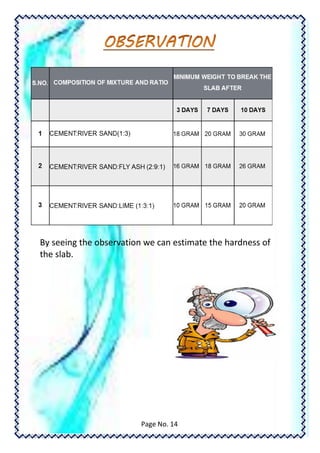
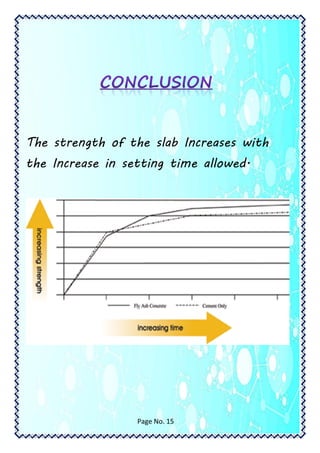
This document is a student's chemistry lab demonstration file on the topic of cement. It summarizes the student's procedures for creating cement mixtures with varying compositions and allowing them to set over different time periods. The strength of the cement mixtures was tested after 3, 7, and 30 days. The results showed that the strength of the cement mixtures increased with longer setting times. The student acknowledges the help received from their teacher and laboratory assistant.