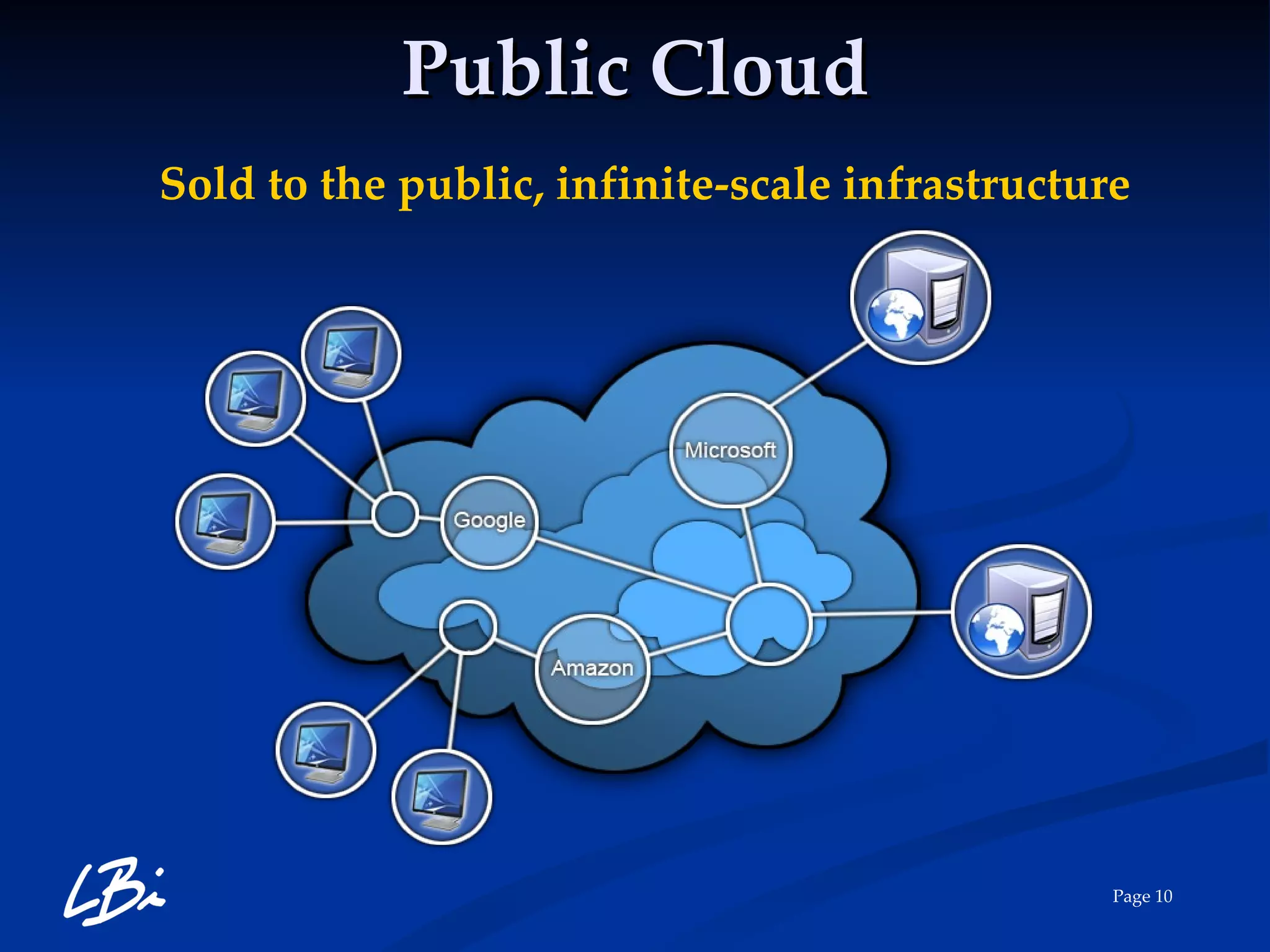
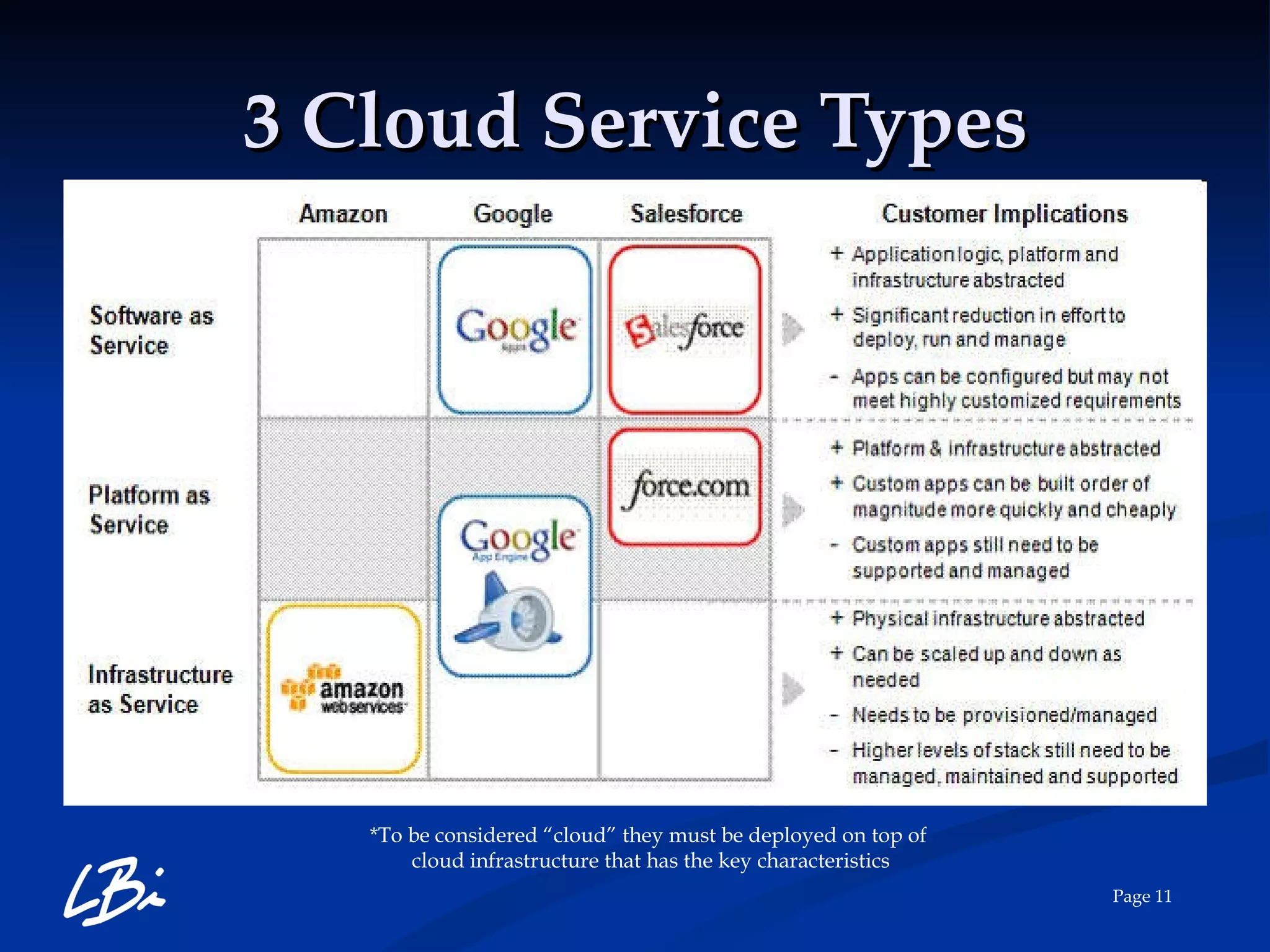
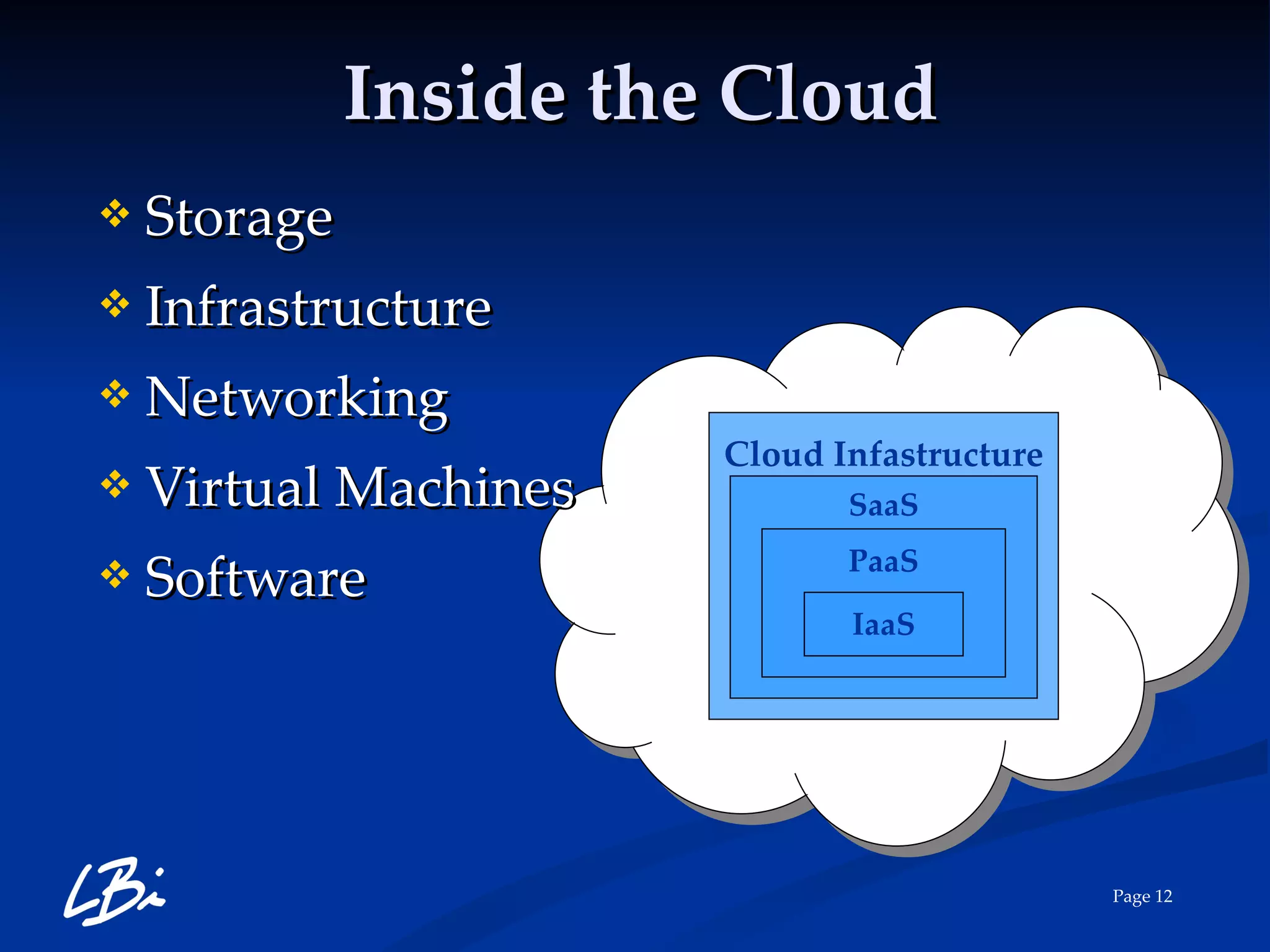
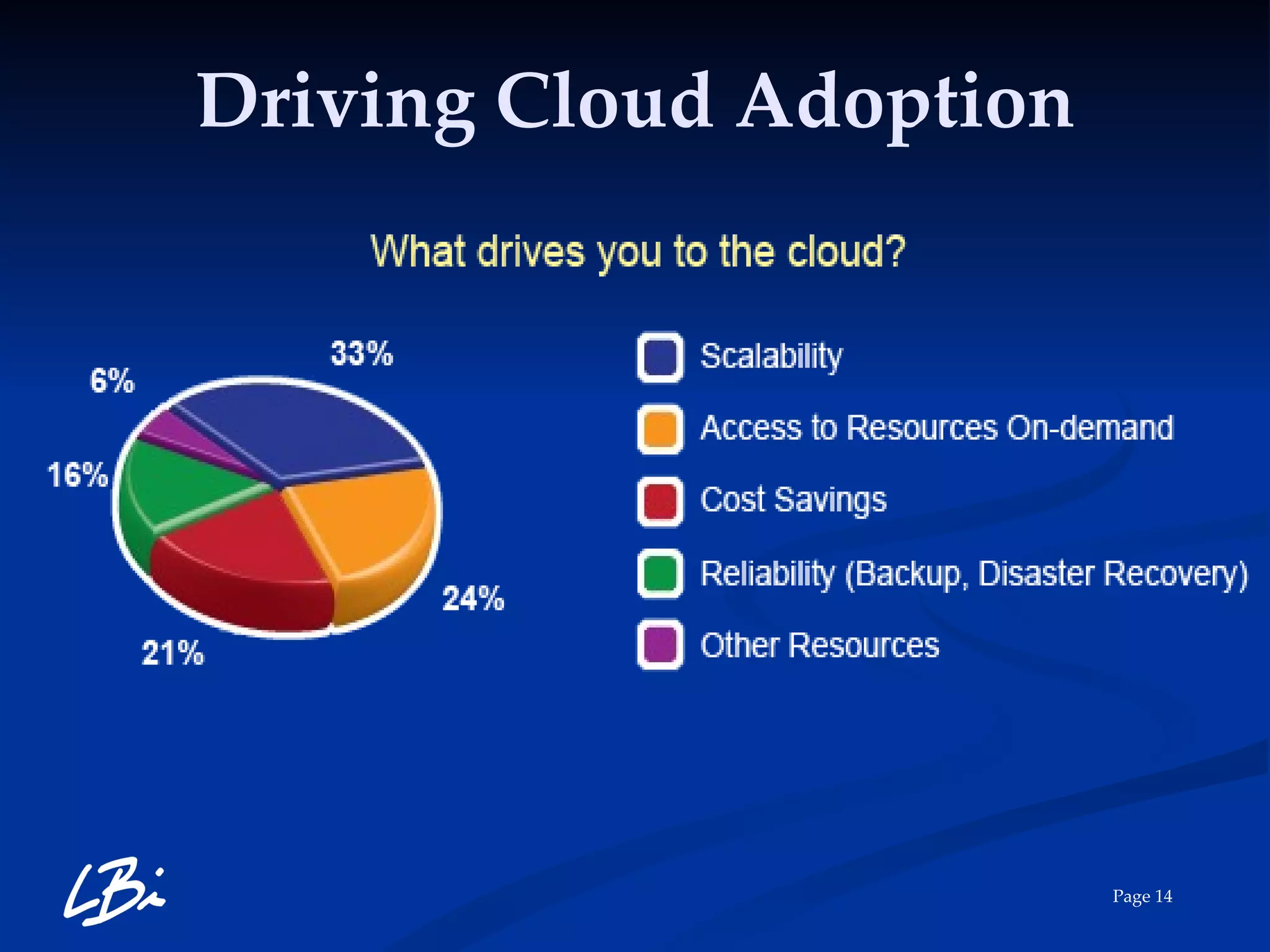
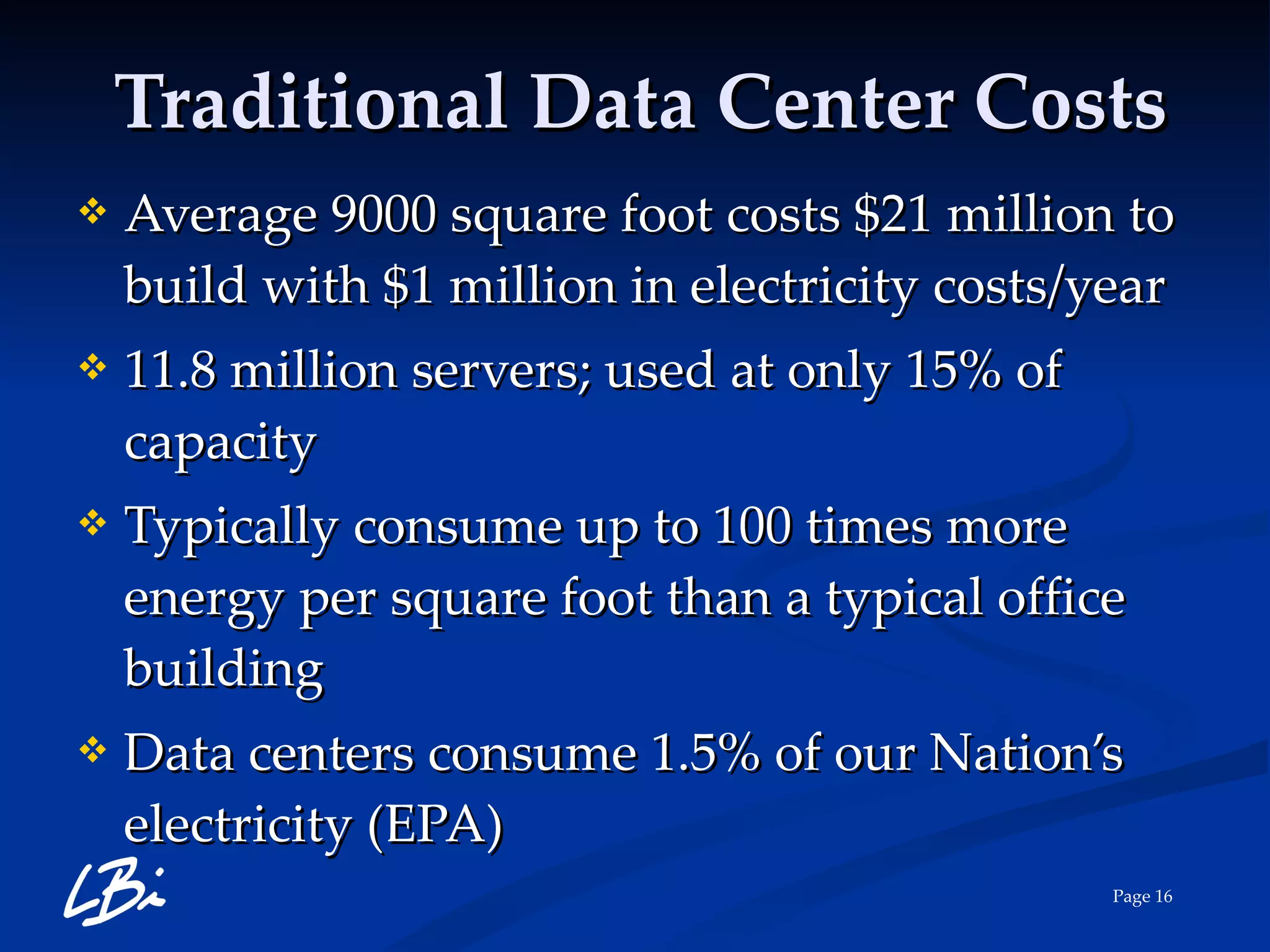
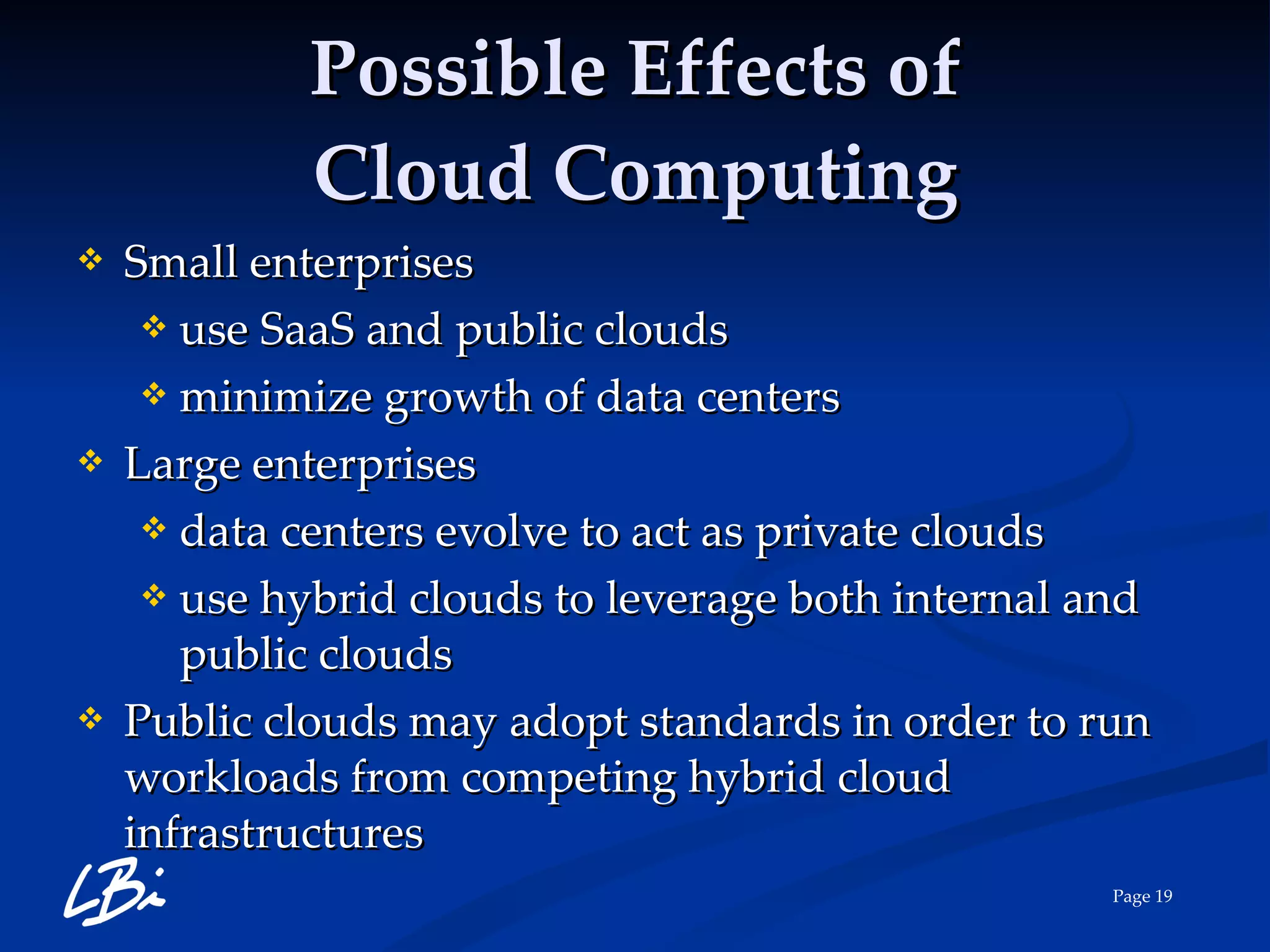
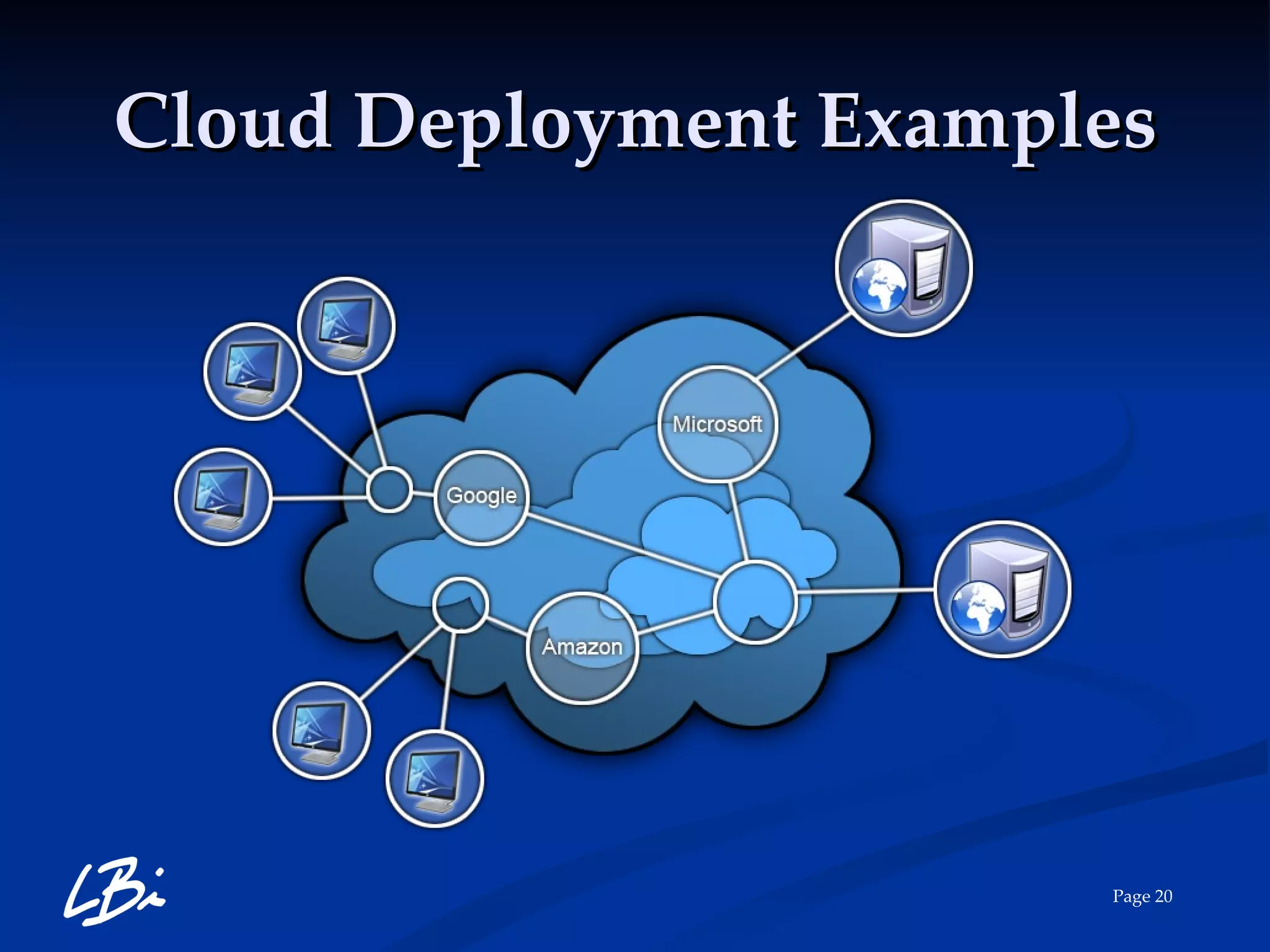
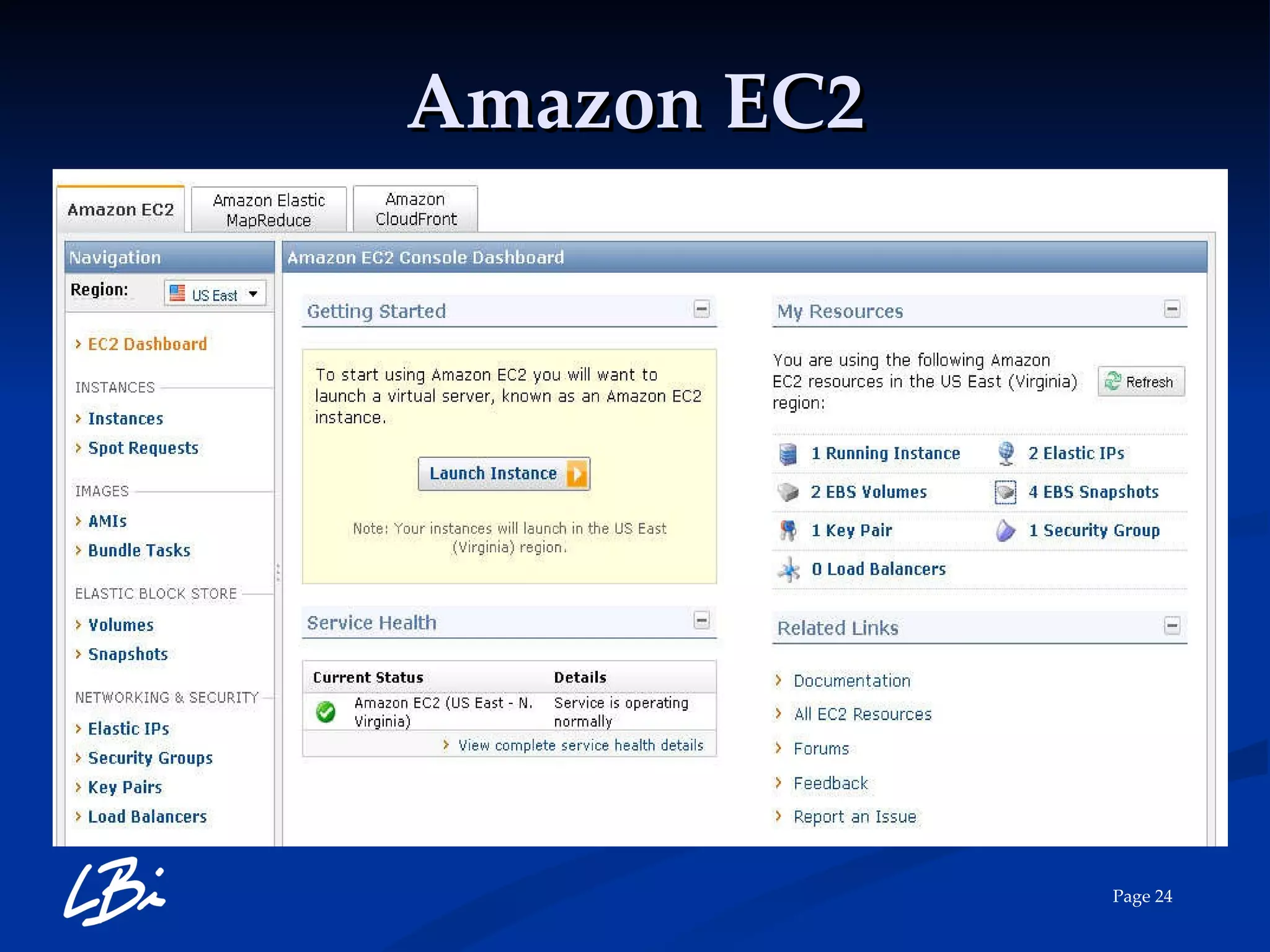
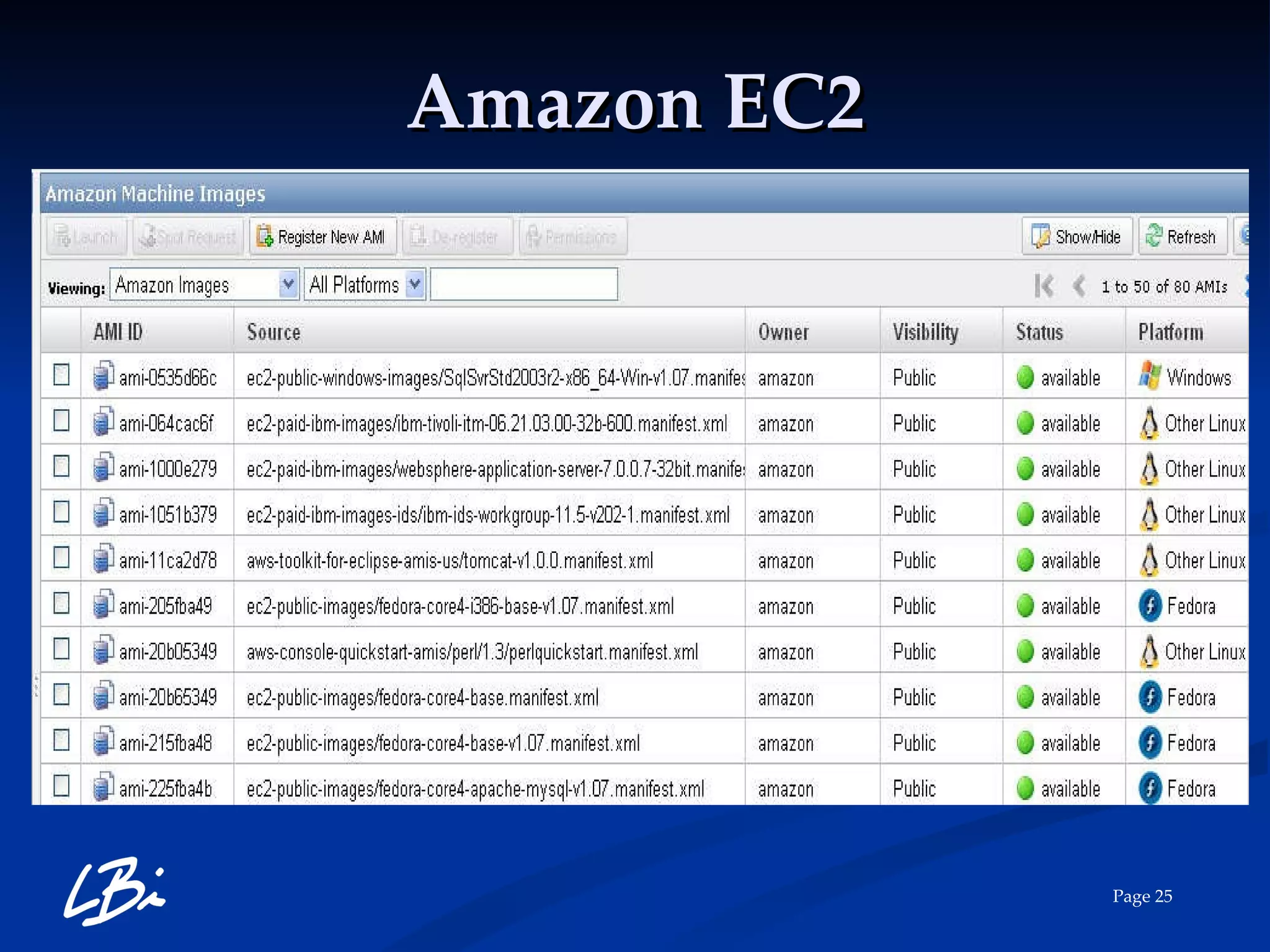
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, explaining its definition, characteristics, deployment models, and service types. It highlights the economic benefits of cloud adoption, comparing traditional IT costs to potential savings from cloud solutions, and includes examples of cloud applications in various sectors. Additionally, it mentions LBI Software's offerings in cloud services, including hosting and backup solutions.