classifying animals & phylum arthropods / classifying plants /dichotomous keys
•Download as ODP, PDF•
3 likes•2,903 views
Presentation on 1.5 classifying animals phylum arthropods and 1.6 classifying plants and dichotomous keys
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
LARVAL FORMS OF MOLLUSCA.pptx

LARVAL FORMS OF MOLLUSCA BHY SHRUTI SINGH MSC 1ST SEM FROM GEVPG COLLAGE KORBA CHHATTISGARGH,Types of larva are found in mollusca
Classification of amphibia

Amphibians are teterapod vertebrata, transition stage between aquatic and terrestial mode of life.
Phylum Annelida - Class Polychaeta, Class Oligochaeta, Class Hirudinea

The document summarizes the annelid phylum, focusing on the class Polychaeta. Some key points:
- Polychaeta are segmented marine worms with parapodia used for locomotion and respiration. They display a range of feeding modes from predation to filter feeding.
- They have a distinct head with sensory organs and a retractable pharynx with jaws. Their body segments bear appendages called parapodia with setae.
- Reproduction varies but often involves asexual budding or releasing gametes into the water column in mass spawnings tied to lunar cycles.
- Examples discussed include clam worms, blood worms, fanworms and tubeworms, which may bur
Class Polychaeta Notes

The document discusses the phylum Annelida, class Polychaeta. Polychaetes, also known as bristle worms, are segmented worms that live in a variety of marine habitats like the ocean floor, under rocks and shells, or in coral reef crevices. They have appendages called setae or parapodia that function as paddles. While some polychaetes are free-swimming predators or scavengers, others like tube worms live sessile in self-made tubes attached to surfaces. Tube worms extend feathery gills and radioles from their tubes to create water currents for filter feeding.
Epidermal derivatives

The document summarizes several epidermal derivatives of the skin including hair, nails, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and ceruminous glands. It states that hair is made of keratinized epithelial cells and consists of a shaft and root surrounded by the hair follicle. Nails cover the ends of fingers and toes and grow from the nail bed and matrix. Sebaceous and sweat glands are also described along with their functions of lubricating skin and regulating body temperature. Ceruminous glands uniquely produce earwax to protect the ear canal.
Foot and shell of molluscs

This document summarizes the foot and shell structures of molluscs. It describes how the foot aids in locomotion and adhesion. It then discusses the different classes of molluscs and how the foot is modified, such as being spade-like in scaphopods or arms in cephalopods. The document also summarizes shell structure, the three layers of shell, types of coiling, composition of shell material, and variations in shells across classes. It concludes by discussing reductions in shells and the protective and other functions shells provide.
Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& af...

Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& affinity to pro,meta &eutheria
structure and development of Stem and Root

The document discusses the structure and development of plant roots and stems. It describes how roots absorb water and minerals to support the plant, transport nutrients, and in some cases store food or enable vegetative reproduction. Roots have a tapered shape to easily penetrate soil. The document also outlines the functions of stems in distributing water and nutrients between roots and leaves. Stems support leaves, flowers, and seeds and can be used for various human purposes. The types of roots include taproots for food storage and fibrous roots for foundation support. Stem types include woody, grass-like, and wet varieties.
Recommended
LARVAL FORMS OF MOLLUSCA.pptx

LARVAL FORMS OF MOLLUSCA BHY SHRUTI SINGH MSC 1ST SEM FROM GEVPG COLLAGE KORBA CHHATTISGARGH,Types of larva are found in mollusca
Classification of amphibia

Amphibians are teterapod vertebrata, transition stage between aquatic and terrestial mode of life.
Phylum Annelida - Class Polychaeta, Class Oligochaeta, Class Hirudinea

The document summarizes the annelid phylum, focusing on the class Polychaeta. Some key points:
- Polychaeta are segmented marine worms with parapodia used for locomotion and respiration. They display a range of feeding modes from predation to filter feeding.
- They have a distinct head with sensory organs and a retractable pharynx with jaws. Their body segments bear appendages called parapodia with setae.
- Reproduction varies but often involves asexual budding or releasing gametes into the water column in mass spawnings tied to lunar cycles.
- Examples discussed include clam worms, blood worms, fanworms and tubeworms, which may bur
Class Polychaeta Notes

The document discusses the phylum Annelida, class Polychaeta. Polychaetes, also known as bristle worms, are segmented worms that live in a variety of marine habitats like the ocean floor, under rocks and shells, or in coral reef crevices. They have appendages called setae or parapodia that function as paddles. While some polychaetes are free-swimming predators or scavengers, others like tube worms live sessile in self-made tubes attached to surfaces. Tube worms extend feathery gills and radioles from their tubes to create water currents for filter feeding.
Epidermal derivatives

The document summarizes several epidermal derivatives of the skin including hair, nails, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and ceruminous glands. It states that hair is made of keratinized epithelial cells and consists of a shaft and root surrounded by the hair follicle. Nails cover the ends of fingers and toes and grow from the nail bed and matrix. Sebaceous and sweat glands are also described along with their functions of lubricating skin and regulating body temperature. Ceruminous glands uniquely produce earwax to protect the ear canal.
Foot and shell of molluscs

This document summarizes the foot and shell structures of molluscs. It describes how the foot aids in locomotion and adhesion. It then discusses the different classes of molluscs and how the foot is modified, such as being spade-like in scaphopods or arms in cephalopods. The document also summarizes shell structure, the three layers of shell, types of coiling, composition of shell material, and variations in shells across classes. It concludes by discussing reductions in shells and the protective and other functions shells provide.
Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& af...

Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& affinity to pro,meta &eutheria
structure and development of Stem and Root

The document discusses the structure and development of plant roots and stems. It describes how roots absorb water and minerals to support the plant, transport nutrients, and in some cases store food or enable vegetative reproduction. Roots have a tapered shape to easily penetrate soil. The document also outlines the functions of stems in distributing water and nutrients between roots and leaves. Stems support leaves, flowers, and seeds and can be used for various human purposes. The types of roots include taproots for food storage and fibrous roots for foundation support. Stem types include woody, grass-like, and wet varieties.
General characters amphibia

1) Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that can live both on land and in water. They have four limbs and lungs as adults.
2) Amphibians are classified into three subclasses: Labyrinthodontia, Lepospondyli, and Lissamphibia.
3) The three orders of modern amphibians (Lissamphibia) are Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Apoda (limbless amphibians).
Leech.pptx

The document summarizes the key characteristics of the Indian cattle leech (Hirudinaria granulosa). It lives in freshwater habitats in parts of Asia and feeds on the blood of various animals, including cattle and humans. The body is soft and elongated, segmented into 33 segments. It has distinctive coloration and two suckers used for attachment and feeding. The document describes the leech's external morphology, internal body structure, and two modes of locomotion.
Respiratory system in insect

The respiratory system of insects involves a network of tubular structures called trachea that distribute oxygen throughout the body. Trachea branch into very fine tracheoles that penetrate tissues and supply oxygen. Trachea are composed of a spiral thickening called taenidia that provides support. They open to the outside through spiracles located on the thorax and abdomen. Spiracles allow gas exchange and can close to prevent water loss. Trachea branch and connect to form a dorsal, ventral and two lateral trunks that supply different body regions. Respiration is classified based on the number and location of functional spiracles. Some insects respire through other structures like gills or cuticular surfaces in the absence of
Types of insect wings

The document discusses the different types of insect wings including their structure, venation, and function. It describes 7 different wing types such as tegmina, elytra, hemelytra, and halteres. The document also covers wing coupling mechanisms like hamulate, amplexiform, and frenate coupling that allow the forewings and hindwings to work together during flight.
Phylum Coelenterata Clear Concept

This document provides information about coral reefs and the process of coral reef formation. It defines coral reefs as underwater structures made of calcium carbonate secreted by coral polyps belonging to the phylum Cnidaria. It then describes the main type of fringing reef, noting that it is distinguished from barrier reefs and atolls by having a shallow backreef zone or none at all, and growing directly from the shoreline or extending hundreds of yards from shore with potential backreef areas.
Flight adaptation and Mechanism Of Flight in Birds.

This document discusses flight adaptations and the mechanism of flight in birds. It describes the key morphological adaptations birds have developed for flight including their streamlined bodies, lightweight feathers, modified forelimbs that form wings, and other adaptations. It also discusses important anatomical modifications such as their lightweight skeletons, strong breast muscles, and efficient respiratory and circulatory systems. Finally, it explains how birds generate lift through their airfoils and use a downward power stroke and upward recovery stroke of their wings to fly through flapping.
Amphibians

Amphibians were the first vertebrates to adapt to living on land, though most still require water for reproduction or parts of their life cycle. They have moist skin, minimal teeth, and undergo metamorphosis from aquatic tadpoles to terrestrial adults. While tadpoles are herbivorous, most adult amphibians are carnivorous. They have complex life cycles and come in three main types: anures without tails, urodels with tails, and legless gymnophions.
Mouth parts of Insect

The document summarizes the different types of insect mouthparts based on their structure and function. It describes 8 main types: 1) biting and chewing, 2) piercing and sucking (bug type), 3) piercing and sucking (mosquito type), 4) chewing and lapping, 5) rasping and sucking, 6) mandibulosuctorial, 7) sponging, and 8) siphoning. Each type has a distinct structure of the mouthparts that determines how the insect feeds, such as biting solid food, piercing and sucking liquids, lapping nectar, or siphoning plant fluids.
arthropoda Phylum 

Insects, spiders, crabs, shrimp, millipedes, and centipedes are all arthropods. Arthropods have jointed feet, a segmented body, and an exoskeleton, a cuticle on the outside of their body. Arthropods have by far the greatest number of species of any animal group, at around 900,000 species
Archaeopteryx

Archaeopteryx is a genus of feathered dinosaurs that lived around 150 million years ago during the late Jurassic period and is considered a transitional form between non-avian dinosaurs and modern birds, exhibiting both avian and reptilian features such as teeth, claws, and a long tail as well as feathers and a wishbone. Discovered in 1860 in Germany, Archaeopteryx has helped establish birds as modern feathered dinosaurs.
Integumentary derivative

vertebrate integument and its derivative
development general structure and function of integument and its derivative
gland, scales,horns, claws,nails, hooves, feathers and hairs.
Classification of aves

All birds are in the Animalia Kingdom, Phylum of Chordata (with a backbone), and Class Aves (birds). At the Order level, the birds begin to diverge. For instance, the pelicans are in the Pelecaniformes Order while the nuthatches are in the Passeriformes Order.
Evolutionary history of insects

this presentation will help you to learn about the evolutionary history of development of insects and their adaptations as the passage of the time.
Osmoregulation in Fishes and Birds 

Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining salt and water balance (osmotic balance) across membranes within the body. The fluids inside and surrounding cells are composed of water, electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. An electrolyte is a compound that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water.
CLASSIFICATION OF MAMMALS

Mammals are classified into 5420 species within 152 families and 29 orders. The two subclasses are Prototheria and Theria. Prototheria contains monotremes like platypuses and echidnas that lay eggs. Theria contains marsupials in the infraclass Metatheria that give birth to immature young developing further in pouches, and placentals in Eutheria that give live birth to mature young. Marsupials include opossums and kangaroos, while placentals make up the majority of mammal species and include humans, whales, bats and more. Classification systems continue to evolve as new genetic and fossil evidence is discovered.
Mouthparts of insect.pdf

1. Insects have different types of mouthparts depending on their feeding habits. The two main types are mandibulate, for feeding on solid food, and haustellate, for feeding on liquid food.
2. Examples of different mouthpart types include: biting and chewing (cockroaches, grasshoppers), piercing and sucking (plant bugs, mosquitoes), chewing and lapping (honey bees), rasping and sucking (thrips), mandibulosuctorial (antlion grubs), sponging (house flies), and siphoning (moths, butterflies).
3. Each mouthpart type is adapted to the insect's method of feeding, such as having
Phylum arthropoda characteristics

Phylum Arthropoda includes insects, crustaceans, arachnids and makes up over 82% of all living things. They are characterized by having a segmented body, jointed appendages, and an exoskeleton made of chitin. Arthropods have a head with sensory organs and mouthparts, a thorax for appendage attachment, and some have an abdomen. Their exoskeleton provides protection but limits growth, requiring molting. They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and have open circulatory, digestive and nervous systems adapted for their habitat.
Reproductive system of Ascaris lumbricoides

The reproductive systems of male and female Ascaris lubricoides worms are described. The male system includes a single coiled testis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, ejaculatory duct, and two penial spicules. The female system includes two long coiled ovaries, oviducts, uteri which store fertilized eggs, and a vagina. Gametes are formed through a process called telogony, where gametogonia bud off from the gonads and differentiate into gametocytes as they move through zones of proliferation, growth, and maturation.
Accssory respiratiory organs in fishes

Gills are primary respiratory organs in fishes, Extra branchial respiration is highly useful for survival when oxygen supplied by gills is not sufficient.
Mollusca

Second-largest phylum in number of species- over 100,000 described.
Ecologically widespread- marine, freshwater, terrestrial (gastropods very successful on land)
Variety of body plans (therefore, many classes within the phylum)
Variety in body size- from ~1 mm to ~18 m (60 feet). 80% are under 5 cm, but many are large and therefore significant as food for man.
Diversity in organisms

The document summarizes key concepts around classification of living organisms. It discusses how organisms are classified into taxonomic groups like domain, kingdom, phylum etc. based on their similarities. For humans, the taxonomic classification includes Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Mammalia, Primates, Hominidae, Homo and H. sapiens. It also provides classifications for major kingdoms like Plantae, Animalia and describes characteristics of key phyla under these kingdoms including porifera, coelenterata, platyhelminthes, nematoda, annelida and arthropoda.
Unit-1 Master of forestry(Entomology) final.pptx

This document provides an overview of insect morphology and physiology. It begins by defining entomology and forest entomology, and describing the scope of forest entomology. It then discusses the external morphology of insects, including their body surface, segmentation, head, thorax, abdomen and appendages. The document also describes the internal systems of insects, focusing on the digestive system including the foregut, midgut and hindgut, as well as the respiratory system consisting of trachea and spiracles, and the nervous system composed of a nerve cord and ganglia.
More Related Content
What's hot
General characters amphibia

1) Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that can live both on land and in water. They have four limbs and lungs as adults.
2) Amphibians are classified into three subclasses: Labyrinthodontia, Lepospondyli, and Lissamphibia.
3) The three orders of modern amphibians (Lissamphibia) are Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Apoda (limbless amphibians).
Leech.pptx

The document summarizes the key characteristics of the Indian cattle leech (Hirudinaria granulosa). It lives in freshwater habitats in parts of Asia and feeds on the blood of various animals, including cattle and humans. The body is soft and elongated, segmented into 33 segments. It has distinctive coloration and two suckers used for attachment and feeding. The document describes the leech's external morphology, internal body structure, and two modes of locomotion.
Respiratory system in insect

The respiratory system of insects involves a network of tubular structures called trachea that distribute oxygen throughout the body. Trachea branch into very fine tracheoles that penetrate tissues and supply oxygen. Trachea are composed of a spiral thickening called taenidia that provides support. They open to the outside through spiracles located on the thorax and abdomen. Spiracles allow gas exchange and can close to prevent water loss. Trachea branch and connect to form a dorsal, ventral and two lateral trunks that supply different body regions. Respiration is classified based on the number and location of functional spiracles. Some insects respire through other structures like gills or cuticular surfaces in the absence of
Types of insect wings

The document discusses the different types of insect wings including their structure, venation, and function. It describes 7 different wing types such as tegmina, elytra, hemelytra, and halteres. The document also covers wing coupling mechanisms like hamulate, amplexiform, and frenate coupling that allow the forewings and hindwings to work together during flight.
Phylum Coelenterata Clear Concept

This document provides information about coral reefs and the process of coral reef formation. It defines coral reefs as underwater structures made of calcium carbonate secreted by coral polyps belonging to the phylum Cnidaria. It then describes the main type of fringing reef, noting that it is distinguished from barrier reefs and atolls by having a shallow backreef zone or none at all, and growing directly from the shoreline or extending hundreds of yards from shore with potential backreef areas.
Flight adaptation and Mechanism Of Flight in Birds.

This document discusses flight adaptations and the mechanism of flight in birds. It describes the key morphological adaptations birds have developed for flight including their streamlined bodies, lightweight feathers, modified forelimbs that form wings, and other adaptations. It also discusses important anatomical modifications such as their lightweight skeletons, strong breast muscles, and efficient respiratory and circulatory systems. Finally, it explains how birds generate lift through their airfoils and use a downward power stroke and upward recovery stroke of their wings to fly through flapping.
Amphibians

Amphibians were the first vertebrates to adapt to living on land, though most still require water for reproduction or parts of their life cycle. They have moist skin, minimal teeth, and undergo metamorphosis from aquatic tadpoles to terrestrial adults. While tadpoles are herbivorous, most adult amphibians are carnivorous. They have complex life cycles and come in three main types: anures without tails, urodels with tails, and legless gymnophions.
Mouth parts of Insect

The document summarizes the different types of insect mouthparts based on their structure and function. It describes 8 main types: 1) biting and chewing, 2) piercing and sucking (bug type), 3) piercing and sucking (mosquito type), 4) chewing and lapping, 5) rasping and sucking, 6) mandibulosuctorial, 7) sponging, and 8) siphoning. Each type has a distinct structure of the mouthparts that determines how the insect feeds, such as biting solid food, piercing and sucking liquids, lapping nectar, or siphoning plant fluids.
arthropoda Phylum 

Insects, spiders, crabs, shrimp, millipedes, and centipedes are all arthropods. Arthropods have jointed feet, a segmented body, and an exoskeleton, a cuticle on the outside of their body. Arthropods have by far the greatest number of species of any animal group, at around 900,000 species
Archaeopteryx

Archaeopteryx is a genus of feathered dinosaurs that lived around 150 million years ago during the late Jurassic period and is considered a transitional form between non-avian dinosaurs and modern birds, exhibiting both avian and reptilian features such as teeth, claws, and a long tail as well as feathers and a wishbone. Discovered in 1860 in Germany, Archaeopteryx has helped establish birds as modern feathered dinosaurs.
Integumentary derivative

vertebrate integument and its derivative
development general structure and function of integument and its derivative
gland, scales,horns, claws,nails, hooves, feathers and hairs.
Classification of aves

All birds are in the Animalia Kingdom, Phylum of Chordata (with a backbone), and Class Aves (birds). At the Order level, the birds begin to diverge. For instance, the pelicans are in the Pelecaniformes Order while the nuthatches are in the Passeriformes Order.
Evolutionary history of insects

this presentation will help you to learn about the evolutionary history of development of insects and their adaptations as the passage of the time.
Osmoregulation in Fishes and Birds 

Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining salt and water balance (osmotic balance) across membranes within the body. The fluids inside and surrounding cells are composed of water, electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. An electrolyte is a compound that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water.
CLASSIFICATION OF MAMMALS

Mammals are classified into 5420 species within 152 families and 29 orders. The two subclasses are Prototheria and Theria. Prototheria contains monotremes like platypuses and echidnas that lay eggs. Theria contains marsupials in the infraclass Metatheria that give birth to immature young developing further in pouches, and placentals in Eutheria that give live birth to mature young. Marsupials include opossums and kangaroos, while placentals make up the majority of mammal species and include humans, whales, bats and more. Classification systems continue to evolve as new genetic and fossil evidence is discovered.
Mouthparts of insect.pdf

1. Insects have different types of mouthparts depending on their feeding habits. The two main types are mandibulate, for feeding on solid food, and haustellate, for feeding on liquid food.
2. Examples of different mouthpart types include: biting and chewing (cockroaches, grasshoppers), piercing and sucking (plant bugs, mosquitoes), chewing and lapping (honey bees), rasping and sucking (thrips), mandibulosuctorial (antlion grubs), sponging (house flies), and siphoning (moths, butterflies).
3. Each mouthpart type is adapted to the insect's method of feeding, such as having
Phylum arthropoda characteristics

Phylum Arthropoda includes insects, crustaceans, arachnids and makes up over 82% of all living things. They are characterized by having a segmented body, jointed appendages, and an exoskeleton made of chitin. Arthropods have a head with sensory organs and mouthparts, a thorax for appendage attachment, and some have an abdomen. Their exoskeleton provides protection but limits growth, requiring molting. They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and have open circulatory, digestive and nervous systems adapted for their habitat.
Reproductive system of Ascaris lumbricoides

The reproductive systems of male and female Ascaris lubricoides worms are described. The male system includes a single coiled testis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, ejaculatory duct, and two penial spicules. The female system includes two long coiled ovaries, oviducts, uteri which store fertilized eggs, and a vagina. Gametes are formed through a process called telogony, where gametogonia bud off from the gonads and differentiate into gametocytes as they move through zones of proliferation, growth, and maturation.
Accssory respiratiory organs in fishes

Gills are primary respiratory organs in fishes, Extra branchial respiration is highly useful for survival when oxygen supplied by gills is not sufficient.
Mollusca

Second-largest phylum in number of species- over 100,000 described.
Ecologically widespread- marine, freshwater, terrestrial (gastropods very successful on land)
Variety of body plans (therefore, many classes within the phylum)
Variety in body size- from ~1 mm to ~18 m (60 feet). 80% are under 5 cm, but many are large and therefore significant as food for man.
What's hot (20)
Flight adaptation and Mechanism Of Flight in Birds.

Flight adaptation and Mechanism Of Flight in Birds.
Similar to classifying animals & phylum arthropods / classifying plants /dichotomous keys
Diversity in organisms

The document summarizes key concepts around classification of living organisms. It discusses how organisms are classified into taxonomic groups like domain, kingdom, phylum etc. based on their similarities. For humans, the taxonomic classification includes Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Mammalia, Primates, Hominidae, Homo and H. sapiens. It also provides classifications for major kingdoms like Plantae, Animalia and describes characteristics of key phyla under these kingdoms including porifera, coelenterata, platyhelminthes, nematoda, annelida and arthropoda.
Unit-1 Master of forestry(Entomology) final.pptx

This document provides an overview of insect morphology and physiology. It begins by defining entomology and forest entomology, and describing the scope of forest entomology. It then discusses the external morphology of insects, including their body surface, segmentation, head, thorax, abdomen and appendages. The document also describes the internal systems of insects, focusing on the digestive system including the foregut, midgut and hindgut, as well as the respiratory system consisting of trachea and spiracles, and the nervous system composed of a nerve cord and ganglia.
Arthropods: An Introduction for Beginners

This document provides an overview of arthropods. It begins by defining arthropods as bilateral invertebrates with jointed appendages and an exoskeleton. The document then discusses the origin of the name "arthropod" and provides background on the phylum's classification. It proceeds to describe key characteristics of arthropods generally and of the major subphyla (trilobita, crustaceans, chelicerates, and uniramia) specifically. Examples are given for most groups. In closing, the document outlines some of the economic importance of arthropods.
Diversityinlivingorganisms for class 9 by kr

1. This document discusses the classification of plants and animals according to their characteristics and evolutionary relationships.
2. It outlines the classification systems for the plant and animal kingdoms, dividing plants into cryptogams and phanerogams and further subclassifying them, and dividing animals into various phyla based on their features.
3. The classification systems aim to arrange diverse organisms in an orderly manner to facilitate the study of biological diversity.
Diversity in living organisms

The document provides a detailed overview of the hierarchical classification system used to classify living organisms. It describes the five kingdom system including Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Each kingdom is then broken down into smaller subgroups like phylum, class, order, family, genus and species. Examples are provided for important subgroups in each kingdom like bacteria, fungi, ferns, flowering plants, sponges, jellyfish, worms, insects, fish and mammals.
Insects in out

Insects play important roles in ecosystems through pollination, decomposition, and as a food source. They can be beneficial or harmful depending on the situation. Insects are classified scientifically with a two-part Latin name at the genus and species levels. Their bodies have three main regions - head, thorax, and abdomen - and they undergo different life cycles ranging from incomplete to complete metamorphosis. Internally, insects have organ systems adapted for digestion, circulation, nerves, and respiration via tracheae, though these differ significantly from human and other mammal systems.
Classification

The document discusses the five kingdom classification system of life proposed by R.H. Whittaker. It describes the five kingdoms as Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Monera consists of unicellular prokaryotes. Protista includes unicellular eukaryotes. Fungi are multicellular organisms that cannot produce their own food. Plantae are multicellular organisms capable of photosynthesis. Animalia includes all multicellular animals.
Classification

The document discusses the five kingdom classification system of life proposed by R.H. Whittaker. It divides life into five kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Monera consists of unicellular prokaryotes. Protista consists of unicellular eukaryotes. Fungi are multicellular organisms that cannot produce their own food. Plantae includes multicellular photosynthetic organisms. Animalia includes multicellular organisms that consume other organisms for food.
U-5-Classification.pptx

This document provides information on the five-kingdom system of classification of living organisms:
1. Kingdom Protista includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms like algae and protozoa.
2. Kingdom Fungi includes multicellular organisms like molds, mushrooms and yeasts that feed by absorbing nutrients.
3. Kingdom Plantae includes multicellular photosynthetic organisms ranging from mosses to trees.
4. Kingdom Animalia includes multicellular heterotrophic organisms like sponges, jellyfish, insects, fish and humans.
5. Kingdom Monera was proposed for prokaryotic organisms but is now recognized as not forming a natural group.
Chapter 1- Characteristics and Classifications of Living Things.pdf

IGCSE Biology Chapter 1- Characteristics and Classification of Living Things
Diversity in Living Organism

The document provides a detailed overview of the classification of living organisms across five kingdoms - Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Each kingdom is further divided into smaller sub-groups at various levels from phylum down to species. Key points include that Monera contains prokaryotes, Protista and Fungi contain eukaryotes, and Plantae and Animalia contain multicellular eukaryotes. The document also describes the five-kingdom system of classification and provides examples of representative groups within each kingdom.
Diversityinlivingorganisms 130829215931-phpapp02

The document provides information on the classification of living organisms into five kingdoms - Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. It then describes some of the main groups within the plant and animal kingdoms. The plant kingdom is divided into cryptogams and phanerogams. The animal kingdom includes porifera, coelenterata, nematoda, annelida, arthropoda, mollusca, echinodermata, protochordata, and vertebrata. Examples are given for important groups like fungi, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms, and the five classes of vertebrates.
Diversity in living organisms

The document provides information on the classification of living organisms. It discusses the need for classification due to the huge diversity of life. It explains the levels of classification from kingdom down to species. The five kingdom system of Whittaker is described, including the kingdoms of Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Characteristics of each kingdom are provided. The classification of plants and animals is then outlined down to class levels. Finally, scientific naming conventions are explained.
Diversity IN Living Organisms Class 9 Biology (1).pptx

This document provides information on classifying living organisms. It discusses the five kingdoms of life proposed by Whitaker: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Each kingdom is characterized based on cell structure, nutrition, and body organization. Within kingdoms, organisms are further classified into taxa such as phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and species. Examples of different phyla are described for plants, fungi, protists, animals, including their key distinguishing characteristics. The document also covers classification of seed plants and discusses characteristics of major groups like porifera, cnidaria, nematodes, annelids, and arthropods.
Diversity in living organisms by pi yush mishra 

- well this presentation has the full capabitlity to clear your doubts on Diversity in living organisms.........Only the basics :) :) :) :) :) :)
gohgcghghgghgngghhghhtthththhthhgghghghgh

This document discusses the classification of living organisms into taxonomic groups from the broadest domains down to specific species. It covers the five kingdoms of life proposed by Whitaker (Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia) and modifications made by Woese. Key details are provided on classification within the plant and animal kingdoms, describing distinguishing characteristics of major groups like thallophytes, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms, porifera, coelenterates, platyhelminthes, nematodes, annelids, arthropods, molluscs, echinoderms, protochordates, and verte
Diversity in Living Organisms

This document provides an overview of the classification of living organisms into taxonomic groups from the cellular level to multicellular organisms. It summarizes key biologists like Whittaker who classified organisms into five kingdoms - Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Each kingdom is then further divided into subordinate taxa with defining characteristics described. The classifications of plants, animals and protists are summarized in a hierarchical outline.
Evolution topic 5.3

The binomial system of names for species is universal among biologists and has been agreed and developed at a series of congresses.
When species are discovered they are given scientific names using the binomial system.
All organisms are classified into three domains.
Taxonomists classify species using a hierarchy of taxa.
The principal taxa for classifying eukaryotes are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species.
In a natural classification, the genus and accompanying higher taxa consists of all the species that have evolved from one common ancestral species.
Introductory Entomology (ENT 201)

- The document provides information on the course "Introductory Entomology" including the course code, credit hours, and an introduction to the definition and study of insects.
- It defines entomology and its branches, and provides characteristics of the class Insecta including their body structure, respiratory and excretory systems.
- Reasons for the dominance of insects over other animals include their large numbers, widespread distribution, small size, flight ability, reproduction rates, and protective adaptations. Insects play both beneficial roles such as pollination and biocontrol, as well as harmful roles as agricultural pests.
Similar to classifying animals & phylum arthropods / classifying plants /dichotomous keys (20)
Chapter 1- Characteristics and Classifications of Living Things.pdf

Chapter 1- Characteristics and Classifications of Living Things.pdf
Diversity IN Living Organisms Class 9 Biology (1).pptx

Diversity IN Living Organisms Class 9 Biology (1).pptx
More from Vasiliki Makrygianni
Cells cell structure-cells and organisms

The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are the smallest unit that can be said to be alive and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology and their structure and functions can vary between plant and animal cells as well as single-celled and multi-celled organisms.
Onion cell practical worksheet

The document discusses microscope safety levels and calculating magnification. It explains that level 3 safety involves using simple equipment correctly, while level 4 means using equipment safely. It also provides instructions for calculating magnification by multiplying the lens magnification by 10, and gives an example of a 40x lens yielding 400x magnification. The document appears to include images and descriptions of onion cells at different magnifications.
preparing-onion-cell-slides-lesson-element-teacher-instructions

1) The document provides instructions for an activity where students prepare and observe onion cell slides under a light microscope.
2) Students will peel onion skin, place a small piece on a microscope slide with iodine, and view the cells under low and high magnification.
3) Under low power, students should see cells arranged like bricks; under high power, they may identify structures like the nucleus and cell membrane.
Coordination and response the nervous system

Powepoint presentation on the Nervous System, its function and composition. Nerves and neurons - Nerve impulses- Synapse- Reflex action- Reflex arc. - Notes on the eye. links to further study
Igcse biology coursebook sample r pickering p222 to 289

The document discusses the benefits of exercise for mental health. Regular physical activity can help reduce anxiety and depression and improve mood and cognitive functioning. Exercise causes chemical changes in the brain that may help boost feelings of calmness, happiness and focus.
IGCSE Biology - classifying animals phylum vertebrates - five classes

Vertebrates are divided into five classes: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Birds are distinguished by their feathers, toothless beaked jaws, egg-laying, and high metabolism. The platypus is a venomous mammal that has a duck-like bill and webbed feet, beaver-like tail, and otter-like body and fur, making it a hodgepodge of other animal features.
Cell - cell structure - Tissues, Organ systems and organisms (IGCSE Biology)

Presentation on the Cell structure, organelles, tissues, organ systems and organisms. Designed for IGCSE Cambridge Biology
Added sample exam style questions to test your knowledge at the end of the slides.
IGCSE Cambridge biology r. pickering 

The document discusses the benefits of meditation for reducing stress and anxiety. It notes that meditation can help calm the mind and body by lowering heart rate and easing muscle tension. Regular meditation of 10-20 minutes per day is recommended to experience stress-relieving benefits.
Require Practical Activities - Microscopy - Plant cell practical - IGCSE Biol...

Require Practical Activities - Microscopy - Plant cell practical - IGCSE Biol...Vasiliki Makrygianni
This document contains the required practical activities for the GCSE Biology qualification. By undertaking the required practical activities, students will have the opportunity to experience all of the required apparatus and techniques needed for the qualifications. However, these activities are
only suggestions and teachers are encouraged to develop activities, resources and contexts that
provide the appropriate level of engagement and challenge for their own students.
These sample activities have been written by practising teachers and use apparatus and materials
that are commonly found in most schools.
When planning your lessons, remember that the required practical activities listed as ‘biology only’
(practicals 2, 8 and 10) are only required by GCSE Biology and not for either of the combined
science specificationsIGCSE Biology 0610 - Introduction to Biology - Characteristics of living orga...

IGCSE Biology 0610 - Introduction to Biology - Characteristics of living orga...Vasiliki Makrygianni
IGCSE Biology 0610/ Syllabus 2020-2022/
Coursebook: Cambridge IGCSE Biology Coursebook (third edition), Mary Jones and Geoff Jones, Cambridge University Press.
note: free to share and use ...is designed for level B1-B2. cheers,...
IGCSE Cambridge Examinations - Biology 0610 - resources - Revision Guide Sample

The document discusses the history and evolution of the automobile industry over the past century. It describes how cars started out as luxury items for the wealthy but became common consumer goods as companies focused on mass production techniques that reduced costs. The document also notes that global competition has intensified as new players have entered the market.
More from Vasiliki Makrygianni (11)
preparing-onion-cell-slides-lesson-element-teacher-instructions

preparing-onion-cell-slides-lesson-element-teacher-instructions
Igcse biology coursebook sample r pickering p222 to 289

Igcse biology coursebook sample r pickering p222 to 289
IGCSE Biology - classifying animals phylum vertebrates - five classes

IGCSE Biology - classifying animals phylum vertebrates - five classes
Cell - cell structure - Tissues, Organ systems and organisms (IGCSE Biology)

Cell - cell structure - Tissues, Organ systems and organisms (IGCSE Biology)
Require Practical Activities - Microscopy - Plant cell practical - IGCSE Biol...

Require Practical Activities - Microscopy - Plant cell practical - IGCSE Biol...
IGCSE Biology 0610 - Introduction to Biology - Characteristics of living orga...

IGCSE Biology 0610 - Introduction to Biology - Characteristics of living orga...
IGCSE Cambridge Examinations - Biology 0610 - resources - Revision Guide Sample

IGCSE Cambridge Examinations - Biology 0610 - resources - Revision Guide Sample
Recently uploaded
The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...

Discover the Simplified Electron and Muon Model: A New Wave-Based Approach to Understanding Particles delves into a groundbreaking theory that presents electrons and muons as rotating soliton waves within oscillating spacetime. Geared towards students, researchers, and science buffs, this book breaks down complex ideas into simple explanations. It covers topics such as electron waves, temporal dynamics, and the implications of this model on particle physics. With clear illustrations and easy-to-follow explanations, readers will gain a new outlook on the universe's fundamental nature.
How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method

Odoo provides an option for creating a module by using a single line command. By using this command the user can make a whole structure of a module. It is very easy for a beginner to make a module. There is no need to make each file manually. This slide will show how to create a module using the scaffold method.
The History of Stoke Newington Street Names

Presented at the Stoke Newington Literary Festival on 9th June 2024
www.StokeNewingtonHistory.com
বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf

বাংলাদেশের অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা ২০২৪ [Bangladesh Economic Review 2024 Bangla.pdf] কম্পিউটার , ট্যাব ও স্মার্ট ফোন ভার্সন সহ সম্পূর্ণ বাংলা ই-বুক বা pdf বই " সুচিপত্র ...বুকমার্ক মেনু 🔖 ও হাইপার লিংক মেনু 📝👆 যুক্ত ..
আমাদের সবার জন্য খুব খুব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ একটি বই ..বিসিএস, ব্যাংক, ইউনিভার্সিটি ভর্তি ও যে কোন প্রতিযোগিতা মূলক পরীক্ষার জন্য এর খুব ইম্পরট্যান্ট একটি বিষয় ...তাছাড়া বাংলাদেশের সাম্প্রতিক যে কোন ডাটা বা তথ্য এই বইতে পাবেন ...
তাই একজন নাগরিক হিসাবে এই তথ্য গুলো আপনার জানা প্রয়োজন ...।
বিসিএস ও ব্যাংক এর লিখিত পরীক্ষা ...+এছাড়া মাধ্যমিক ও উচ্চমাধ্যমিকের স্টুডেন্টদের জন্য অনেক কাজে আসবে ...
South African Journal of Science: Writing with integrity workshop (2024)

South African Journal of Science: Writing with integrity workshop (2024)Academy of Science of South Africa
A workshop hosted by the South African Journal of Science aimed at postgraduate students and early career researchers with little or no experience in writing and publishing journal articles.Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat

Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat
Community pharmacy- Social and preventive pharmacy UNIT 5

Covered community pharmacy topic of the subject Social and preventive pharmacy for Diploma and Bachelor of pharmacy
What is Digital Literacy? A guest blog from Andy McLaughlin, University of Ab...

What is Digital Literacy? A guest blog from Andy McLaughlin, University of Aberdeen
BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...

BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
https://app.box.com/s/y977uz6bpd3af4qsebv7r9b7s21935vdChapter 4 - Islamic Financial Institutions in Malaysia.pptx

Chapter 4 - Islamic Financial Institutions in Malaysia.pptxMohd Adib Abd Muin, Senior Lecturer at Universiti Utara Malaysia
This slide is special for master students (MIBS & MIFB) in UUM. Also useful for readers who are interested in the topic of contemporary Islamic banking.
Main Java[All of the Base Concepts}.docx

This is part 1 of my Java Learning Journey. This Contains Custom methods, classes, constructors, packages, multithreading , try- catch block, finally block and more.
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS Template 2023-2024 by: Irene S. Rueco
Pollock and Snow "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape, Session One: Setting Expec...

Pollock and Snow "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape, Session One: Setting Expec...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
This presentation was provided by Steph Pollock of The American Psychological Association’s Journals Program, and Damita Snow, of The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), for the initial session of NISO's 2024 Training Series "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape." Session One: 'Setting Expectations: a DEIA Primer,' was held June 6, 2024.Recently uploaded (20)
The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...

The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...
How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method

How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method
বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf

বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf
South African Journal of Science: Writing with integrity workshop (2024)

South African Journal of Science: Writing with integrity workshop (2024)
Digital Artefact 1 - Tiny Home Environmental Design

Digital Artefact 1 - Tiny Home Environmental Design
Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat

Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat
Community pharmacy- Social and preventive pharmacy UNIT 5

Community pharmacy- Social and preventive pharmacy UNIT 5
What is Digital Literacy? A guest blog from Andy McLaughlin, University of Ab...

What is Digital Literacy? A guest blog from Andy McLaughlin, University of Ab...
BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...

BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...
Chapter 4 - Islamic Financial Institutions in Malaysia.pptx

Chapter 4 - Islamic Financial Institutions in Malaysia.pptx
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3
Pollock and Snow "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape, Session One: Setting Expec...

Pollock and Snow "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape, Session One: Setting Expec...
classifying animals & phylum arthropods / classifying plants /dichotomous keys
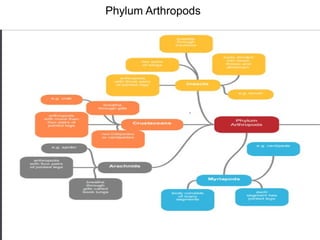
- 2. An arthropod (/ rθrəp d/, from Greek ρθρον arthron,ˈɑː ɒ ἄ "joint" and πούς pous, "foot") is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton (external skeleton), a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages.
- 6. Class Insecta The body is divided into three parts – head, thorax and abdomen. The head, thorax and abdomen are not segments. • They have three pairs of (jointed) legs– attached to the thorax. • They usually have wings– one or two pairs attached to the thorax. • They have one pairof antennae– attached to the head. • They have compound eyes– each one with hundreds of small units called ocelli. • Breathing is through small holes (spiracles), occurring in pairs, one each side of the abdominal segments and two on the thoracic segments. The spiracles lead into branched tubes called tracheae.
- 7. Class Crustaceans These live mostly in water (e.g. a lobster) and those that live on land (e.g. some crabs) live in damp places. As well as the characteristic of arthropods, crustaceans have other features: (Figure 1.7): • There are two pairs of antennae that are attached to the head. • There are three pairs of mouthparts that, with the antennae, make up the fi v epairs of appendages attached to the head. • The exoskeleton is often strengthened with calcium salts. (This protects the animal from predators, but can make the animal very heavy. The additional mass is supported by the water in which most crustaceans live.) • The head and thorax are often joined to form the cephalothorax. • The abdomen often has a pair of limbson each segment, which are modifi ed for many purposes, but often for swimming
- 8. Class Arachnids This group includes the spiders and the scorpions and, as well as those features possessed by arthropods, the arachnids also have the following (Figure 1.8): • A body divided into two parts (the head and thorax, called the cephalothorax, and the abdomen). • Four pairs of jointed legs joined to the cephalothorax. • No antennae
- 9. Class Myriapods Myriapod means ‘countless legs’ and includes the centipedes and millipedes. As well as possessing the features common to arthropods, they also possess (Figure 1.9): • One pair of antennae. • One or two pairs of legs attached to every segment
- 11. Classification of the plant kingdom In plant classification, the term ‘division’ is often used instead of phylum, but like phyla, divisions are divided into classes. Two major divisions of plants are the ferns and the flowering plants. Characteristics of ferns Ferns have the following characteristics : • They are green photosynthesising plants. • They have conducting tissue (xylem and phloem) forming veins. • They have, often compressed, stems called rhizomes. • They do not produce flowers. • Instead, they produce spores that are light and easily carried away by the wind. • Spores are released from spore cases(sporangia) that are found on the lower surfaces of fronds. • Frond is the term for the leaves of ferns
- 12. Classes of flowering plant Monocotyledons Mono = one, cotyledon = a leaf that forms part of the structure of the seed. This class includes the grasses, cereals, lilies and orchids, all of which share the following characteristics (Figure 1.14): • One cotyledon inside each seed • Leavesthatare narrow and strap-like • Leavesthathave parallel veins • A mass of equally sized (fibrous) roots • Flower parts that are usually arranged in threes (i.e. three petals etc.)
- 13. The (eu)dicotyledons This class includes cabbage, hibiscus, geranium and sweet potato, all of which have features that differ from those of the monocotyledons mentioned earlier (Figure 1.15). • Two cotyledons are present inside each seed. Not only do these become the first photosynthesising leaves when the seedling emerges above ground, but generally store food used during the process of seed germination. • The leaves are broad. • The leaves have branched veins usually radiating from a central thicker vein called the midrib with the branches linked by a network of veins. • Fewer, thicker roots which are often joined to one long central root called the tap root. • Flowers have parts usually arranged in fours or fives.
- 14. Dichotomous keys Dichotomous means cutting (or dividing) into two. Organisms are often identified using a book of illustrations. This is possible only if such a book is available, and this is the case only with certain organisms such as common plants, birds and butterflies. Even when such a book is available, identification will rely on the accuracy of the illustration, and it can be a time-consuming process if the organism is at the back of the book! For these reasons, biologists use dichotomous keys. A dichotomous key consists of a series of questions. Each question has two alternative answers. Depending on which answer is chosen, the user is directed to the next question. Thus, by starting at the first question, and then by a process of elimination, a specimen may be identified. This process is reliable because it directs the user to observe particular characteristic features. Also it is quicker since, at each question, possible alternatives are eliminated. Dichotomous keys are usually presented in the following format. The example chosen is a key in its simplest form – namely to identify the kingdom into which an organism should be placed. More detailed keys are used when determining precisely to which speciesfrom many within the same genus an organism belongs.
- 15. 1 Is it unicellular (i.e. made of only one cell)? Yes go to 2 No go to 3 2 Does it have a nucleus? Yes protoctist No bacterium 3 Does it have hyphae? Yes fungus No go to 4 4 Does it have cell walls? Yes plant No animal When identifying one organism from amongst a large number of possibilities, the most effective dichotomous key asks questions that each time divides the remaining possibilities into roughly equal halves. In this way, half the possible organisms are discarded at each step
- 16. Consider the following animals. They are all related, but each is a separate species. Use the dichotomous key below to determine the species of each.
- 17. Answers: A: Deerus magnus B: Deerus pestis C: Deerus octagis D: Deerus purplinis E: Deerus deafus F: Deerus humpis As seen above: the keys are mutually exclusive characteristics of biological organisms. they often begin with general characteristics and lead to more specific characteristics. you simply compare the characteristics of an unknown organism against an appropriate dichotomous key. if the organism falls into one category, you go to the next indicated couplet. By following the key and making the correct choices, you should be able to identify your specimen to the indicated taxonomic level.
