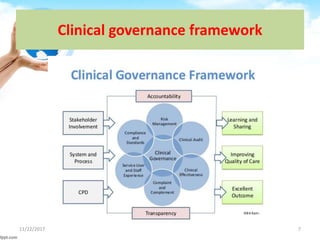
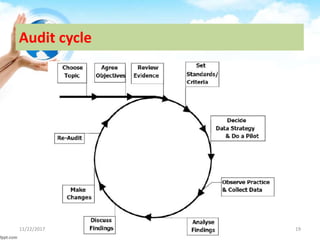
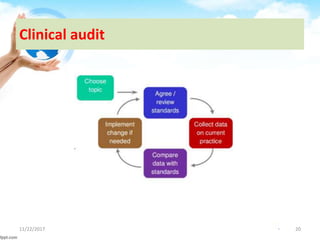
The document outlines the concept of clinical governance, which is a framework aimed at improving healthcare quality and ensuring accountability in health organizations. It describes the seven pillars that support clinical governance: patient and public involvement, risk management, staffing and staff management, education and training, clinical effectiveness and research, using clinical information and IT, and clinical audit. Each pillar focuses on various aspects of care, including risk minimization, staff development, and the continuous improvement of services through structured processes.