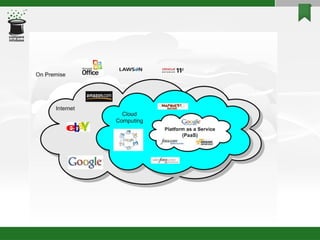
Cloud computing allows users to access computing resources and applications over the Internet. It provides scalability, lower costs, and more efficient utilization of resources compared to local computing. There are different types of cloud services including Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Cloud computing delivers significant business benefits like reduced costs, more agile resource usage, and robust scalability.