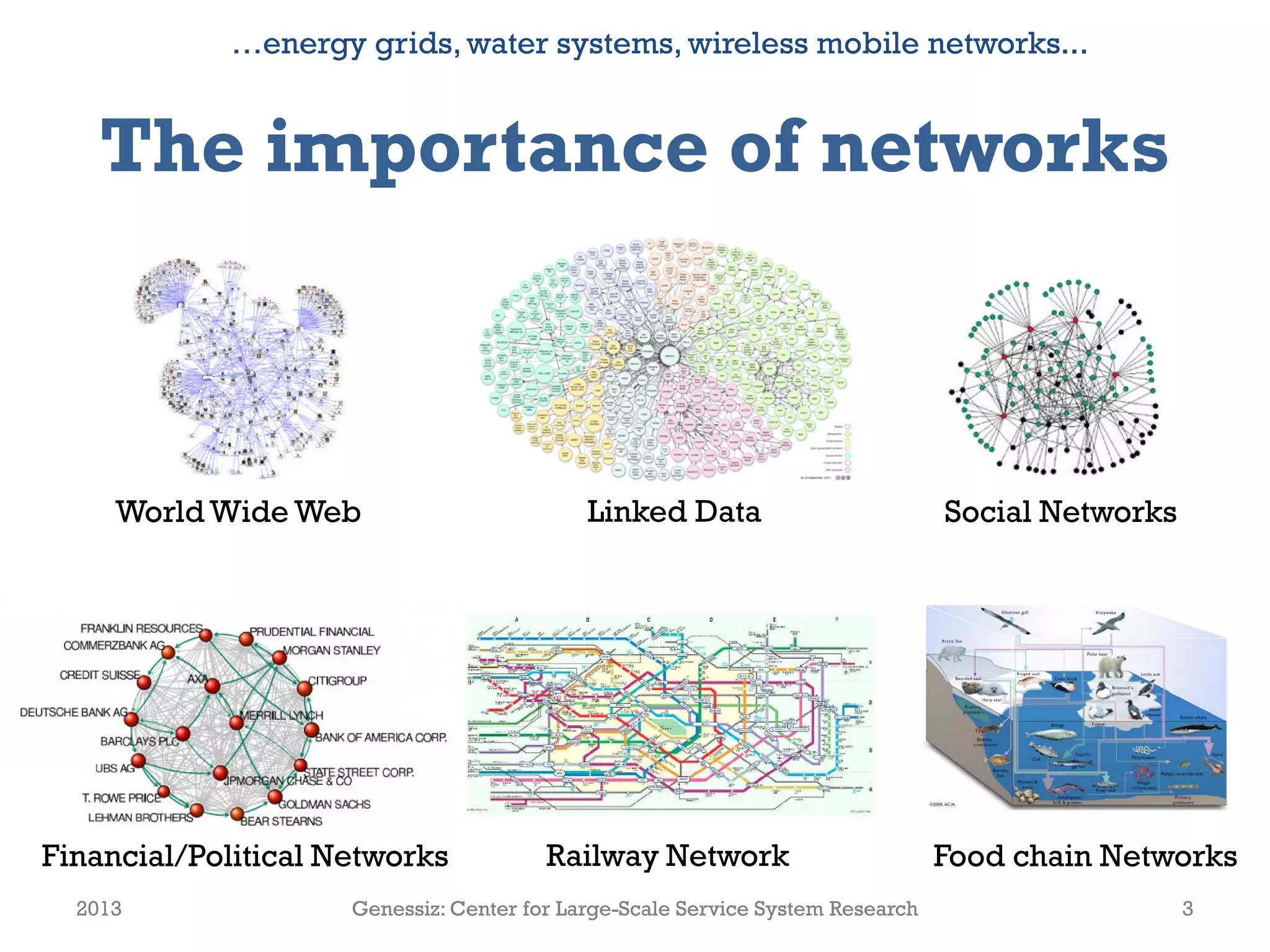
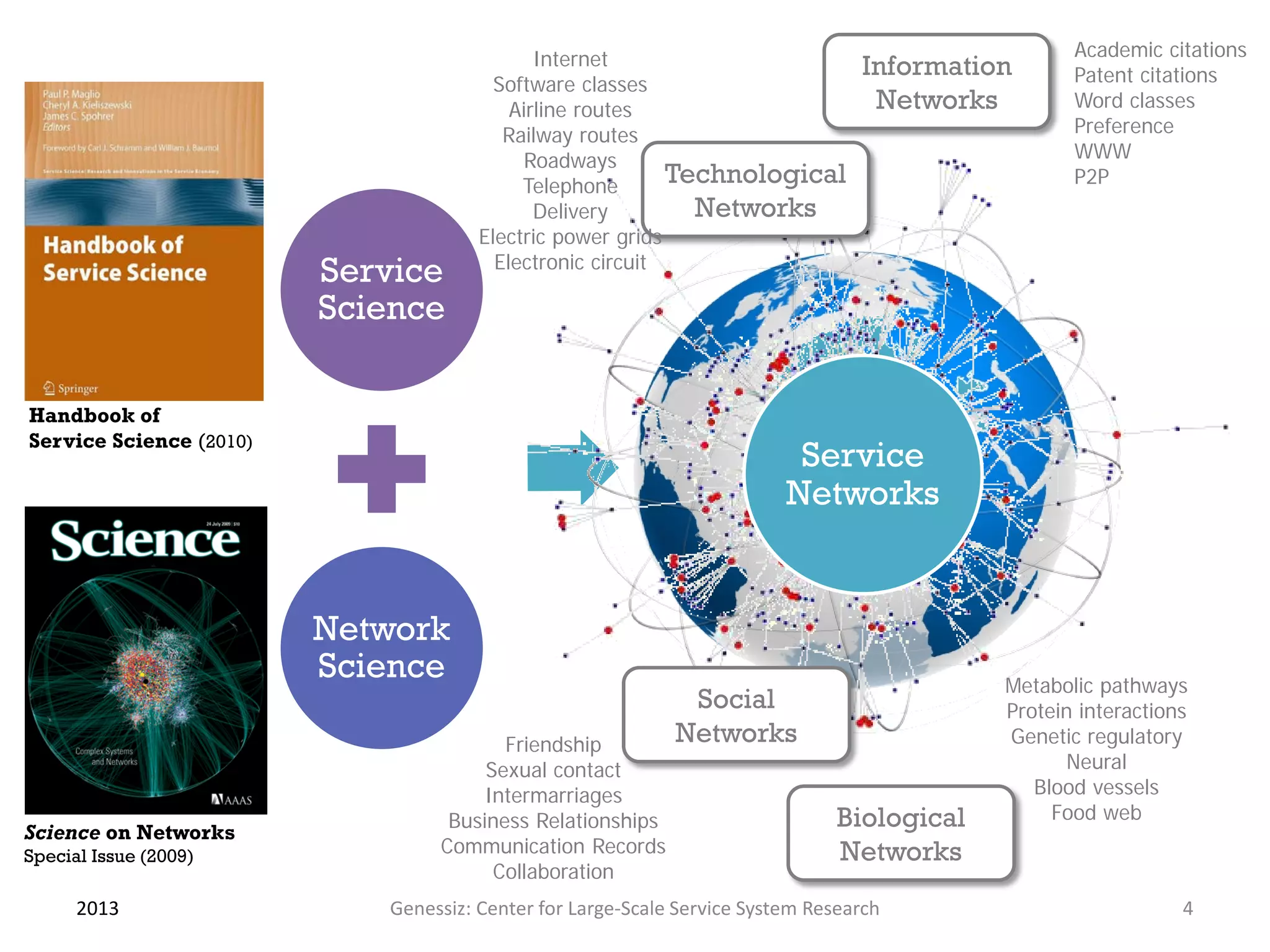
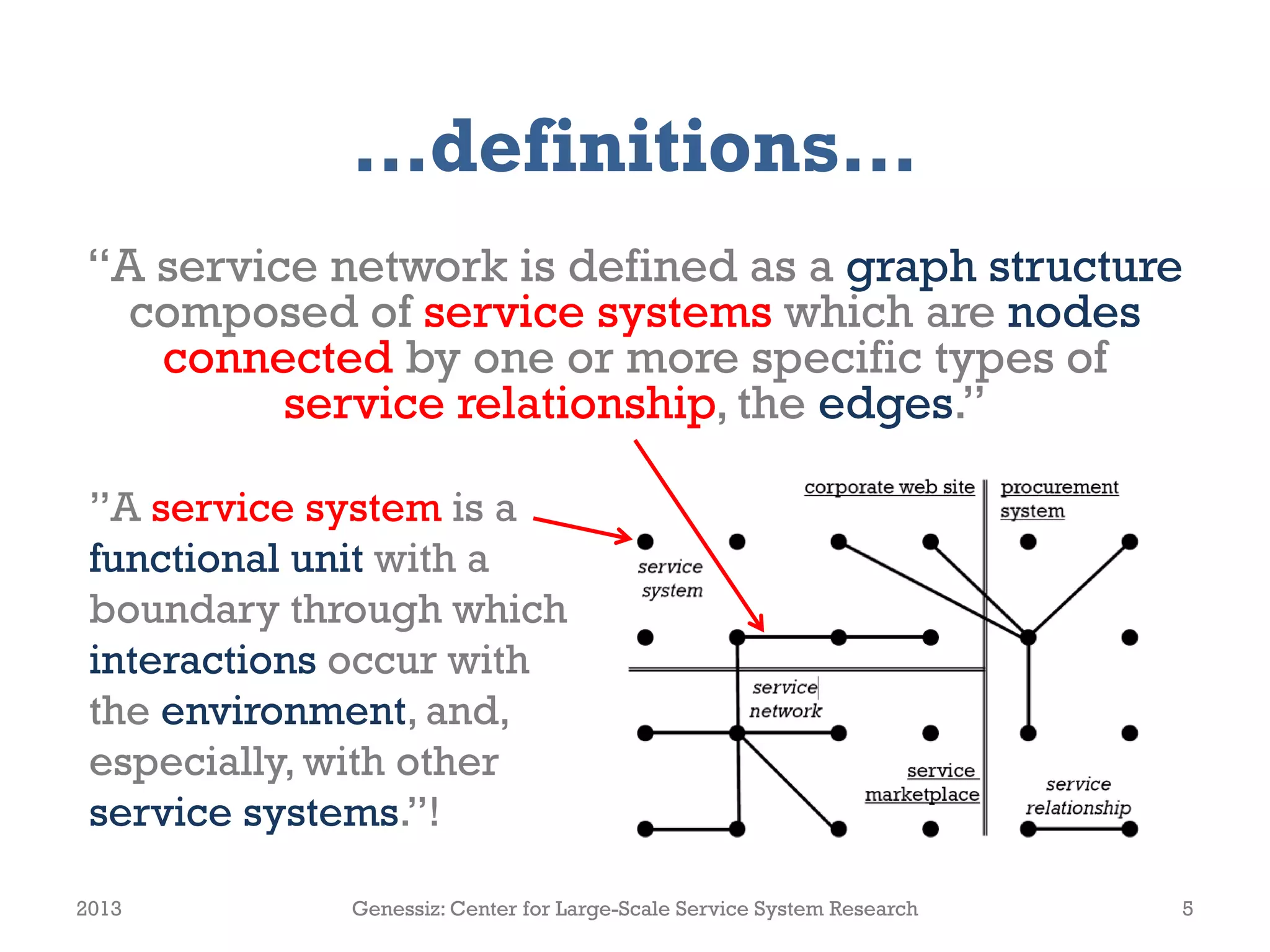
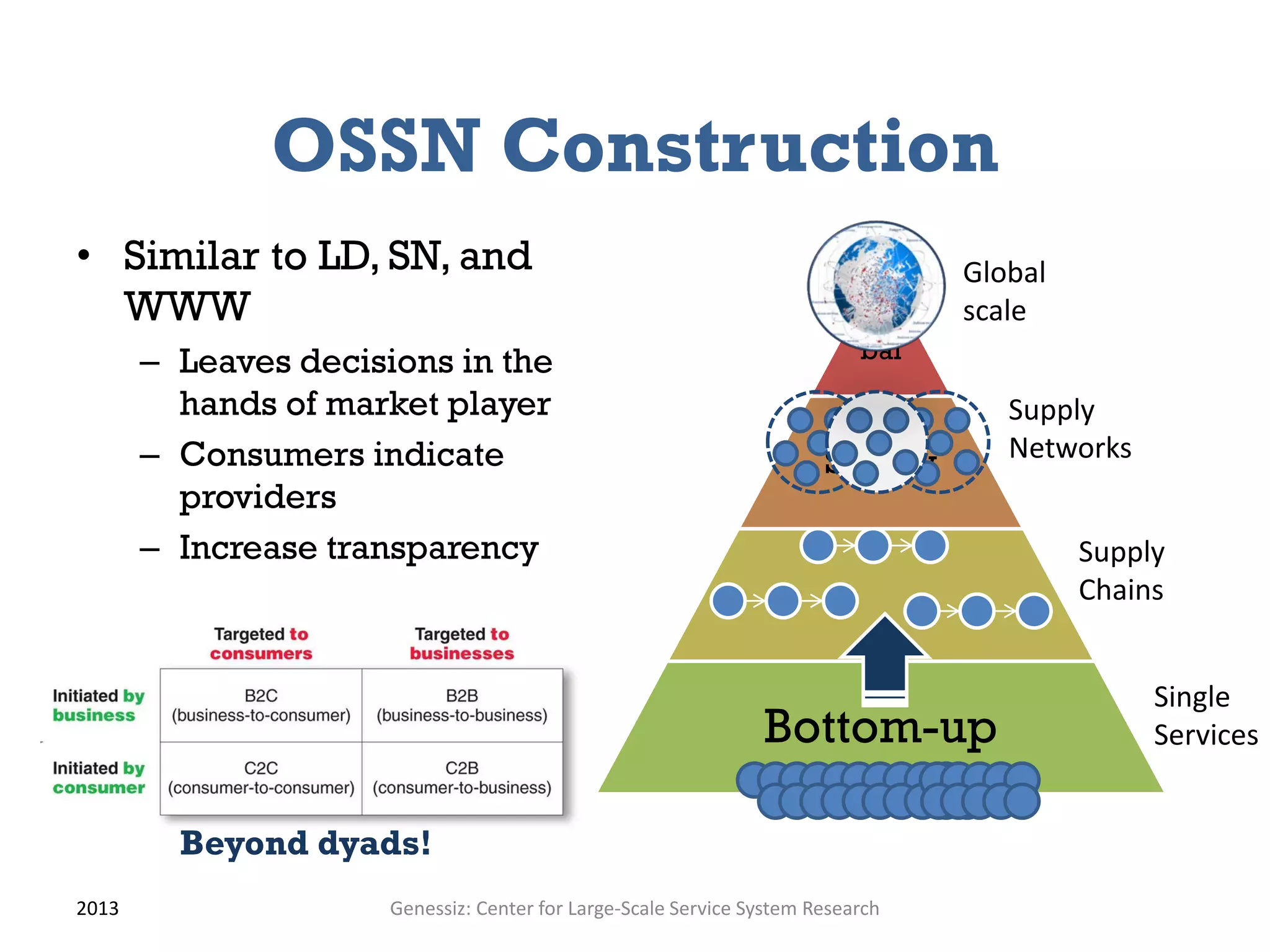
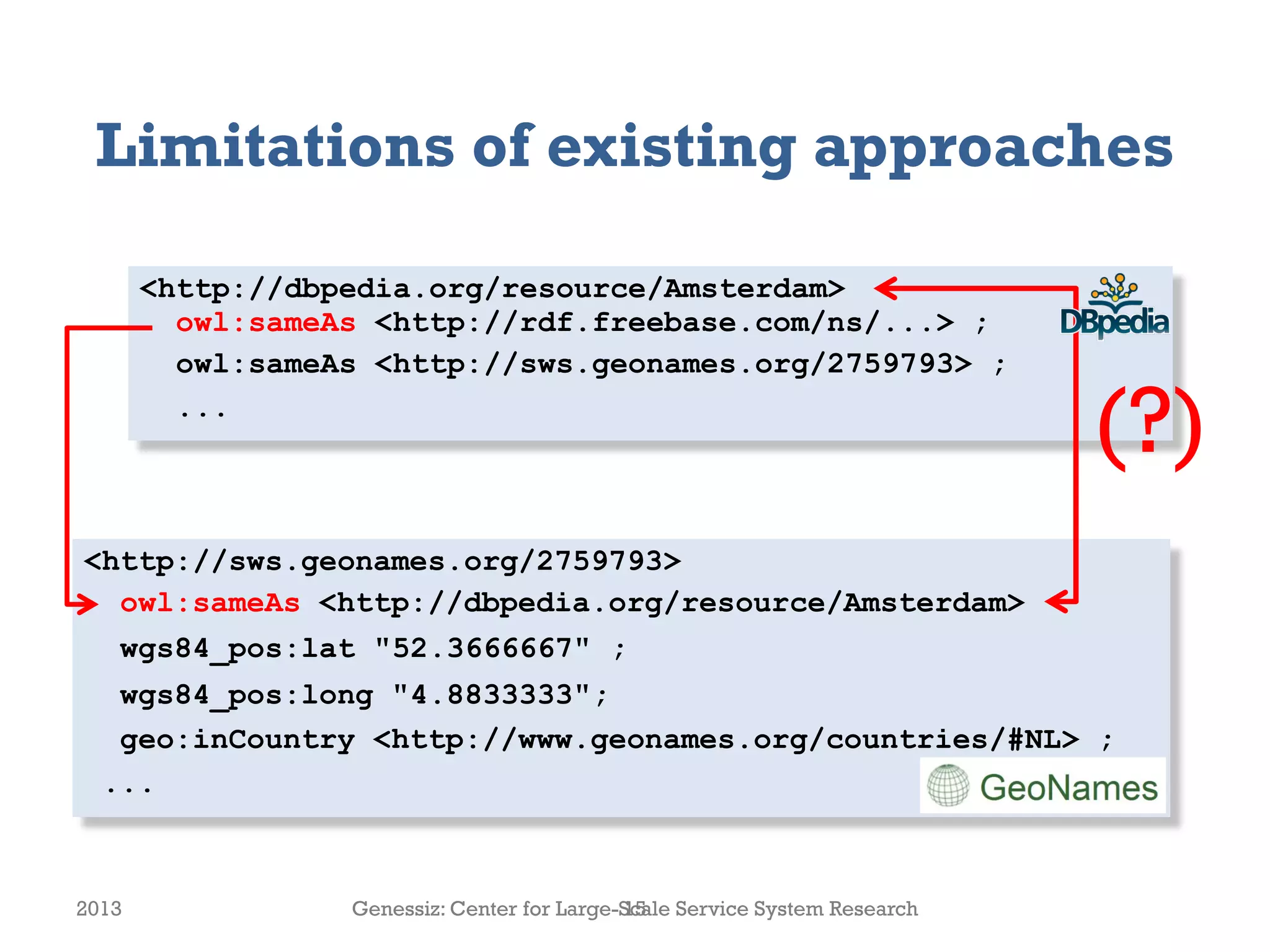
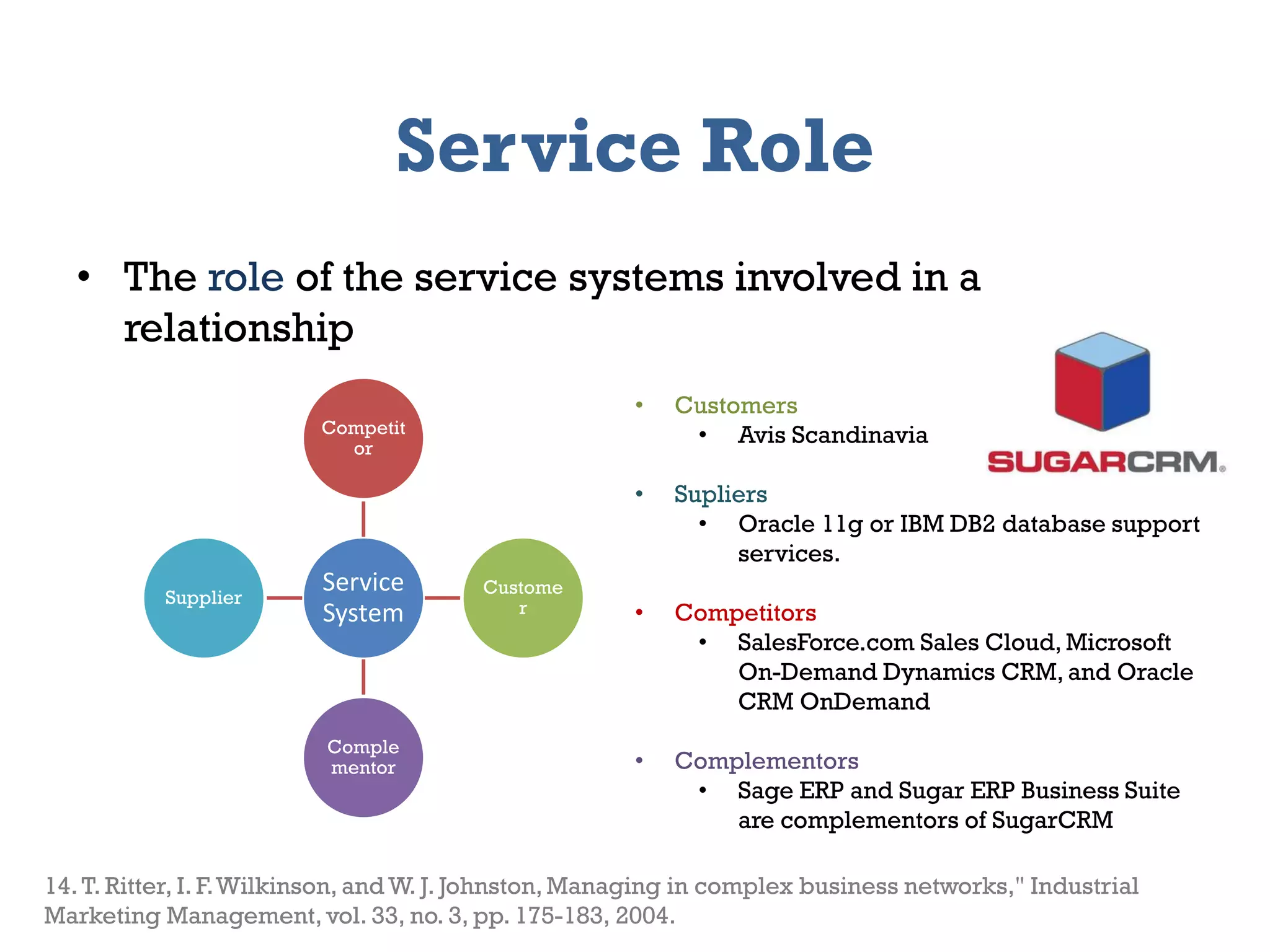
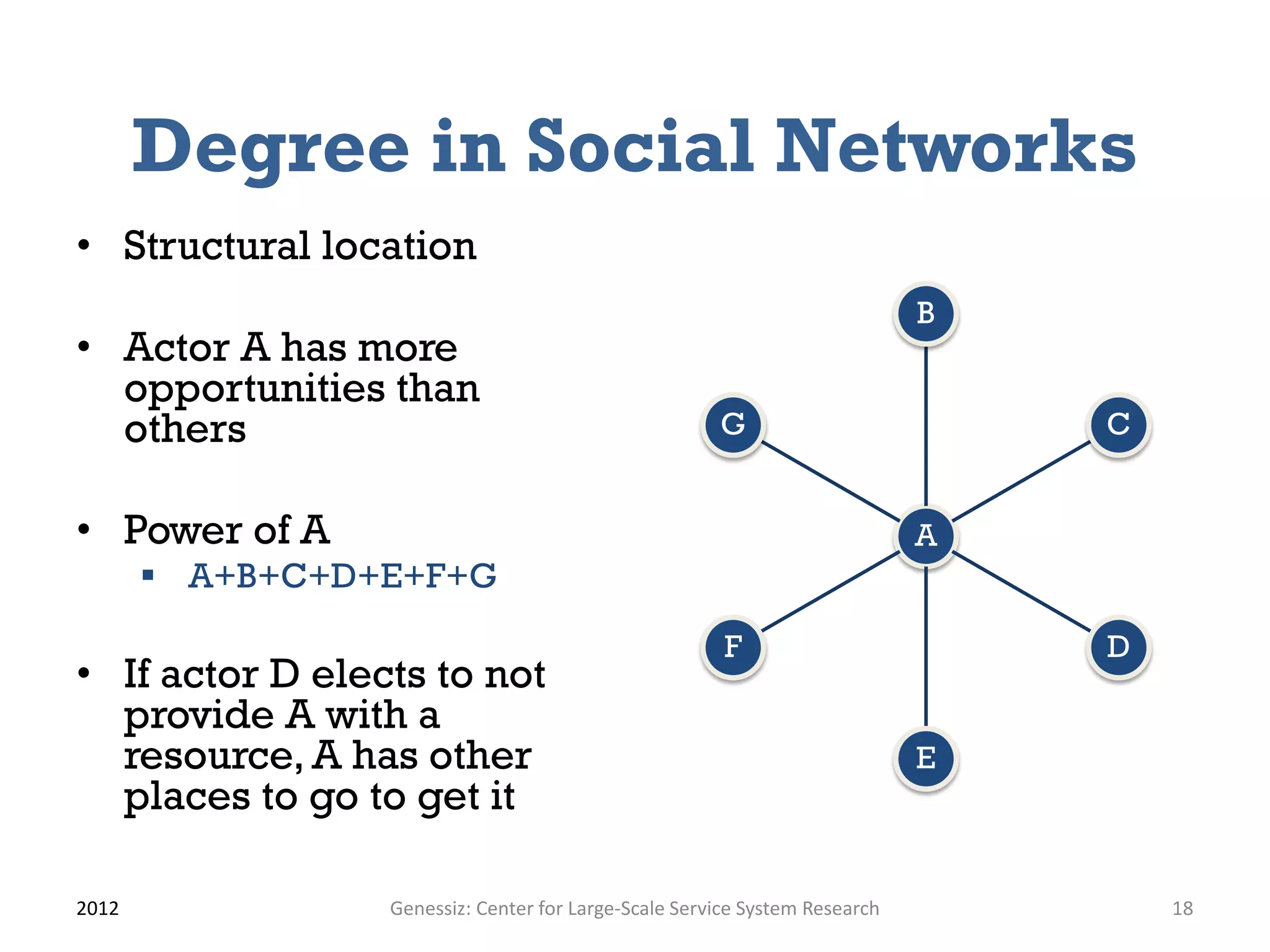
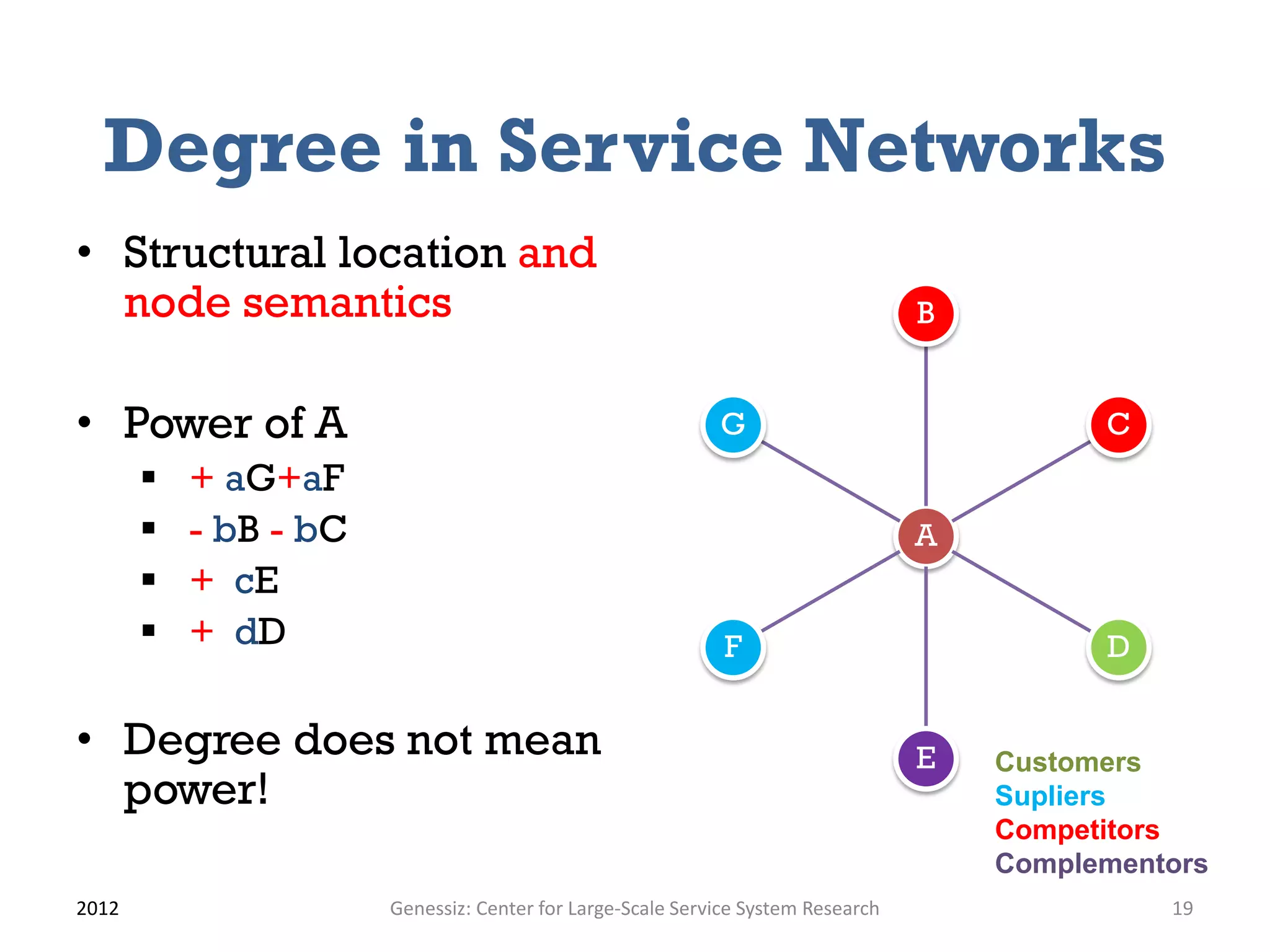
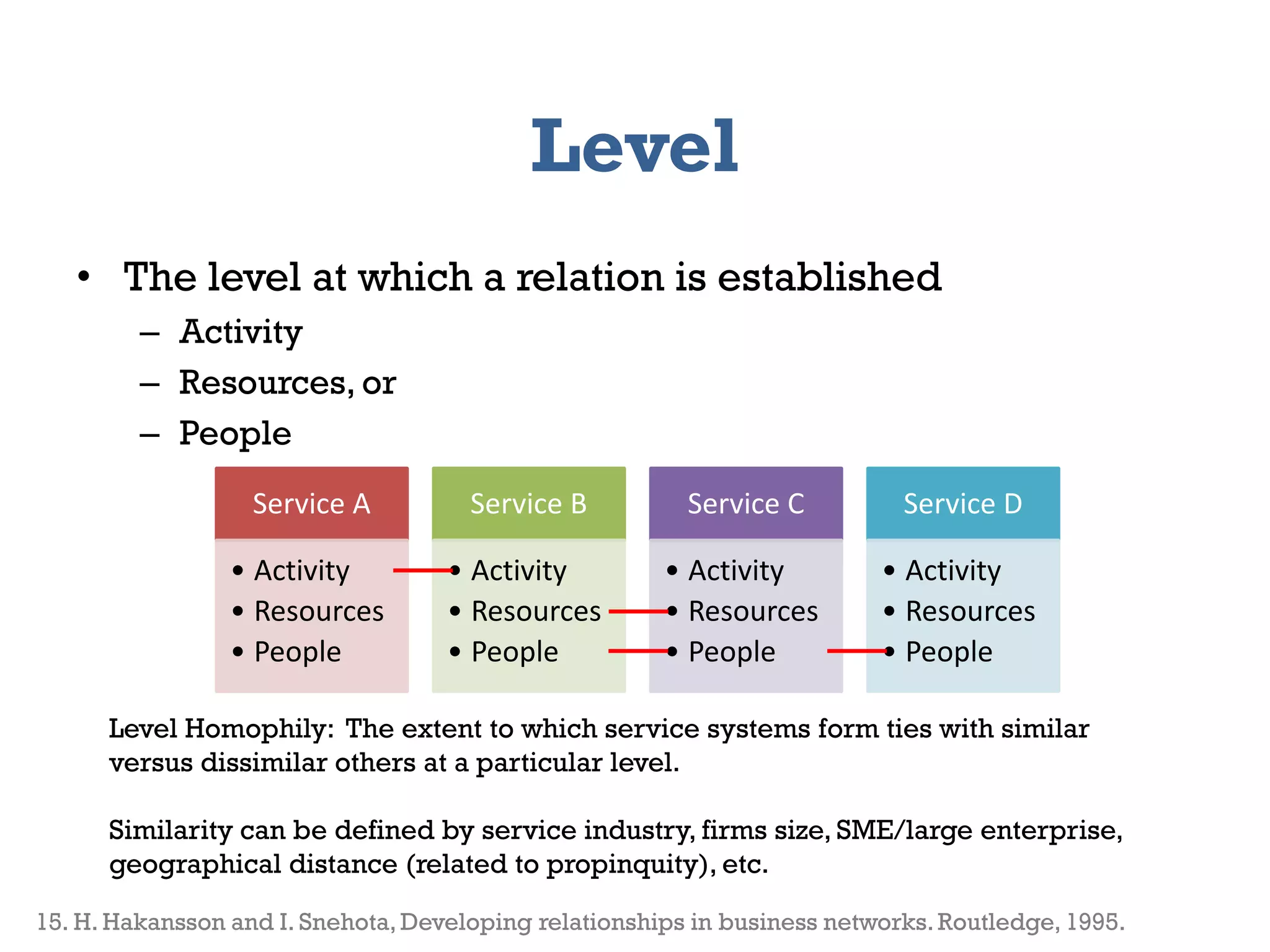
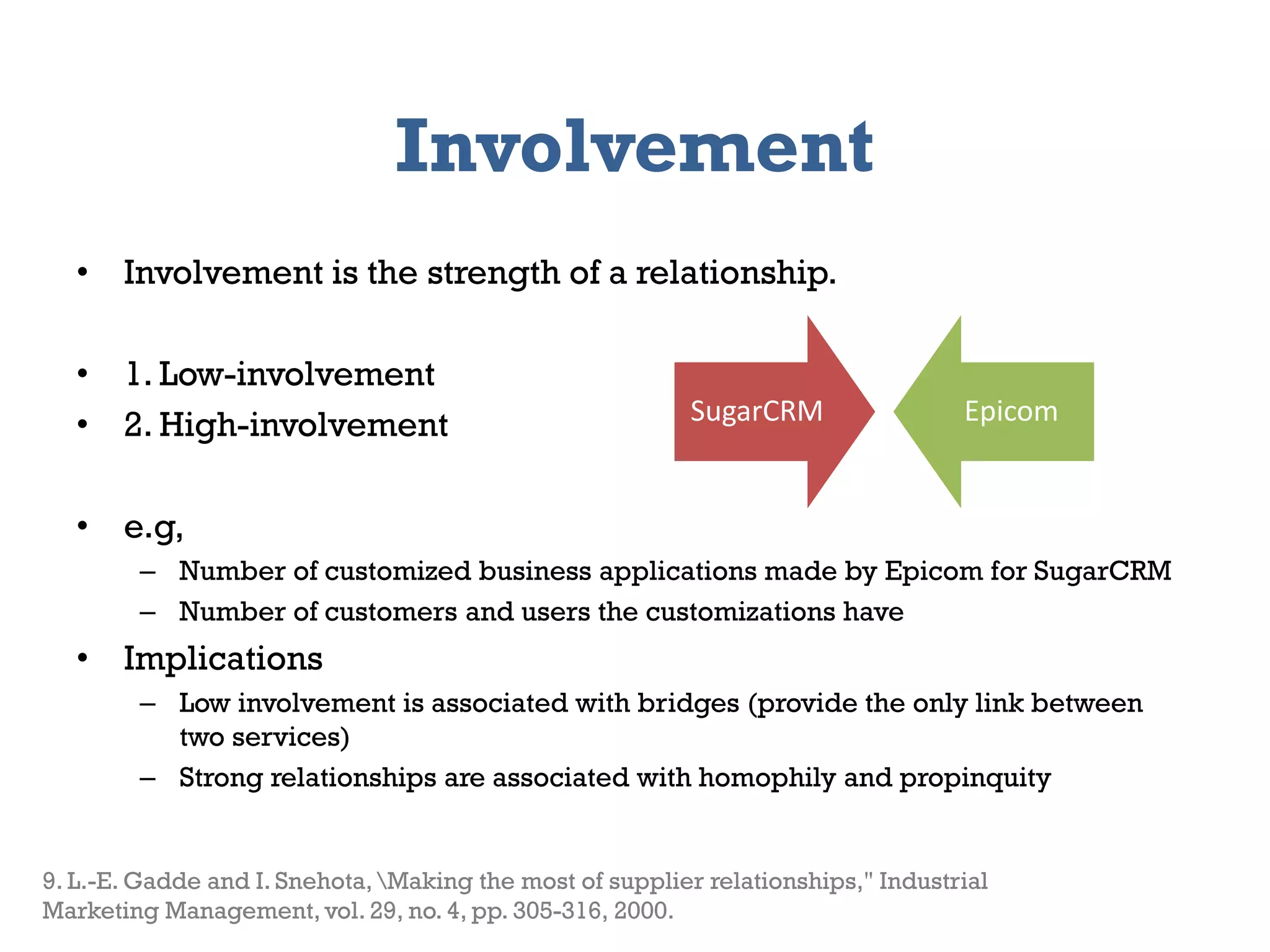
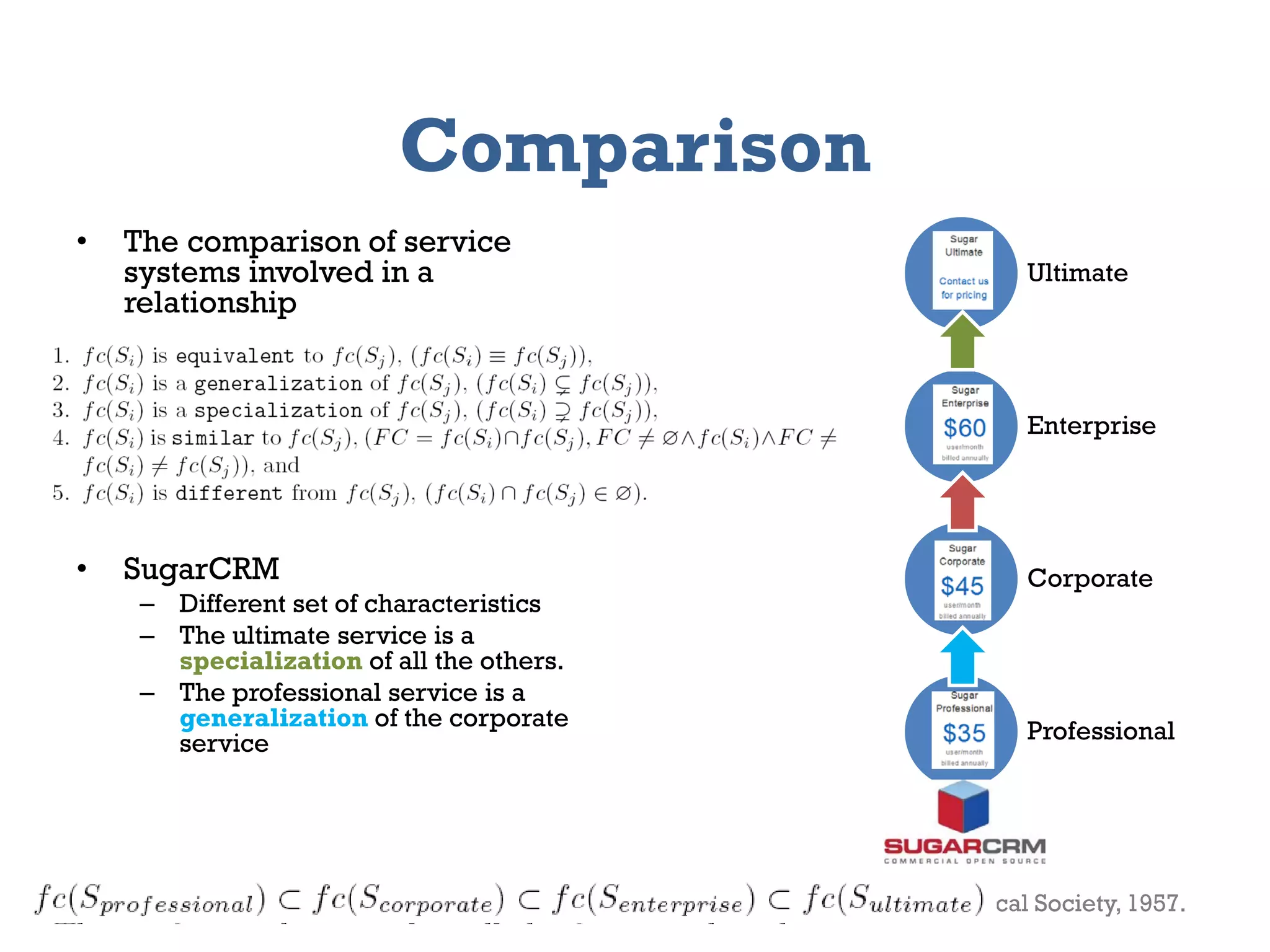
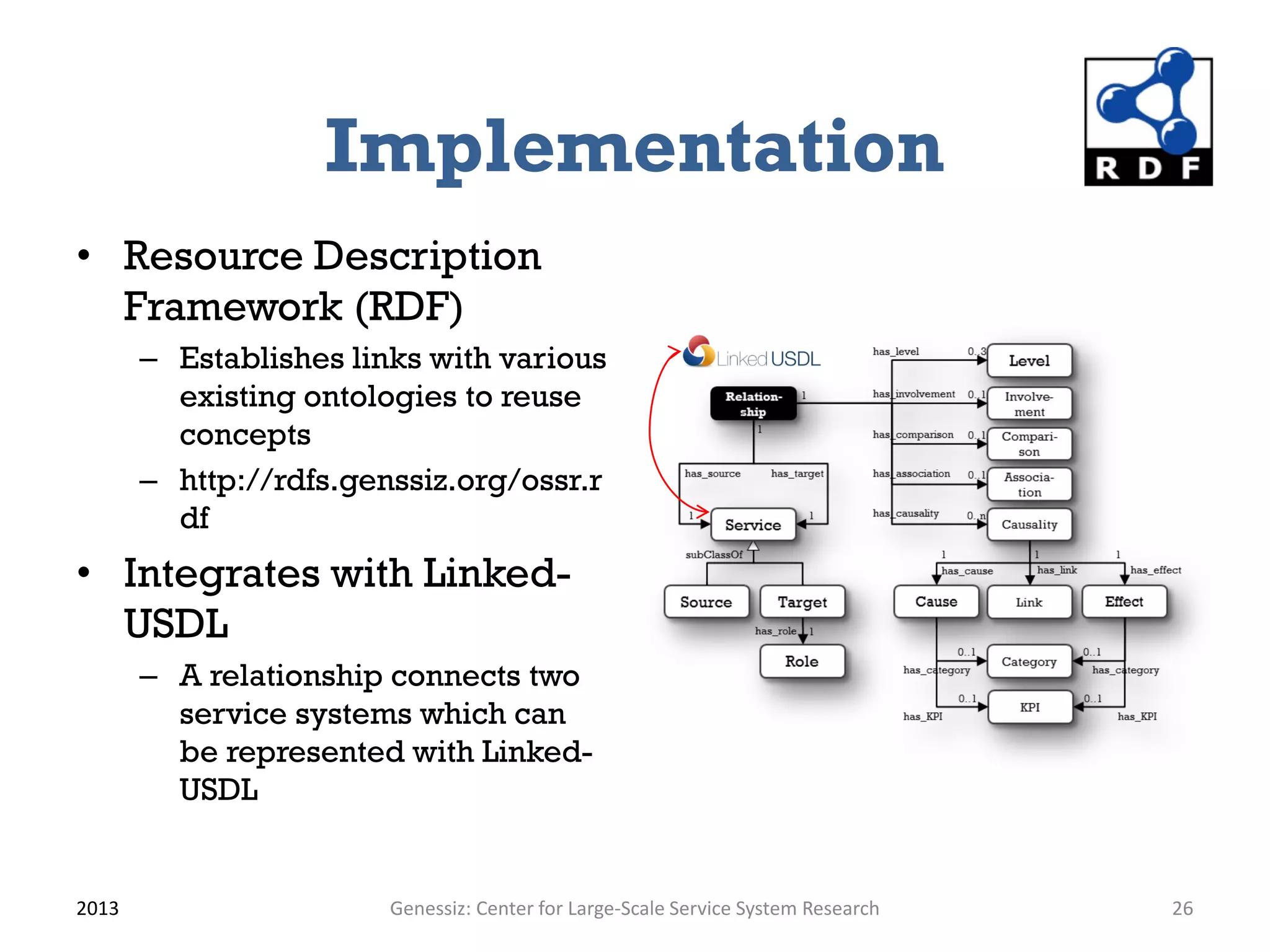
The document presents a framework for modeling service relationships within service networks, emphasizing the definitions and structures that constitute a service network. It discusses various types of service systems, their interconnections, and the importance of capturing the complexities of service relationships to enhance service interactions. Key methodologies and implementations, including the use of semantic frameworks and existing ontologies, are explored to facilitate the analysis and optimization of service systems in various domains.


![Basic Building Blocks
Service System Service Relationship
Open Semantic Service
Relationship (OSSR)
• Service description
• Follows Linked Data principles • Relationship description
• Simplicity for computation and • Interconnects services
modeling
• Multi-layer
• Reuse existing vocabularies
• Follows Linked Data principles
• Means for publishing and
interlinking distributed data • Reuse existing vocabularies
• [CPL+13][CM12][CPL+12][CB • Means for interlinking service
M+10] descriptions/systems
2013 Genessiz: Center for Large-Scale Service System Research 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iess-porto-ossr-2013-02-08-130211130406-phpapp02/75/Modeling-Service-Relationships-for-Service-Networks-8-2048.jpg)

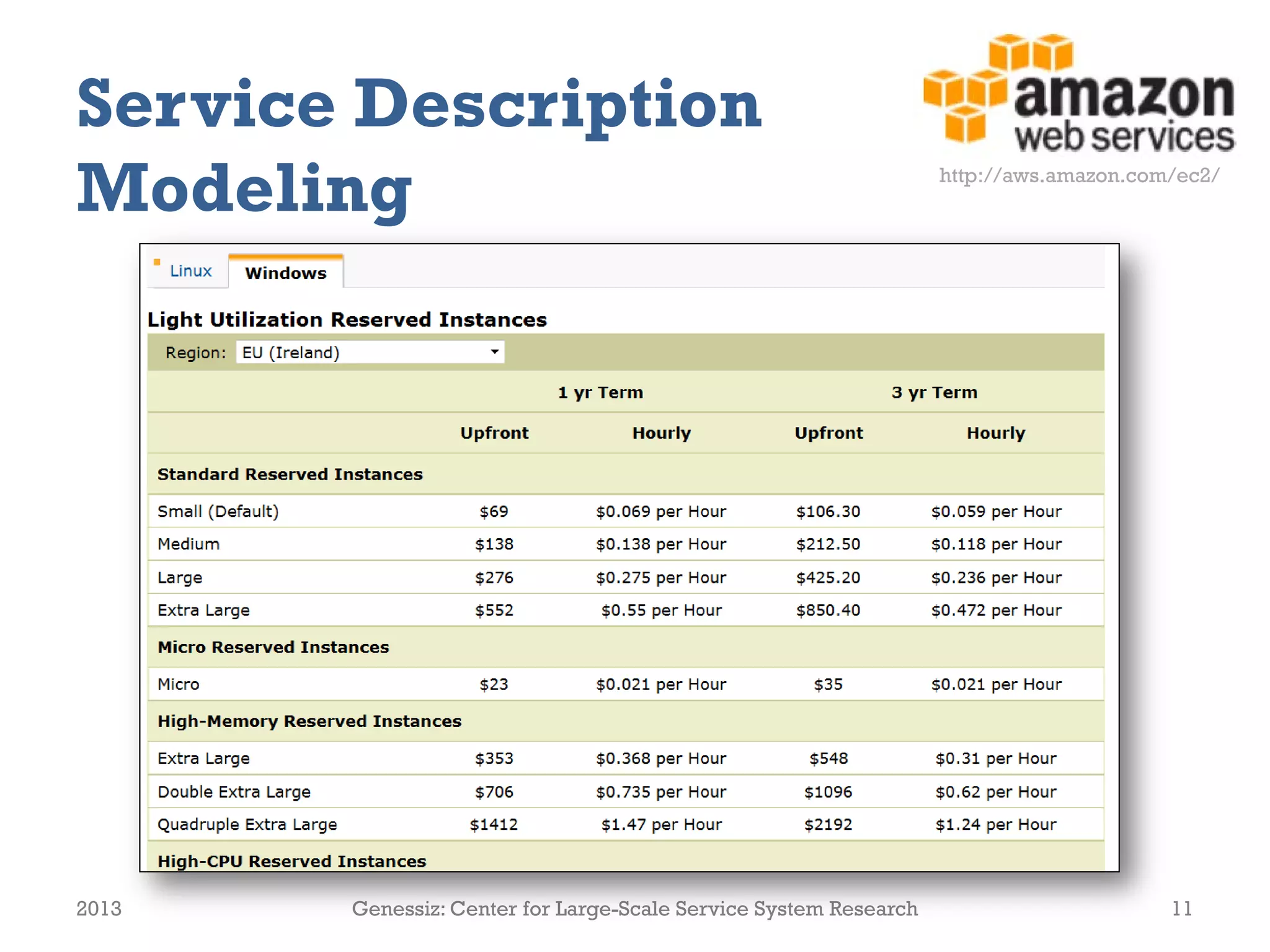
![:pricing_EC2_Small_EU_Windows_ReservedInstance_Light_1yr a price:PricePlan ;
dcterms:description "Price plan for a 'Small' EC2 Reserved Instance in Europe with Windows, light
utilization and a one year contract duration."@en ;
@prefix price: <http://www.linked-usdl.org/ns/usdl-pricing#>
price:hasContractDuration
[ a gr:QuantitativeValue ;
gr:hasValueInteger "1" ;
gr:hasUnitOfMeasurement "ANN" ] ;
price:hasBillingCycle
[ a gr:QuantitativeValue ;
gr:hasValueInteger "1" ;
gr:hasUnitOfMeasurement "MON" ] ;
price:hasPriceComponent
:priceComponent_Small_EU_Windows_ReservedInstance_Light_1yr_General_Upfront ,
:priceComponent_Small_EU_Windows_ReservedInstance_Light_1yr_General_Hourly ,
:priceComponent_Small_EU_Windows_ReservedInstance_Light_1yr_General_Upfront a price:PriceComponent
;
dcterms:title "General costs upfront"@en ;
dcterms:description "One-time fee for general usage of the instance."@en ;
price:isLinkedTo
…
price:hasPrice
[ a gr:UnitPriceSpecification ;
gr:hasCurrency "USD" ;
gr:hasCurrencyValue "69" ;
gr:hasUnitOfMeasurement "C62" ] .
2013 Genessiz: Center for Large-Scale Service System Research 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iess-porto-ossr-2013-02-08-130211130406-phpapp02/75/Modeling-Service-Relationships-for-Service-Networks-12-2048.jpg)

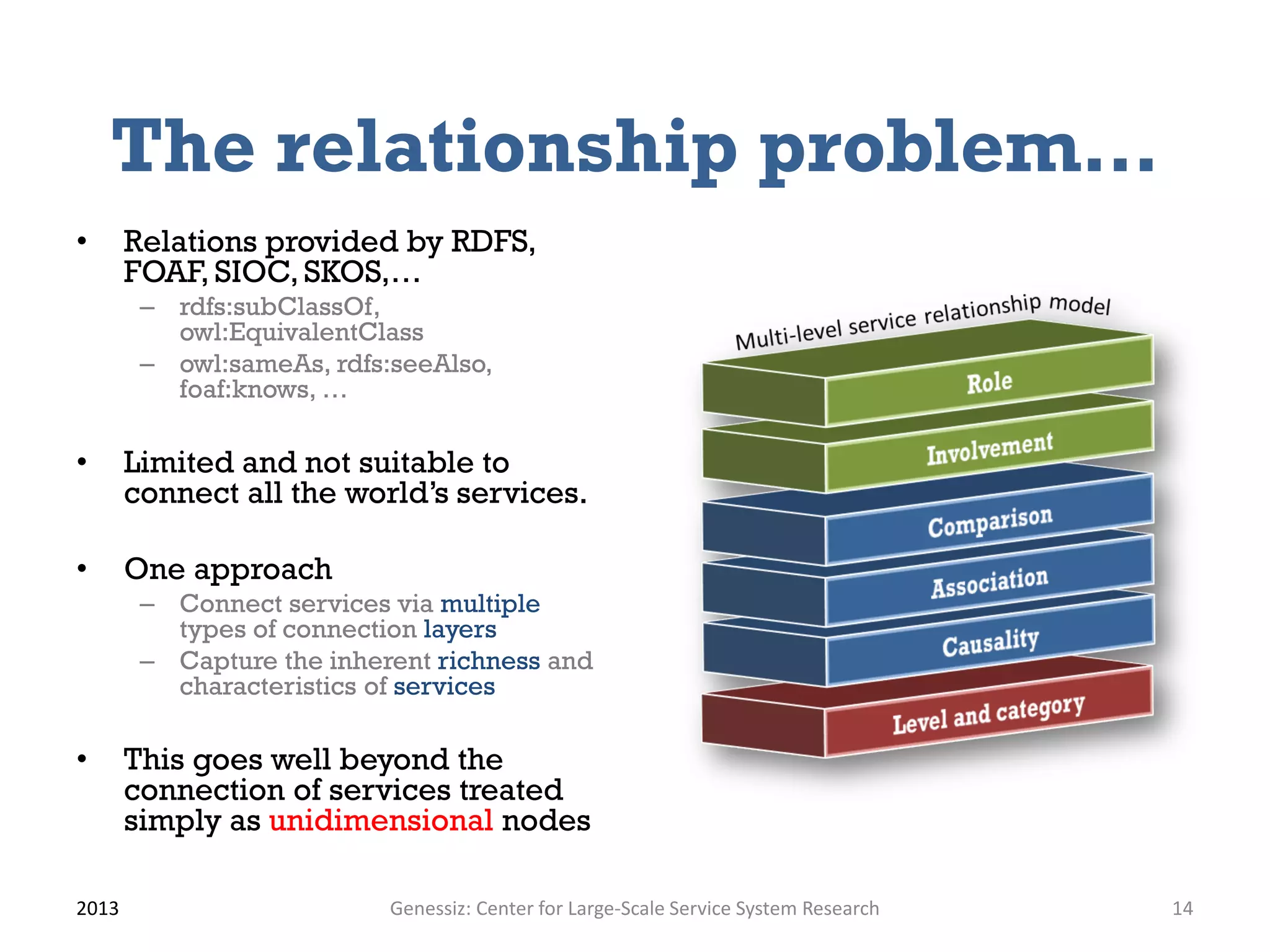



![Causality
• Causality (or cause-effect) describes how a cause event occurring in a
service system has an effect in another service system.
-
Service B
• KPI Invoice • KPI A1
Accuracy • KPI Time • KPI …
• KPI … Delivery
• KPI …
Service A Service C
+
• Expressed using key performance indicators (KPI)
– E.g., Quality of Service (QoS)
– E.g., availability, cost, downtime, errors, response rime, etc.
• Quantitative analysis of the propagation of changes
– System dynamics [19]
– Domino effect in a service network
19. 2013
J. Forrester, Industrial dynamics. Cambridge, Massachusetts:System Press, 1961.
Genessiz: Center for Large-Scale Service M.I.T. Research 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iess-porto-ossr-2013-02-08-130211130406-phpapp02/75/Modeling-Service-Relationships-for-Service-Networks-25-2048.jpg)



![References
• [CPL+13] Cardoso, J.; Pedrinaci, C. and Leenheer, P. D Open Semantic Service Networks:
Modeling and Analysis. In 4th International Conference on Exploring Service Science (IESS
1.3), pages 141-154, Springer, LNBIP, Porto, Portugal, 2013.
• [Car13] Cardoso, J. Modeling Service Relationships for Service Networks. In 4th International
Conference on Exploring Service Science (IESS 1.3), pages 114-128, Springer, LNBIP, Porto,
Portugal, 2013.
• [CM12] Cardoso, J. and Miller, J. A Internet-Based Self-Services: from Analysis and Design to
Deployment. In The 2012 IEEE International Conference on Services Economics (SE 2012),
IEEE Computer Society, Hawaii, USA, 2012.
• [CPL+12] Cardoso, J.; Pedrinaci, C.; Leidig, T.; Rupino, P. and Leenheer, P. D Open semantic
service networks. In The International Symposium on Services Science (ISSS 2012), pages 1-15,
Leipzig, Germany, 2012.
• [CBM+10] Cardoso, J.; Barros, A.; May, N. and Kylau, U. Towards a Unified Service Description
Language for the Internet of Services: Requirements and First Developments. In IEEE
International Conference on Services Computing, IEEE Computer Society Press, Florida, USA,
2010.
2013 Genessiz: Center for Large-Scale Service System Research 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iess-porto-ossr-2013-02-08-130211130406-phpapp02/75/Modeling-Service-Relationships-for-Service-Networks-32-2048.jpg)
