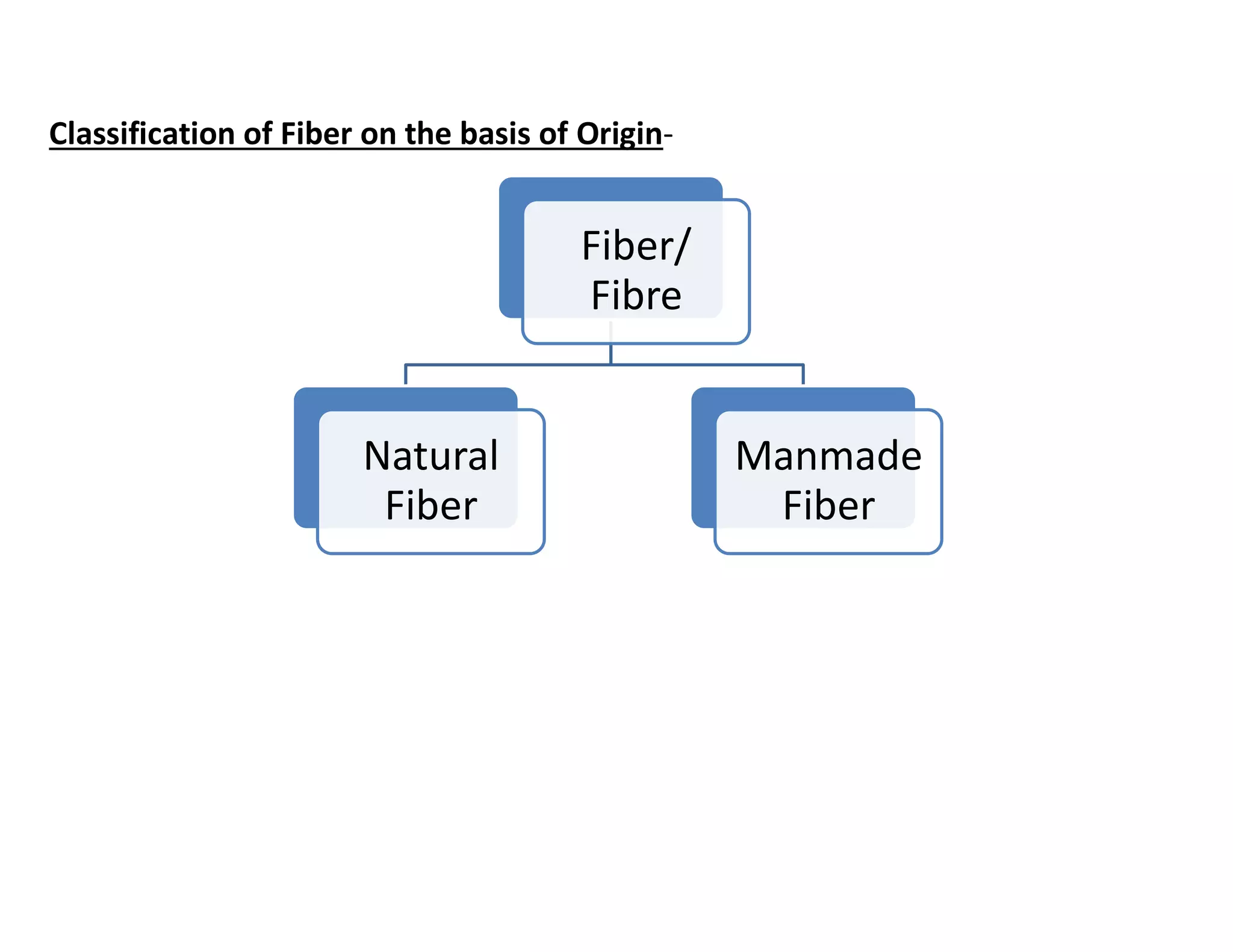
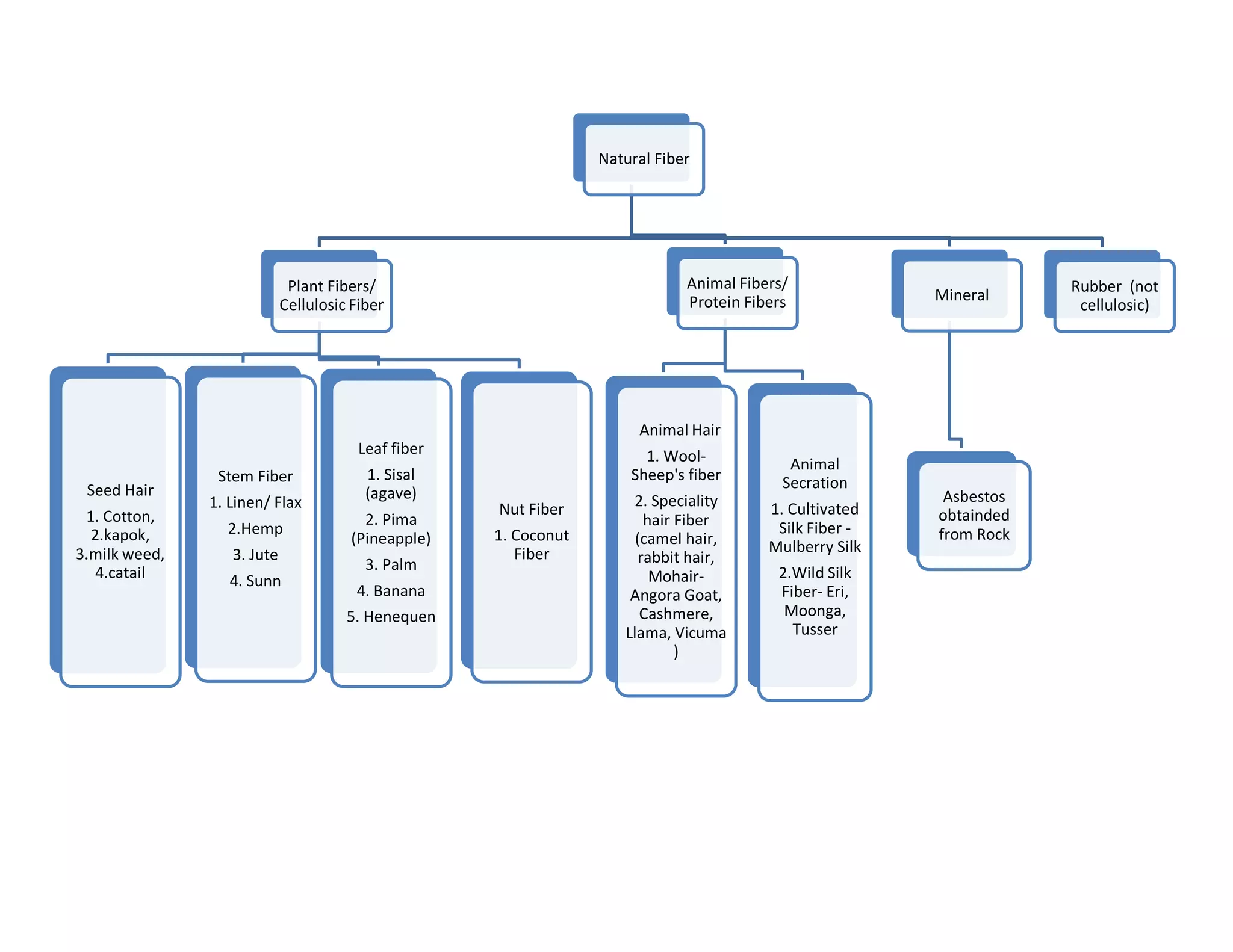
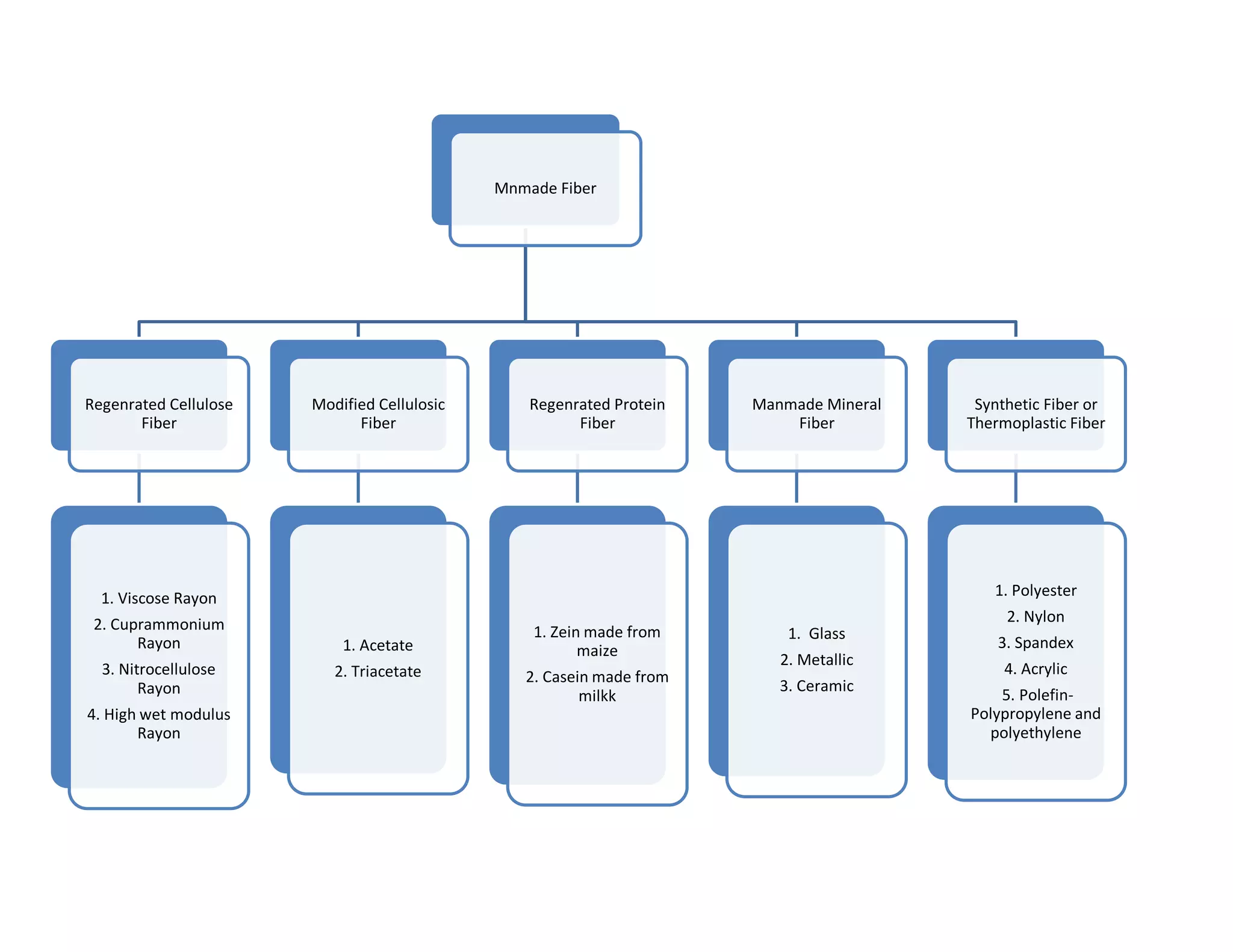
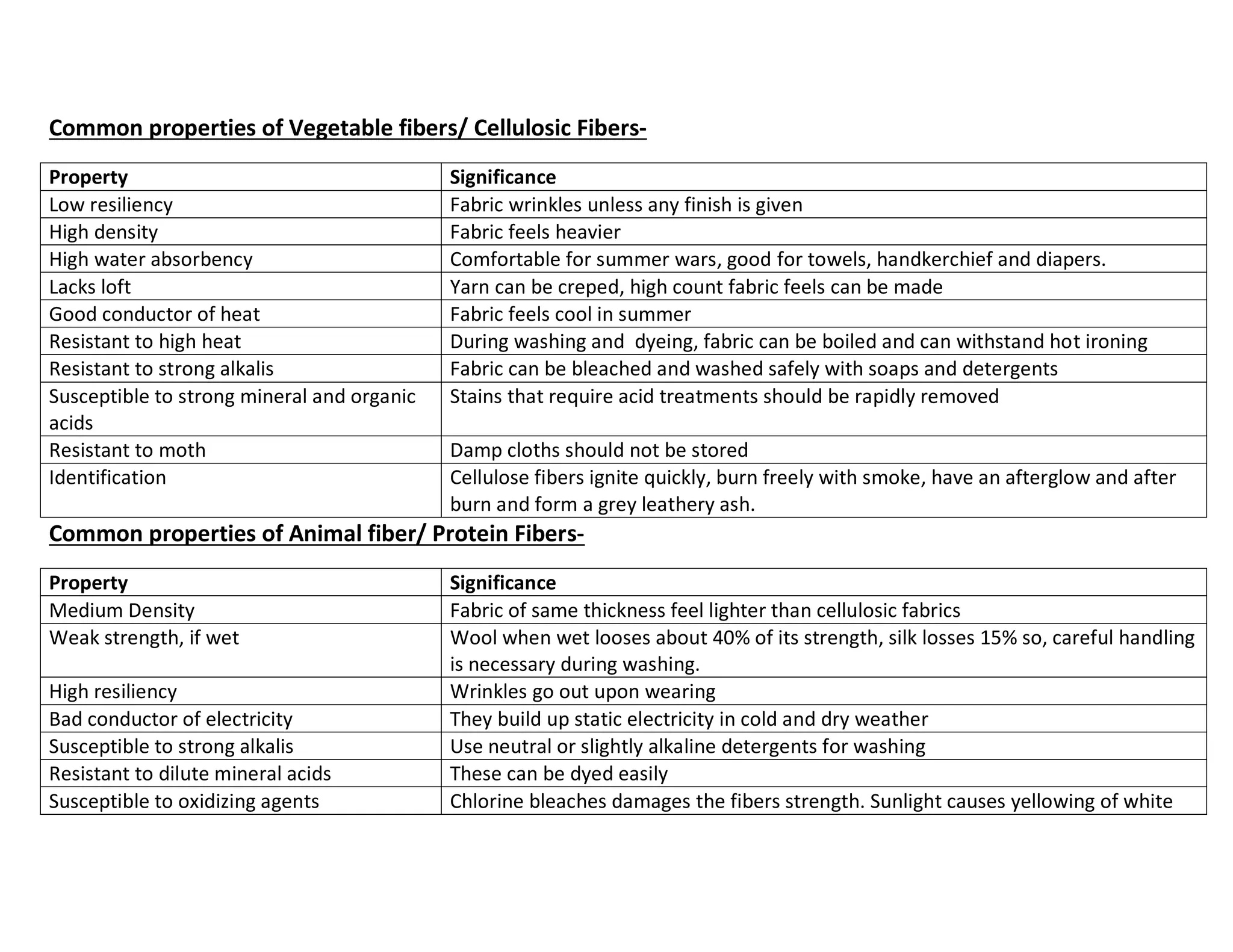
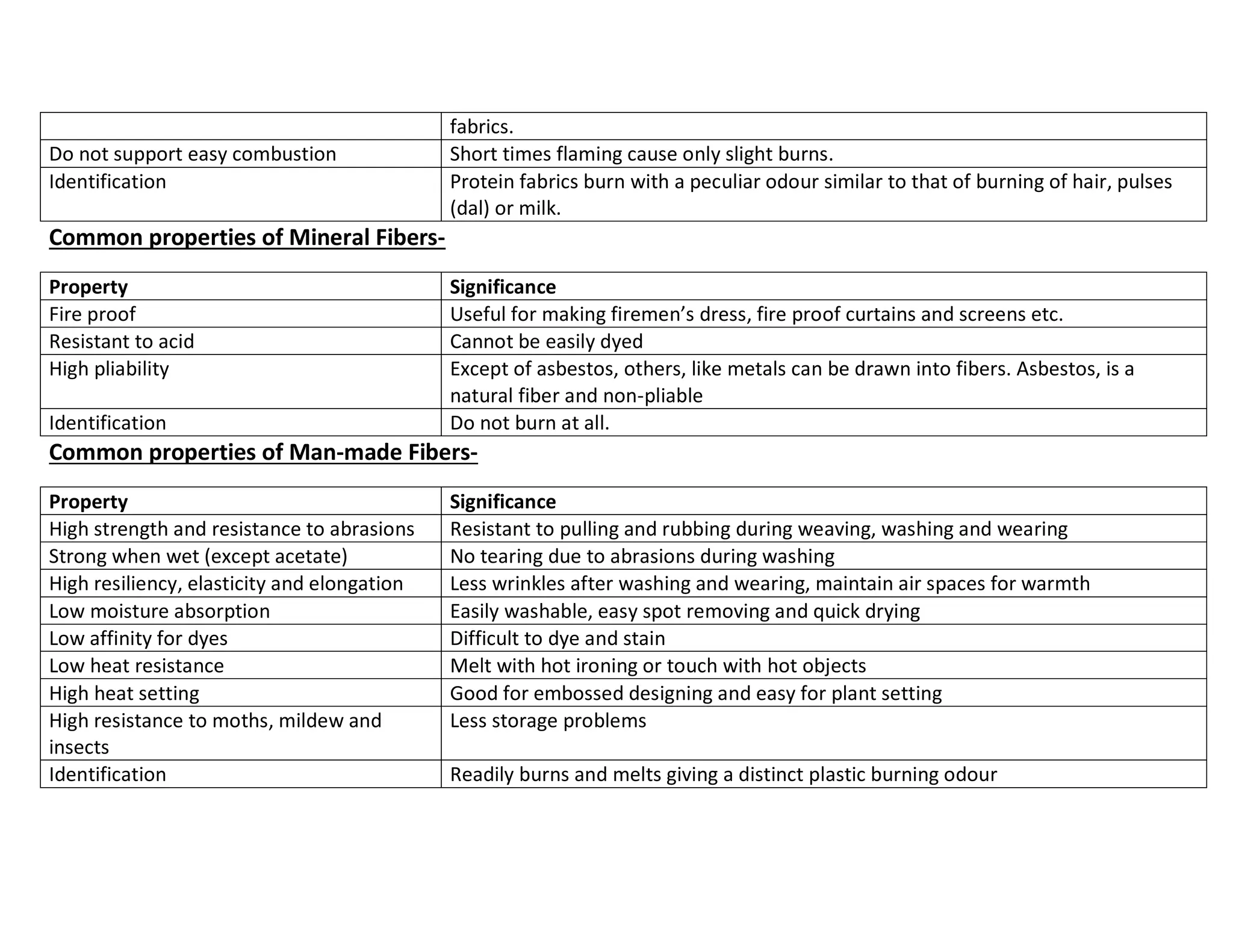
This document defines key textile terms and classifies fibers based on origin. It discusses the basic units of textiles including textiles, fibers, fabrics, and apparel. Fibers can be natural or man-made, with natural fibers coming from plants, animals, or minerals. Man-made fibers are either regenerated from natural sources or completely synthetic. The document also provides common properties of different fiber types including vegetable, animal, mineral, and man-made fibers.