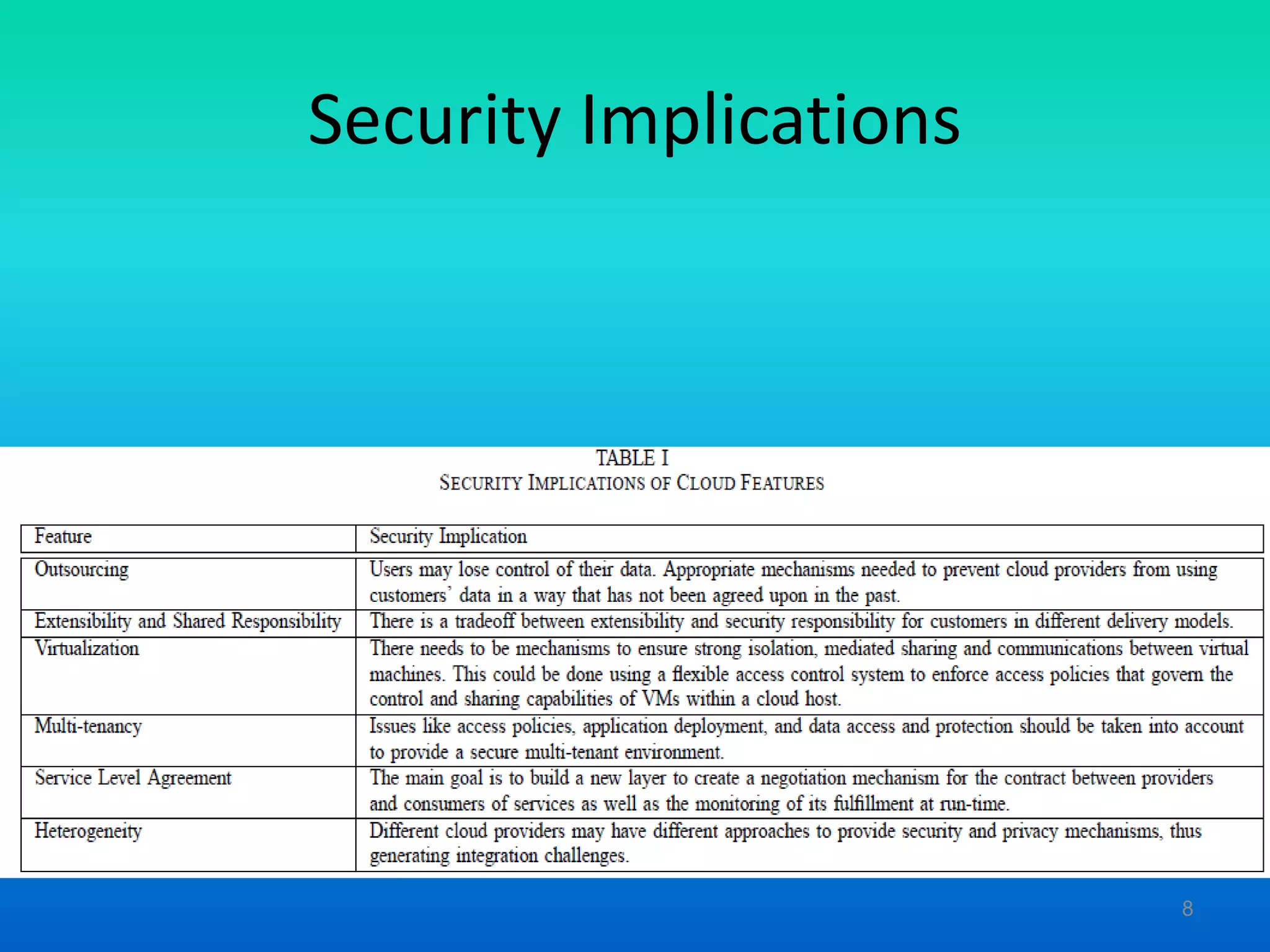
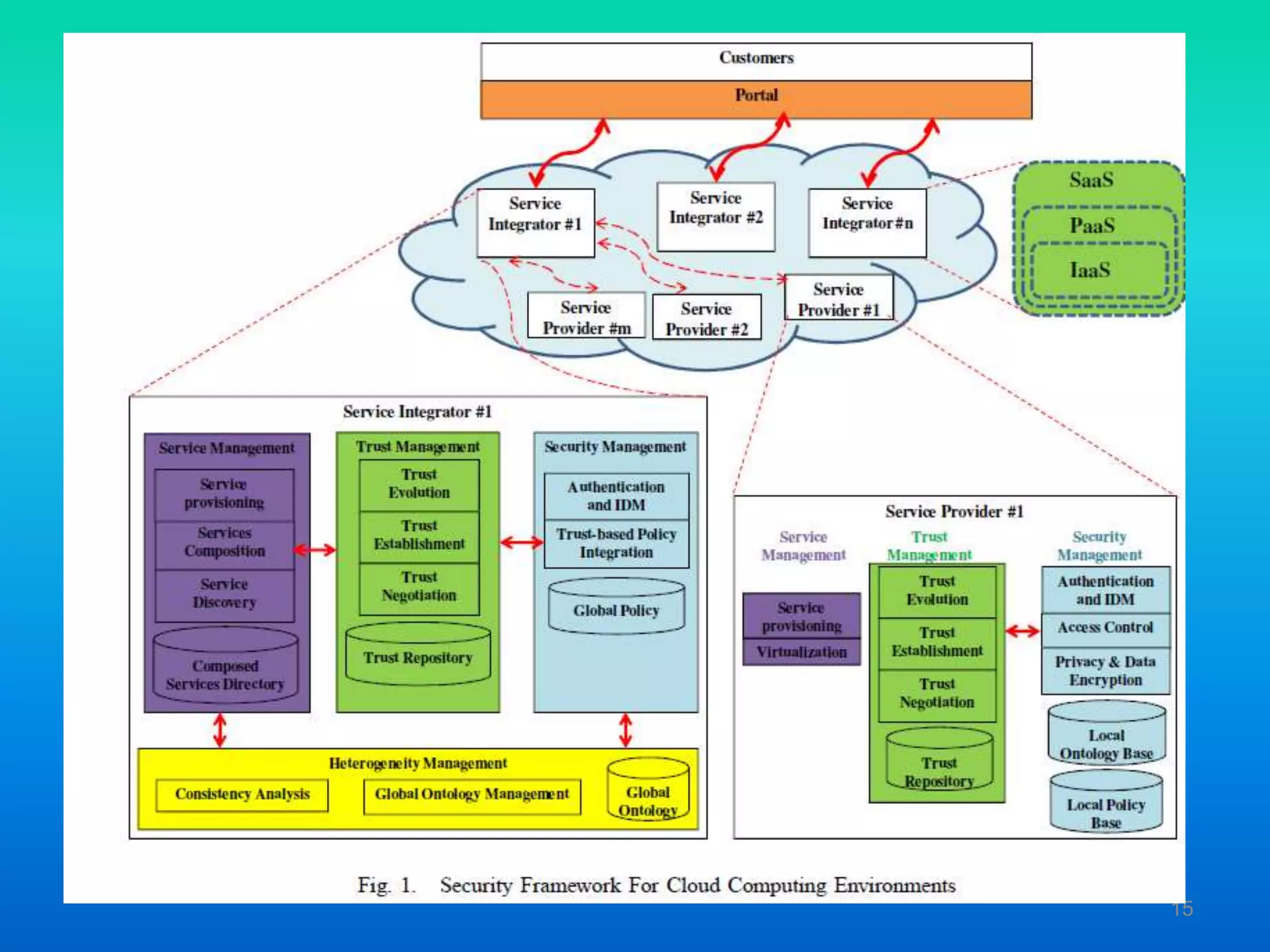
The document discusses cloud security, outlining its advantages such as data fragmentation, dedicated security teams, and enhanced disaster recovery options. It also highlights significant challenges including data privacy regulations, multi-tenancy issues, and the need for effective access control. Finally, various security and privacy approaches are proposed, focusing on identity management, access control, and trust management frameworks.