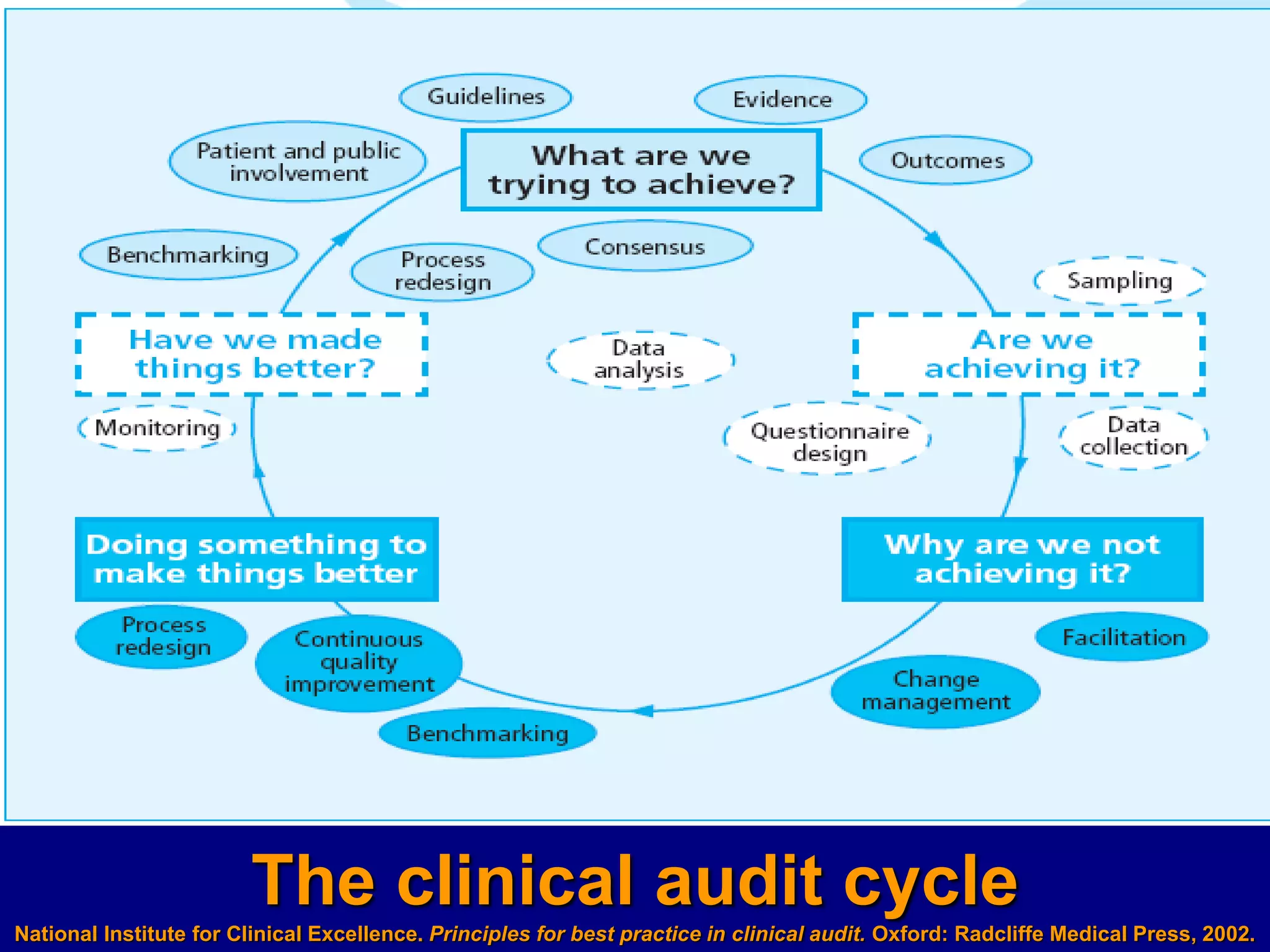
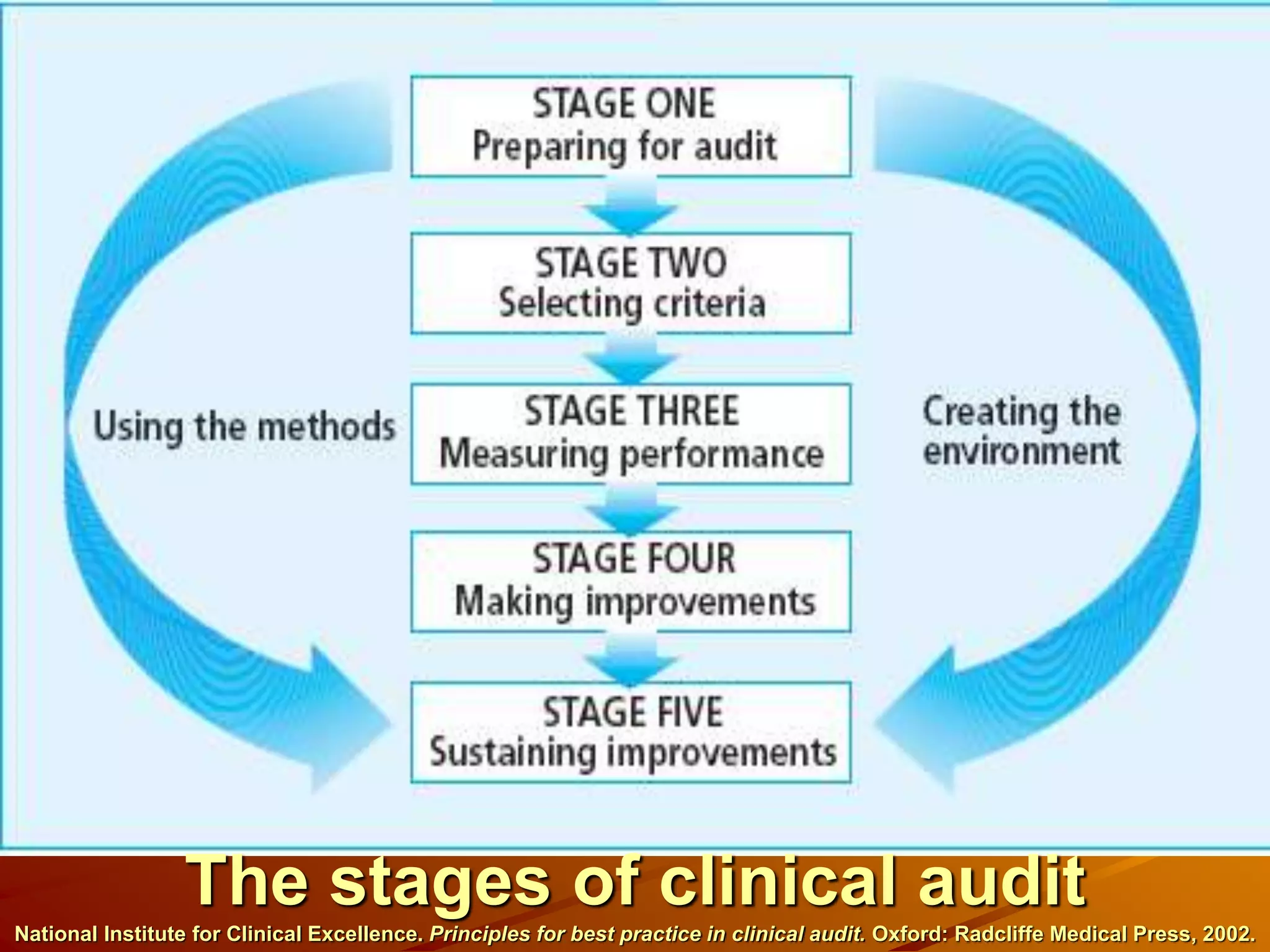
The document discusses clinical audit, which involves systematically analyzing healthcare quality, procedures, resource use, and patient outcomes and life quality. It describes the clinical audit cycle of defining standards, collecting data on performance, comparing performance to standards, implementing changes if needed, and monitoring additional data. The goals of clinical audits are to improve healthcare quality, efficiency, standards, and patient outcomes and satisfaction. Common methods used in clinical audits include reviewing medical records, incidents of adverse patient reactions, diagnostic investigations, and therapeutic practices. Challenges of auditing primary care include difficulties setting standards, measuring outcomes, accounting for patient views, and causing anxiety for some doctors.



![Audit Cycle
What we are doing ?
Collect (data or performance)
Comparison [Assess performance against criteria & standard]
Identify Needs for change
Implementing change
Define Criteria & Standards
Select the issue
Audit Cycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clinicalaudit-230130091631-12a3477d/75/CLINICAL-AUDIT-5-2048.jpg)































![Analysis
Analysis must reflect the audit aim.
Analysis should always be focused.
First step: examine the frequency of
occurrence of each item or event [example 8
out of 40 may be widowed , 15 out of 40 may
be taken more than one drugs…etc] each of
these could be expressed as percentage.
Next step construct the tables that shows
range of each item of data collected this will
highlight unusual event occurrence &analysis
can be focused
As the result production one or more tables
containing only data required.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clinicalaudit-230130091631-12a3477d/75/CLINICAL-AUDIT-38-2048.jpg)




