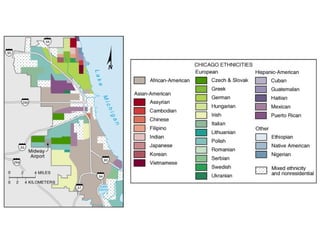
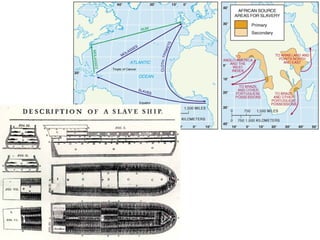
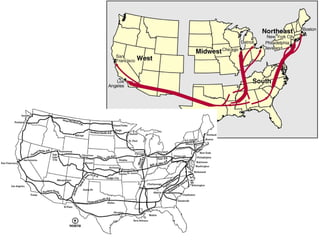
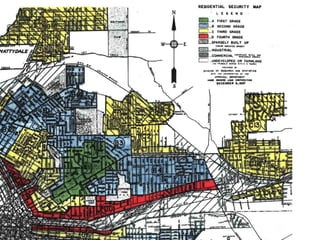
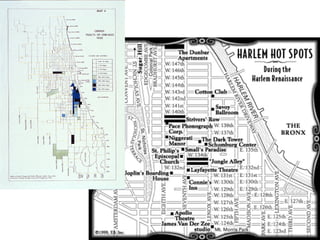
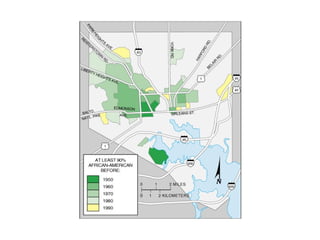
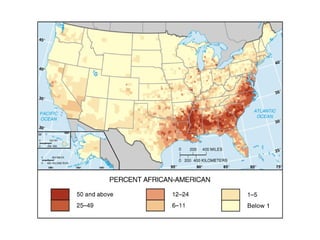
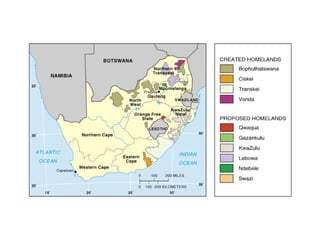
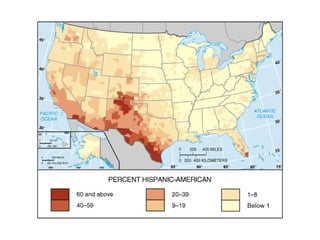
This document defines key terms related to race and ethnicity, discusses the history and experiences of African Americans in the United States, including the Great Migration, and the system of apartheid in South Africa. It also covers how race has been categorized in the US Census over time.