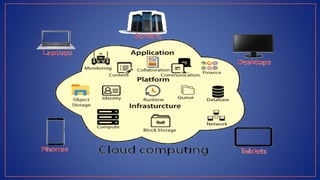
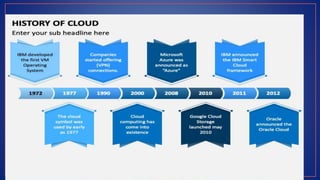
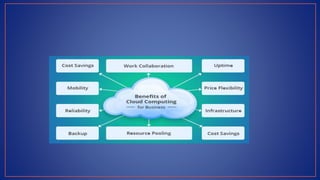
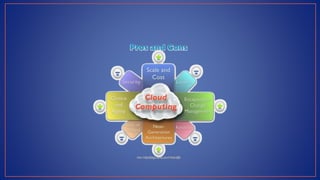
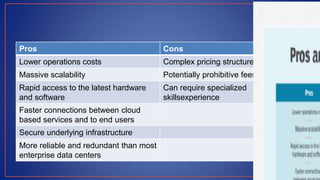
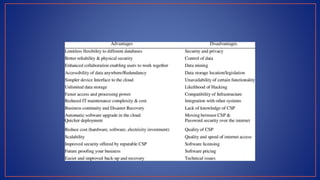
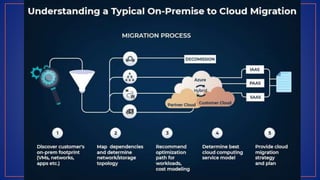
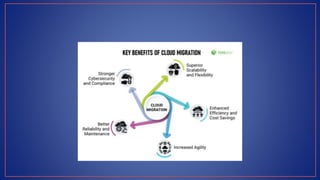
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like servers, storage, databases, networking, software and analytics over the internet. It has several key characteristics including on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity and measured service. Migrating to the cloud involves transferring business processes, applications and data from on-premise systems to cloud platforms and optimizing them to take advantage of cloud features through a seven step model.




![• Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-
demand network access to a shared pool of configurable
computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage,
applications, and services) [Mell_2009], [Berkely_2009].
• It can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal
management effort.
• It provides high level abstraction of computation and
storage model.
• It has some essential characteristics, service models,
and deployment models.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingbasics-230218040542-407b3b64/85/Cloud-Computing-Basics-pptx-5-320.jpg)