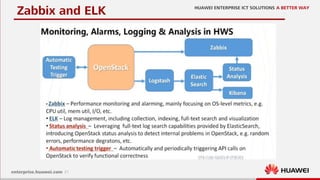
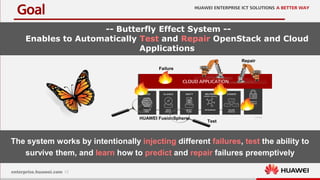
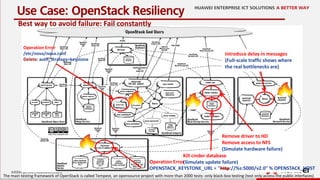
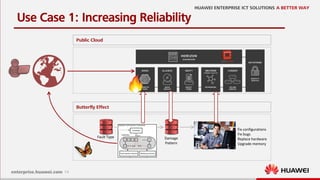
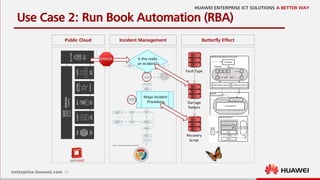
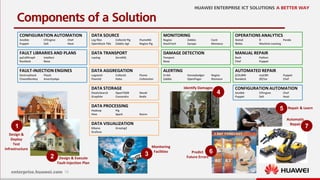
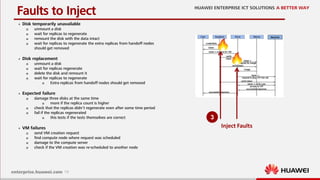
This document discusses increasing cloud resilience through fault injection testing. It describes using the Butterfly Effect system to intentionally inject failures like hardware failures, network issues, and software bugs into OpenStack deployments. This allows failures to be tested, repairs to be learned, and future failures to be predicted. Monitoring tools like Monasca and Zabbix are used to detect damages and visualize results. The goal is to automate repair and increase reliability through continuous testing and learning from failures.






![6
One reason [Netflix]: It’s the lack of control over the underlying
hardware, the inability to configure it to try to ensure 100%
uptime
Why does using a cloud infrastructure requires
advanced approaches for resiliency?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-04-13cloudresiliencebutterflyeffectmeetupopenstack-160418185918/85/Cloud-Resilience-with-Open-Stack-7-320.jpg)


![10
A program designed to increase resilience by purposely injecting
major failures
Discover flaws and subtle dependencies
Amazon AWS: GameDay
“That seems totally bizarre on the face of it, but as you dig down, you end up finding
some dependency no one knew about previously […] We’ve had situations where we
brought down a network in, say, São Paulo, only to find that in doing so we broke our
links in Mexico.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-04-13cloudresiliencebutterflyeffectmeetupopenstack-160418185918/85/Cloud-Resilience-with-Open-Stack-11-320.jpg)



![20
Damage Detection
The main testing framework of OpenStack is called Tempest, an opensource project with more than 2000 tests: only black-box testing (test only access the public interfaces)
Network tests
• create keypairs
• create security
groups
• create networks
Compute tests
• create a keypair
• create a security
group
• boot a instance
Swift tests
• create a volume
• get the volume
• delete the volume
Identity tests
…
Cinder tests
…
Glance tests
…
echo "$ tempest init cloud-01"
echo "$ cp tempest/etc/tempest.conf cloud-01/etc/"
echo "$ cd cloud-01"
echo "Next is the full test suite:"
echo "$ ostestr -c 3 --regex '(?!.*[.*bslowb.*])(^tempest.(api|scenario))'"
echo "Next ist the minimum basic test:"
echo "$ ostestr -c 3 --regex '(?!.*[.*bslowb.*])(^tempest.scenario.test_minimum_basic)'"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-04-13cloudresiliencebutterflyeffectmeetupopenstack-160418185918/85/Cloud-Resilience-with-Open-Stack-21-320.jpg)