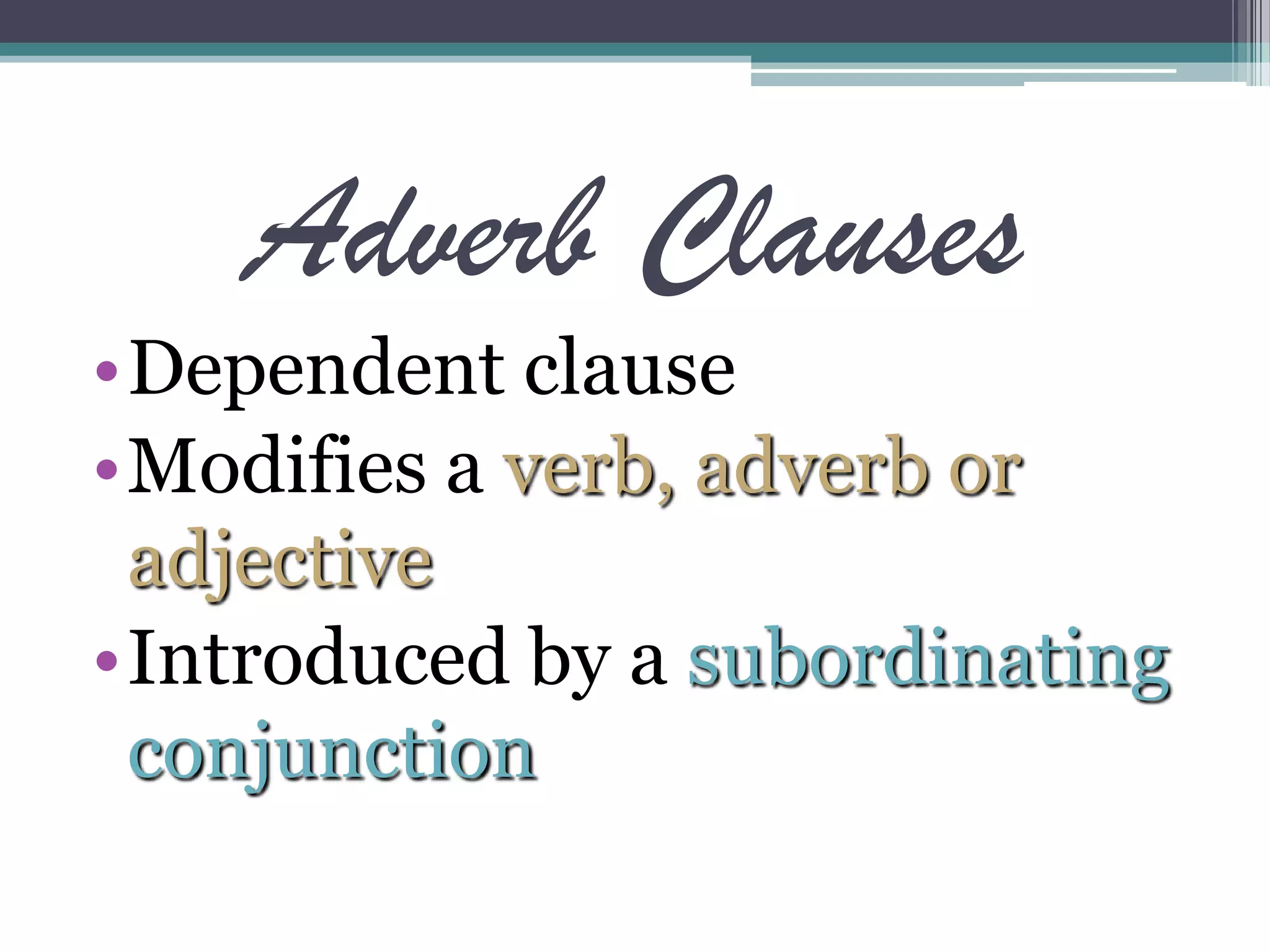
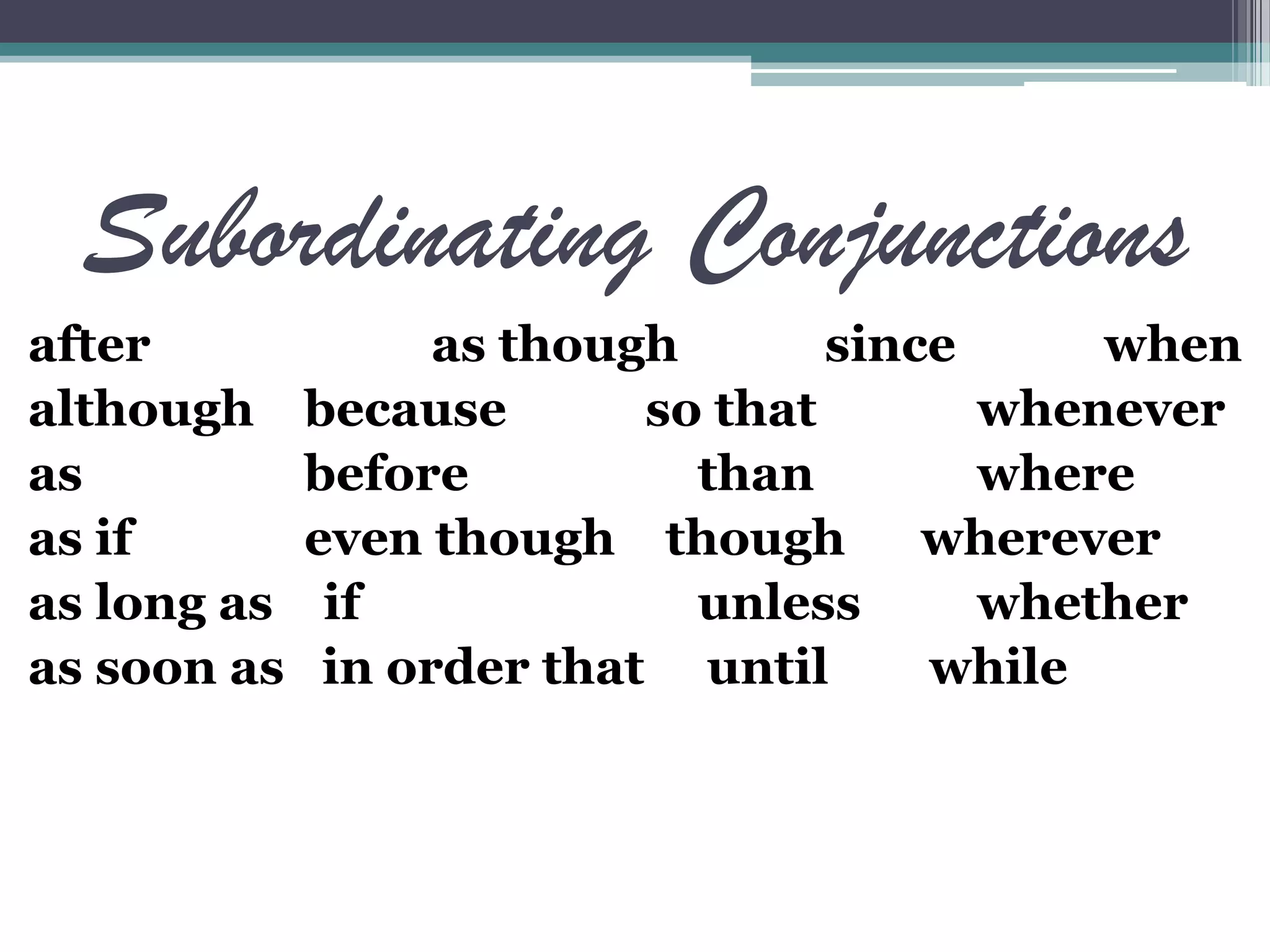
This document defines and provides examples of three types of clauses: adjective clauses, adverb clauses, and noun clauses. Adjective clauses modify nouns and begin with relative pronouns like "who" or "that." Adverb clauses modify verbs, adverbs, or adjectives and are introduced by subordinating conjunctions like "because" or "when." Noun clauses function as subjects, objects, or complements and are introduced by words like "that," "what," or "if." Examples of each type of clause are given.