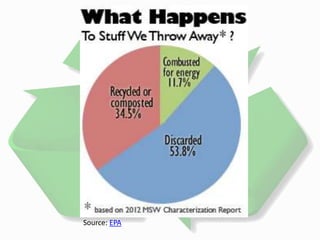
Recycling is the process of collecting, sorting, and remanufacturing used materials into new products to reduce waste. It involves three main steps - collecting and sorting recyclables, manufacturing them into new materials, and selling the recycled products. In the US, only 34% of waste is recycled each year. Recycling helps conserve natural resources, prevents pollution, saves energy, creates jobs, and leads to a more sustainable future. Common items that can be recycled include aluminum cans, plastic bottles, glass bottles, paper, and cardboard. People can recycle through curbside pickup programs, drop-off centers, or by starting their own recycling initiatives.