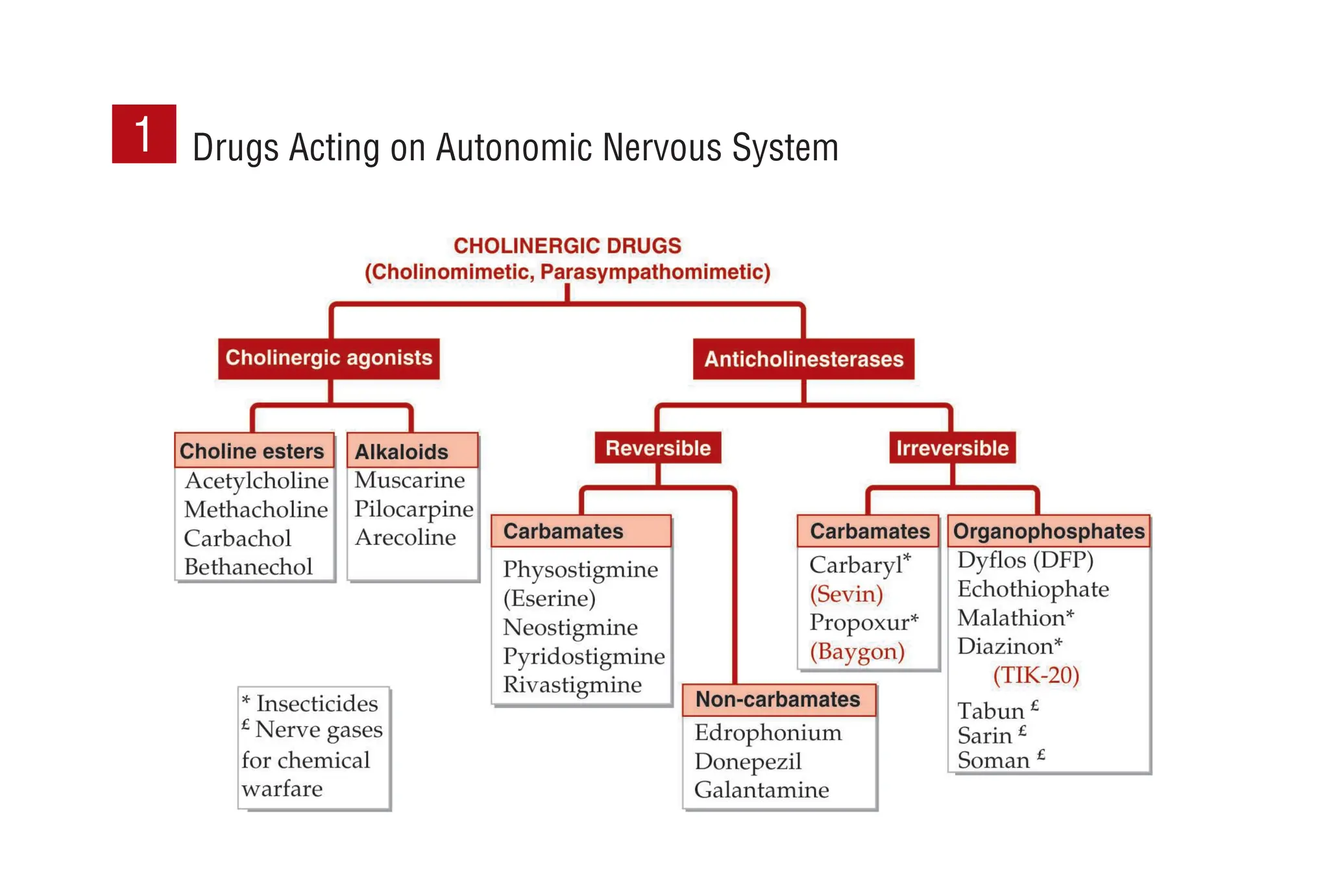
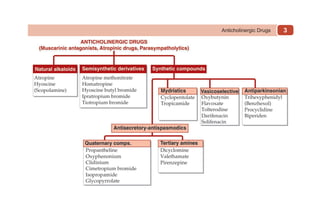
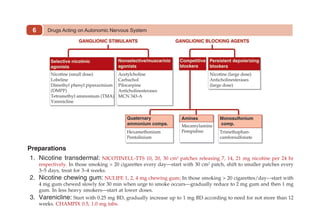
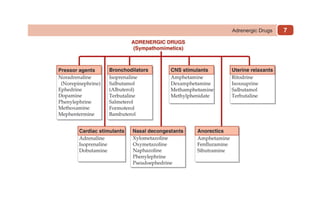
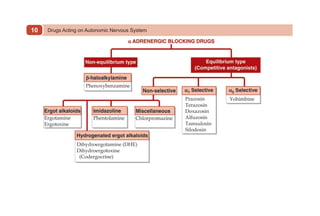
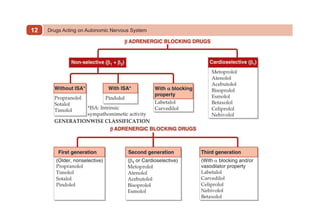
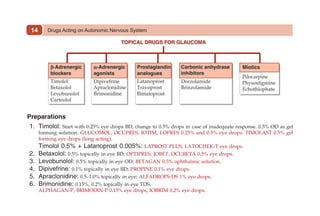
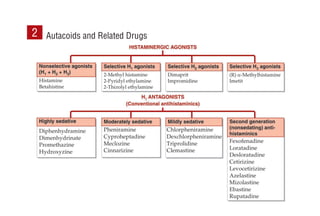
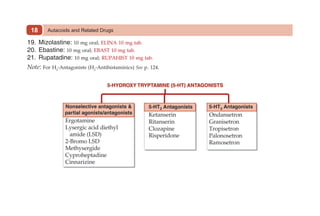
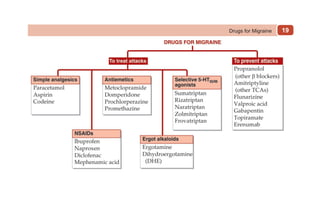
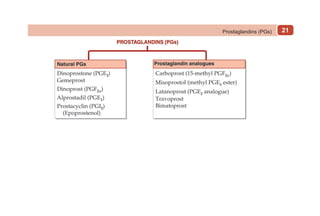
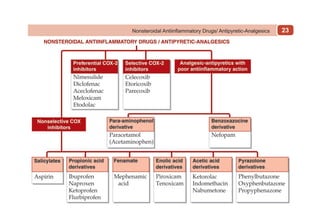
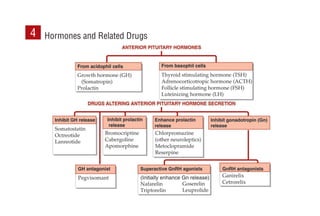
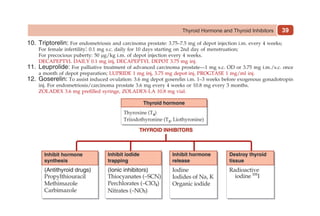
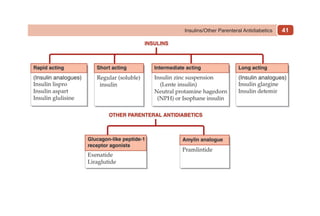
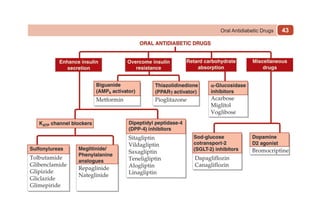
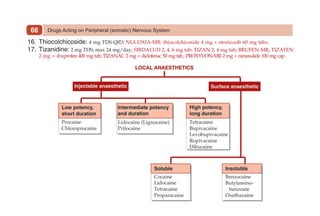
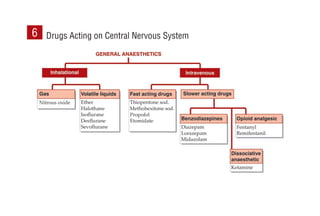
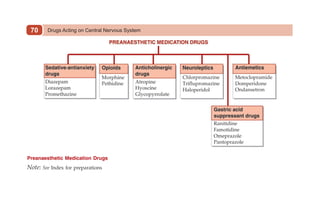
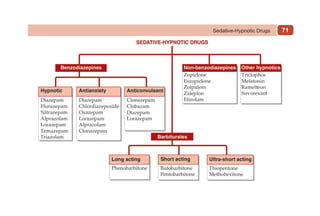
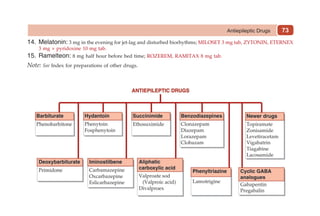
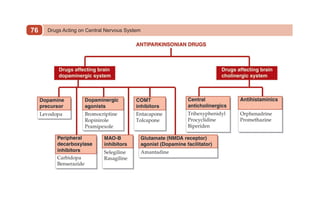
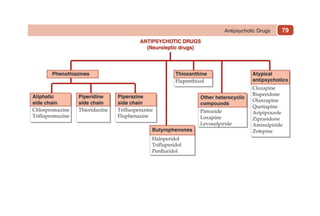
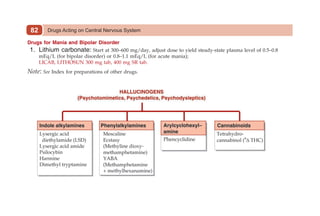
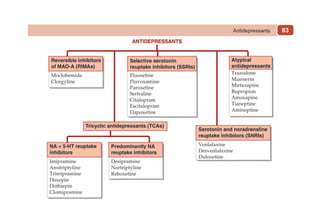
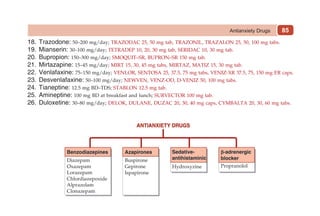
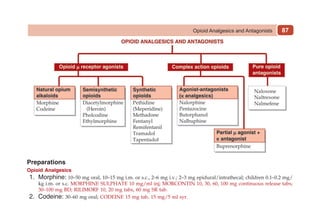
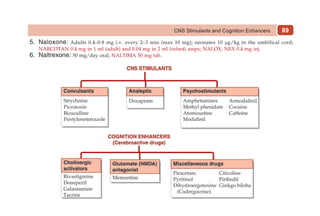
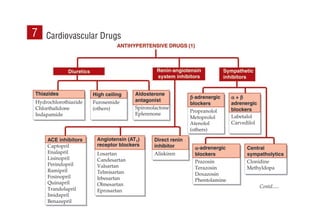
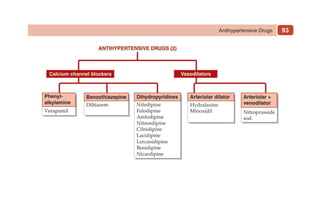
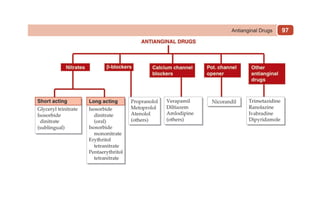
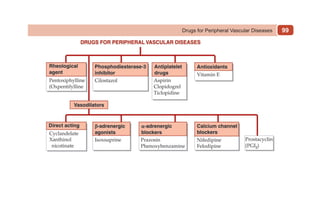
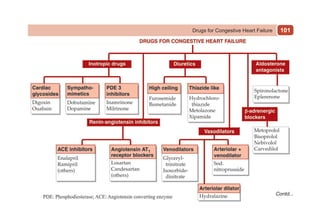
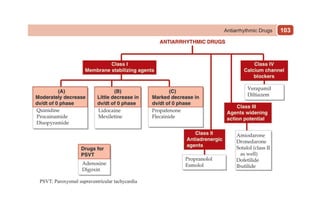
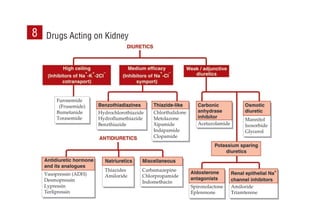
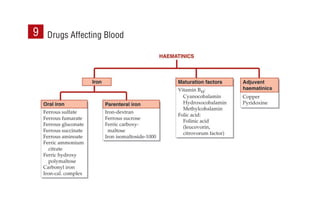
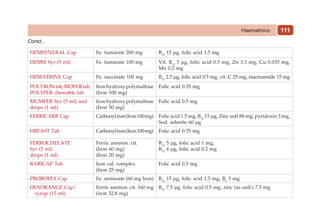
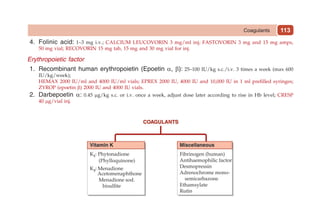
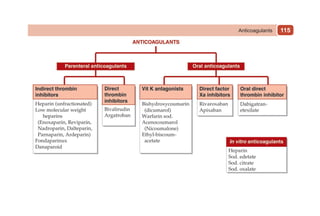
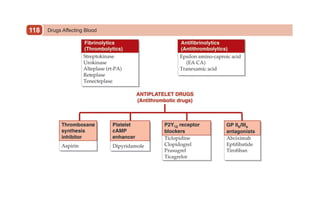
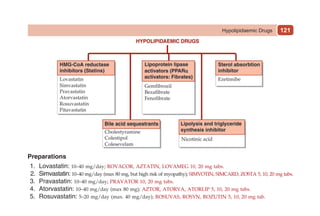
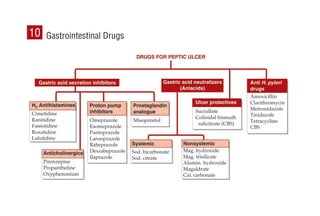
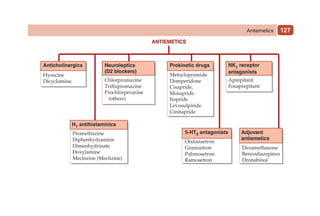
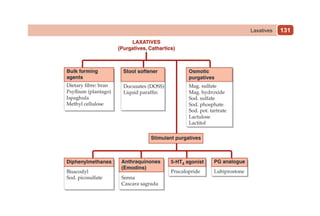
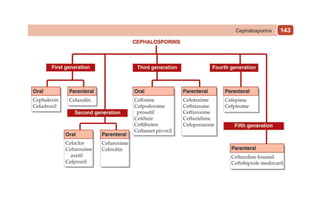
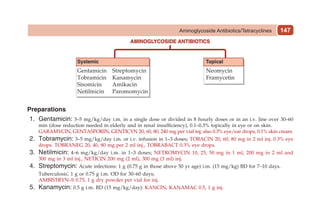
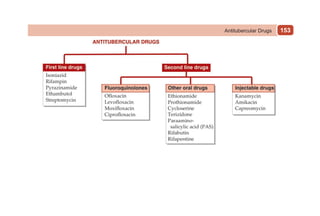
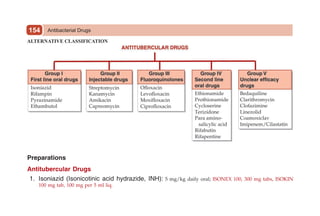
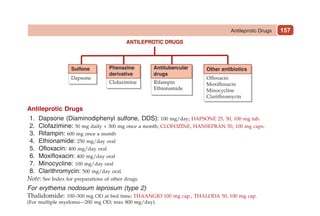
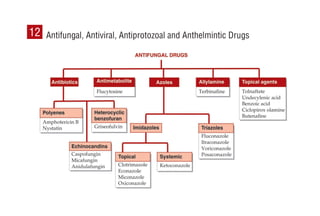
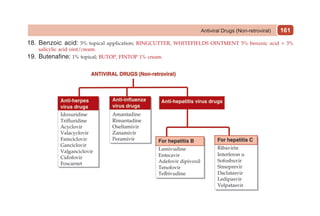
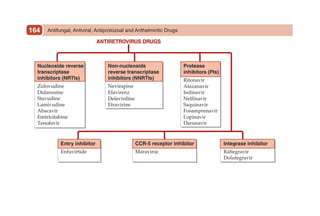
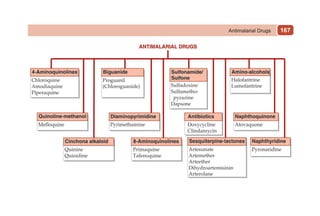
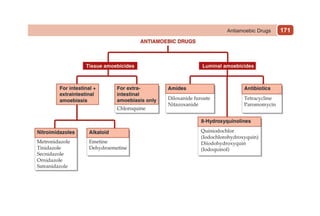
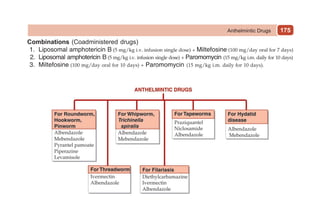
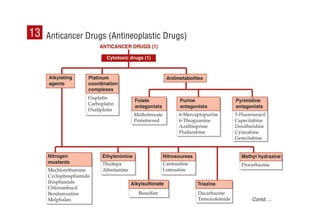
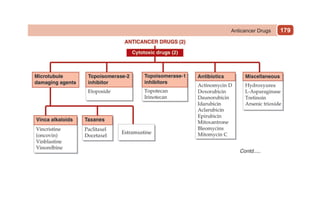
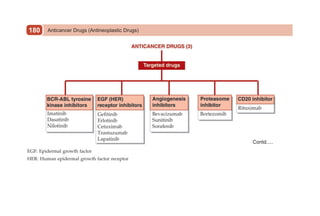
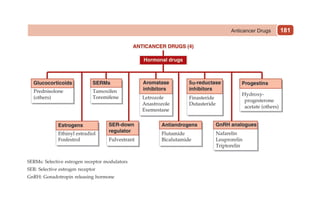
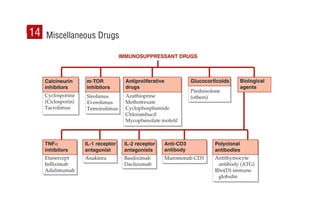
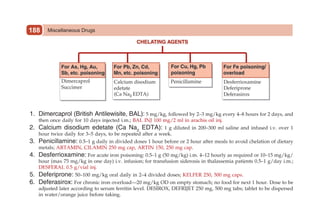
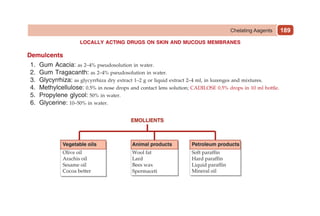
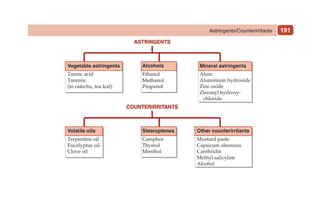
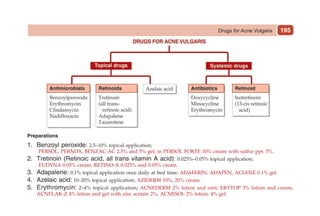
This document provides information on drugs acting on the autonomic nervous system and cardiovascular system. It includes preparations for nicotine replacement therapy drugs to aid smoking cessation, as well as eye drop preparations for glaucoma including timolol, betaxolol, and brimonidine. It also lists preparations for common haematinic medications to treat iron deficiency anemia, including ferrous salts combined with folic acid and vitamin B12 in various formulations.