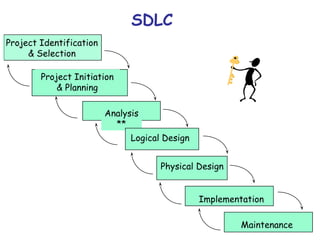
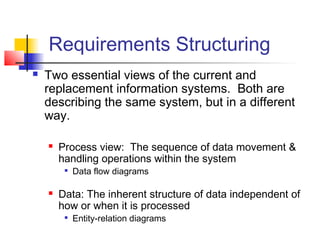
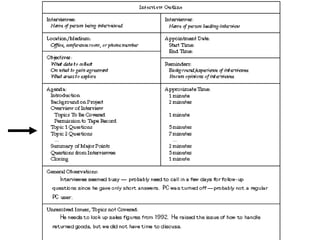
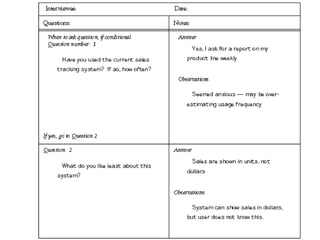
This document discusses various methods for determining system requirements in the systems development life cycle (SDLC). It describes traditional methods like administering questionnaires, interviewing stakeholders, observing users, and analyzing documentation. It also discusses structuring requirements by viewing the system's process flow and data structure. Modern methods mentioned include prototyping, joint application design sessions, using group support systems, business process reengineering, and CASE tools.