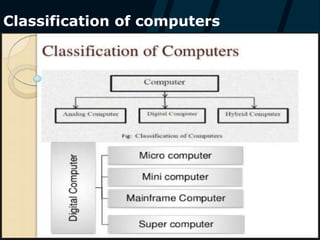
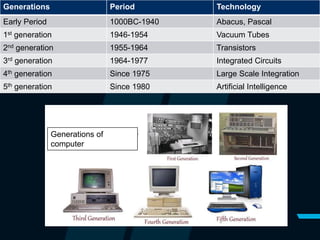
This document discusses the classification and history of computers. It describes the main types of computers as analog, digital, and hybrid. Digital computers are further broken down into supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, and microcomputers like desktops and portables. It provides examples for each type and describes their typical uses. The document also outlines the five generations of computers from the early abacus period to the current era of artificial intelligence.