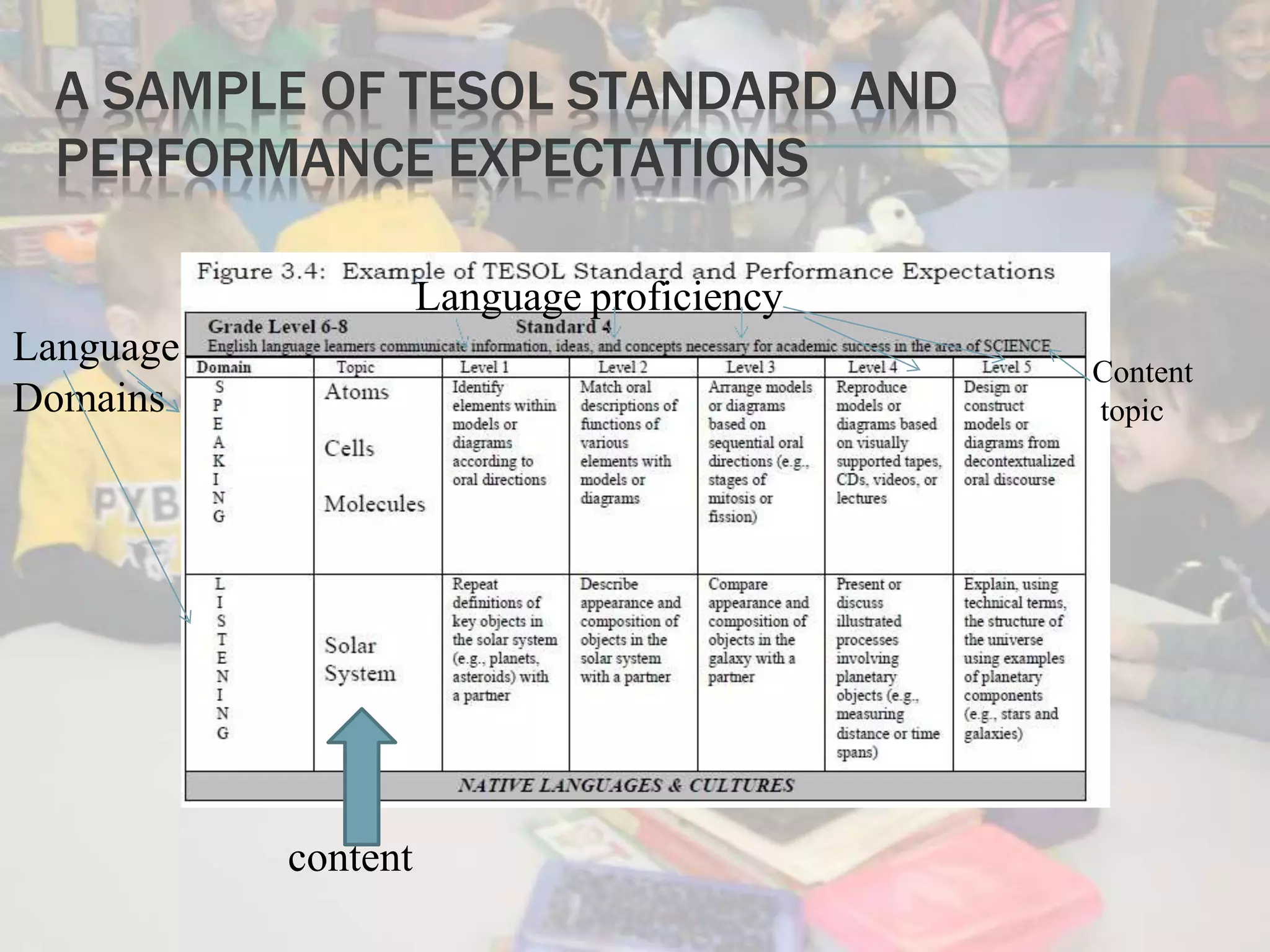
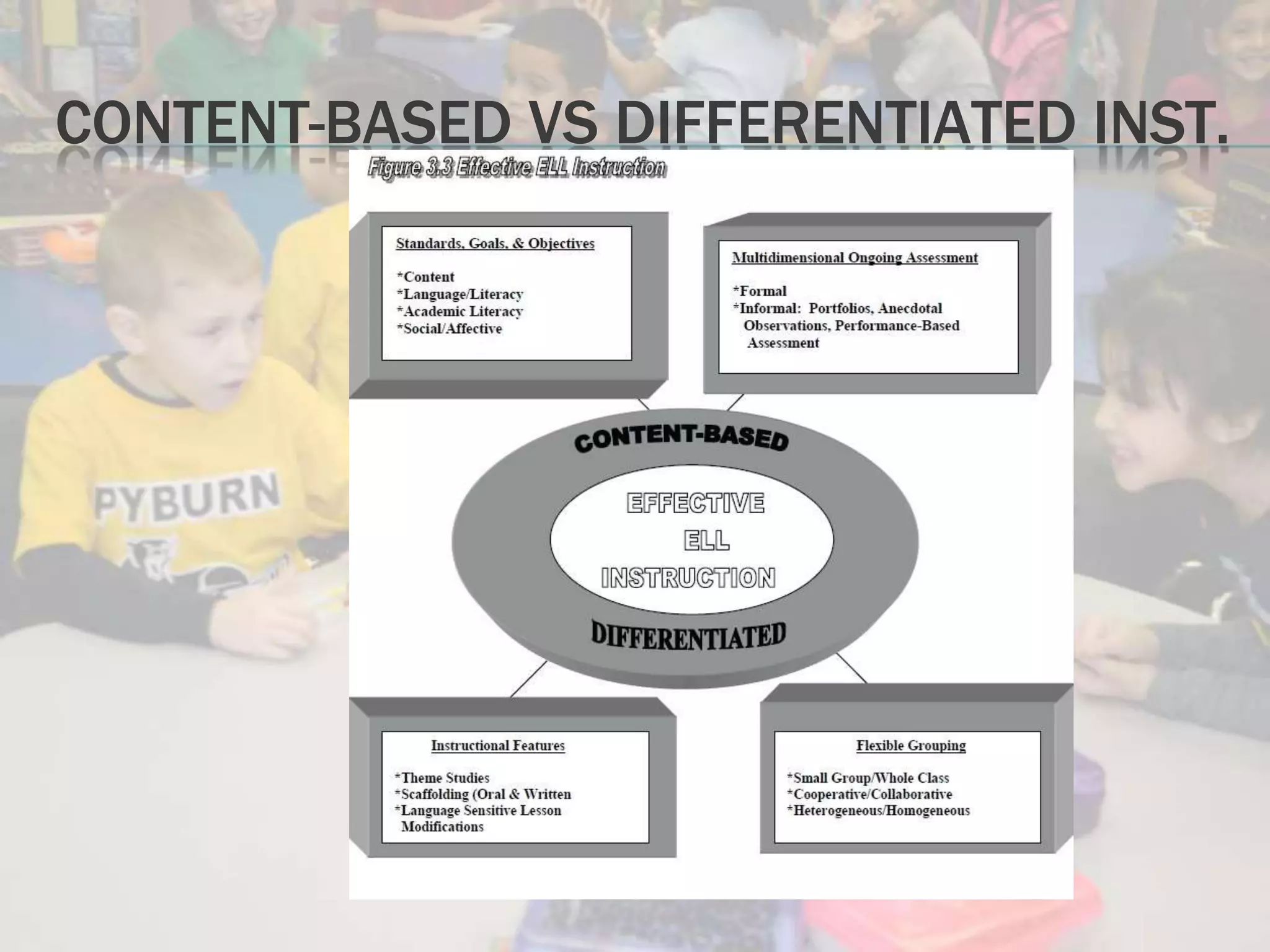
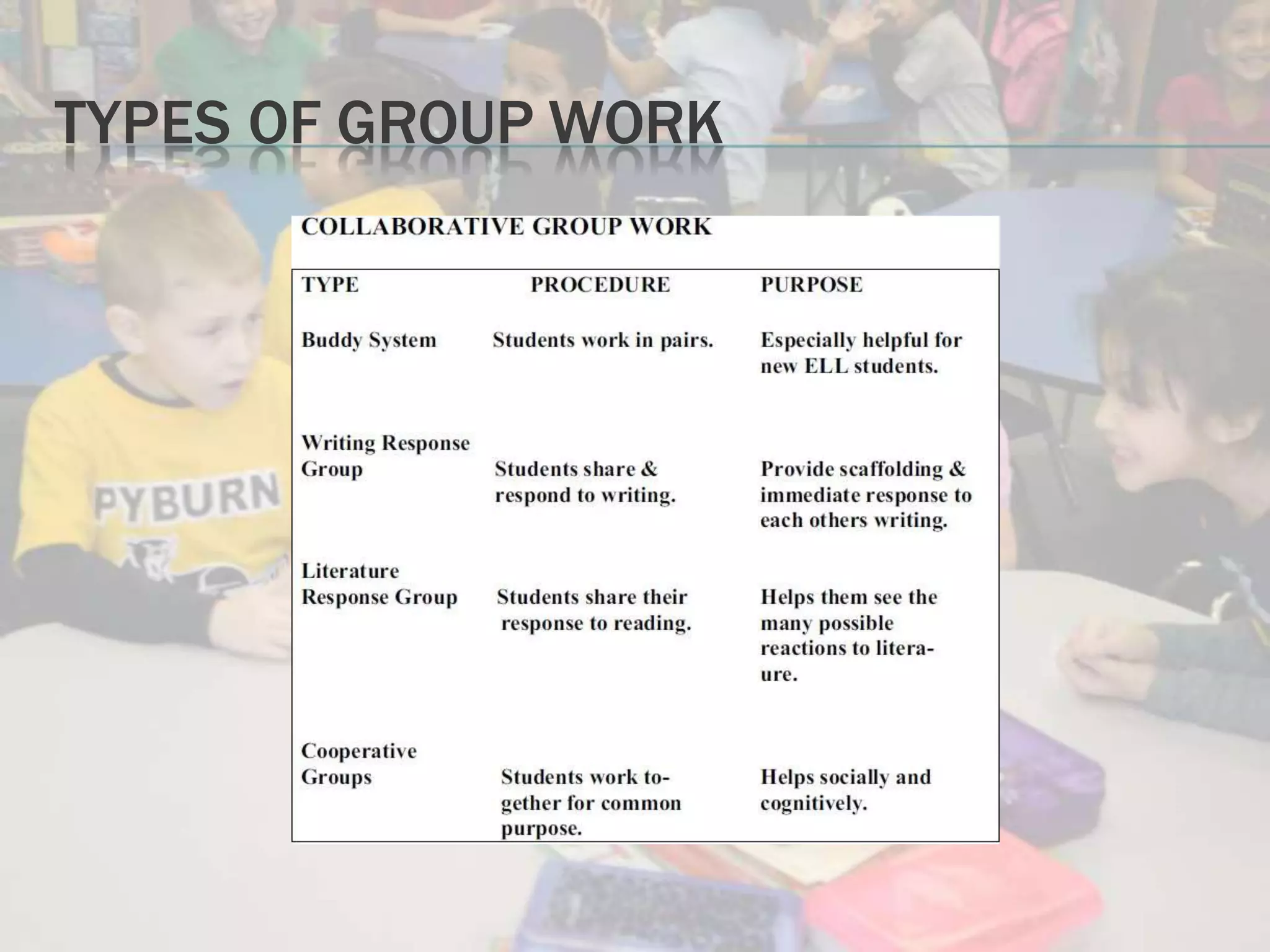
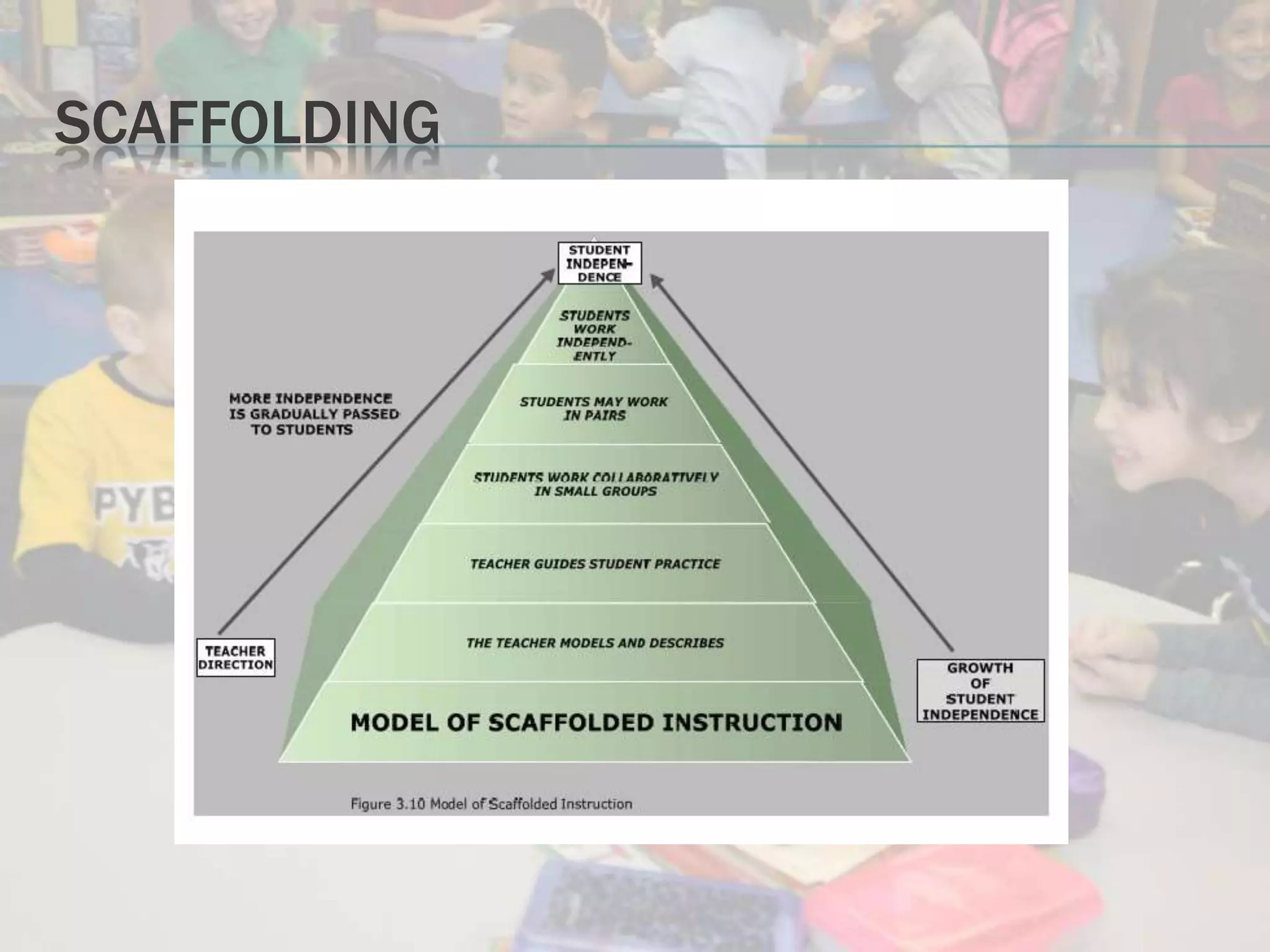
Standards-based instruction for English learners involves aligning content, language, and performance standards. It creates high expectations and meaningful learning contexts framed around what and why students need to learn. Teachers should familiarize themselves with relevant standards and use differentiated instruction, content-based instruction, scaffolding and thematic units to meet student needs. Assessment of English learners should be multidimensional, involving formal and informal methods like portfolios and classroom observations in addition to standardized tests.