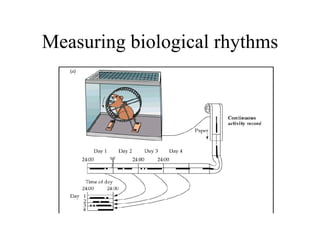
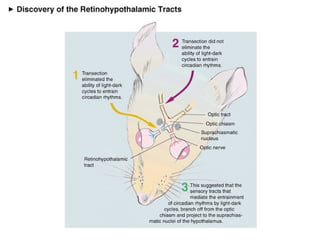
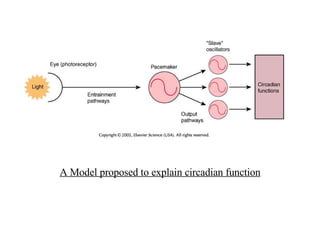
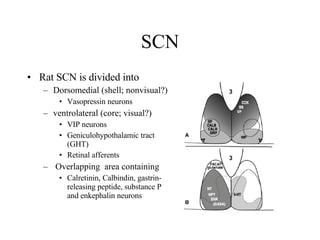
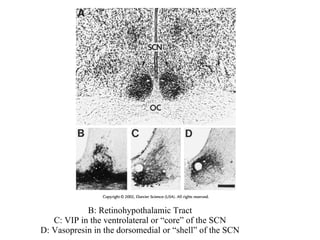
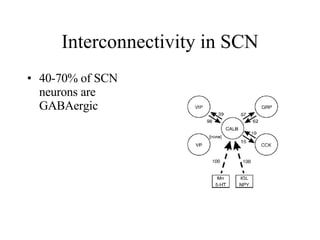
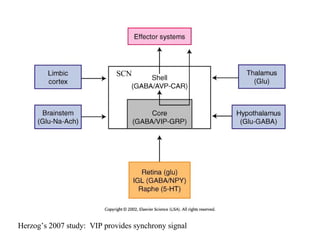
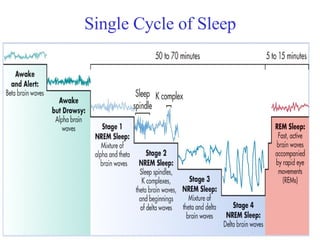
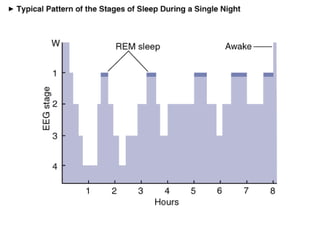
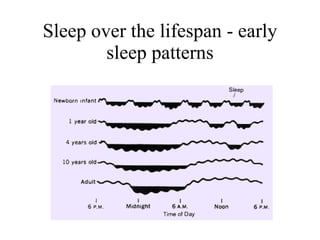
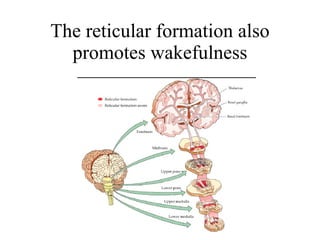
Circadian rhythms refer to biological cycles that occur over approximately 24 hours. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus acts as the master pacemaker regulating circadian rhythms. Lesions to the SCN abolish circadian rhythms, while transplanted SCN tissue can impart rhythms to recipient animals. The SCN receives light input from retinal ganglion cells that contain melanopsin photoreceptors sensitive to blue light wavelengths.