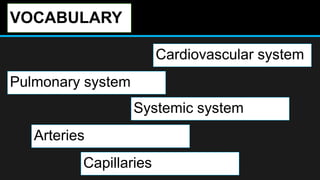
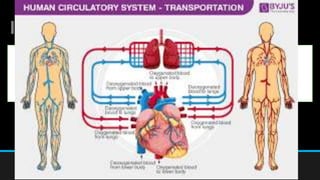
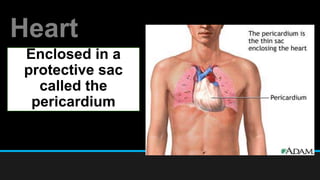
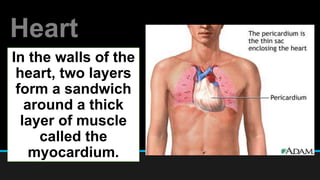
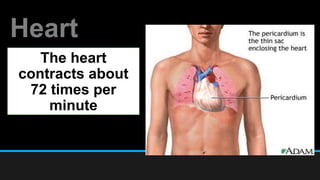
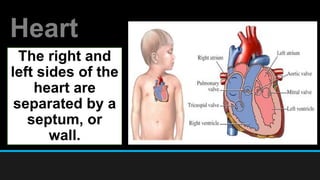
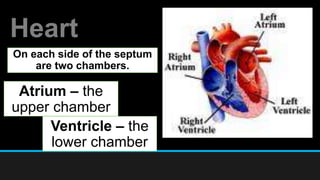
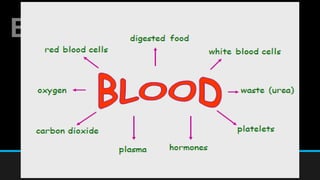
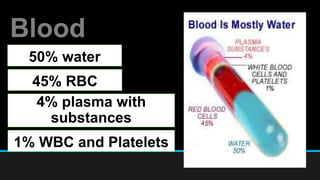
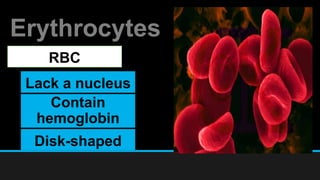
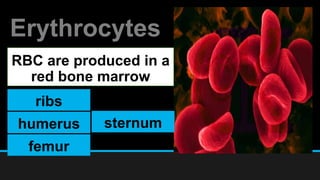
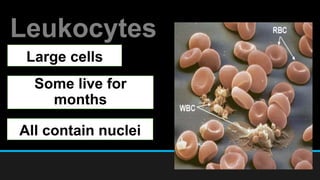
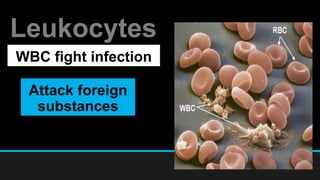
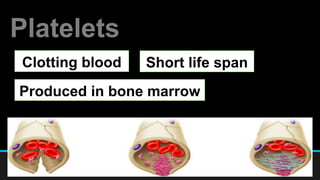
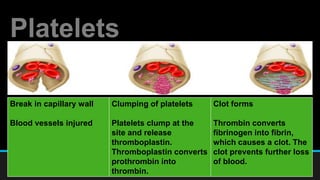
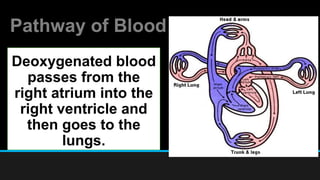
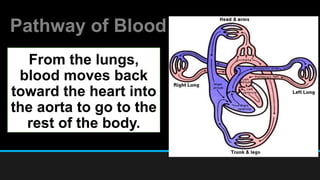
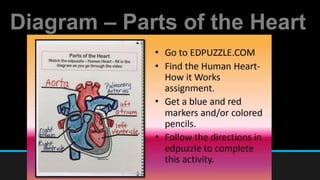
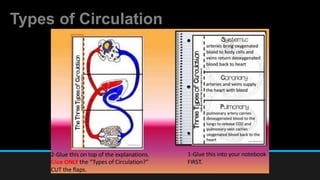
The document discusses the circulatory system, including its major components and functions. It defines key terms like cardiovascular system, pulmonary system, arteries, veins, and capillaries. It describes how the heart pumps blood through two circuits - the pulmonary circulation to the lungs and systemic circulation to the body. Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products as it circulates. The document outlines the pathways blood takes and defines the roles of blood components like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.