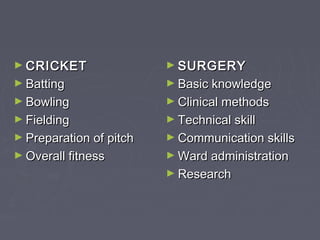
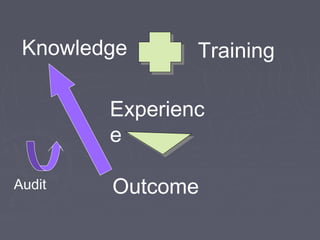
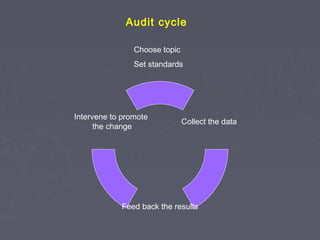
Javed Iqbal draws a comparison between cricket and surgery, noting that both are missing an important element of record keeping. For cricket, it is keeping score, while for surgery it is conducting audits. Without audits, surgical practice would be like playing cricket without keeping score. Audits are a systematic, critical review of clinical care that can help highlight opportunities for improvement. The main goals of audits are to evaluate current practices, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to promote better patient outcomes and evidence-based healthcare.