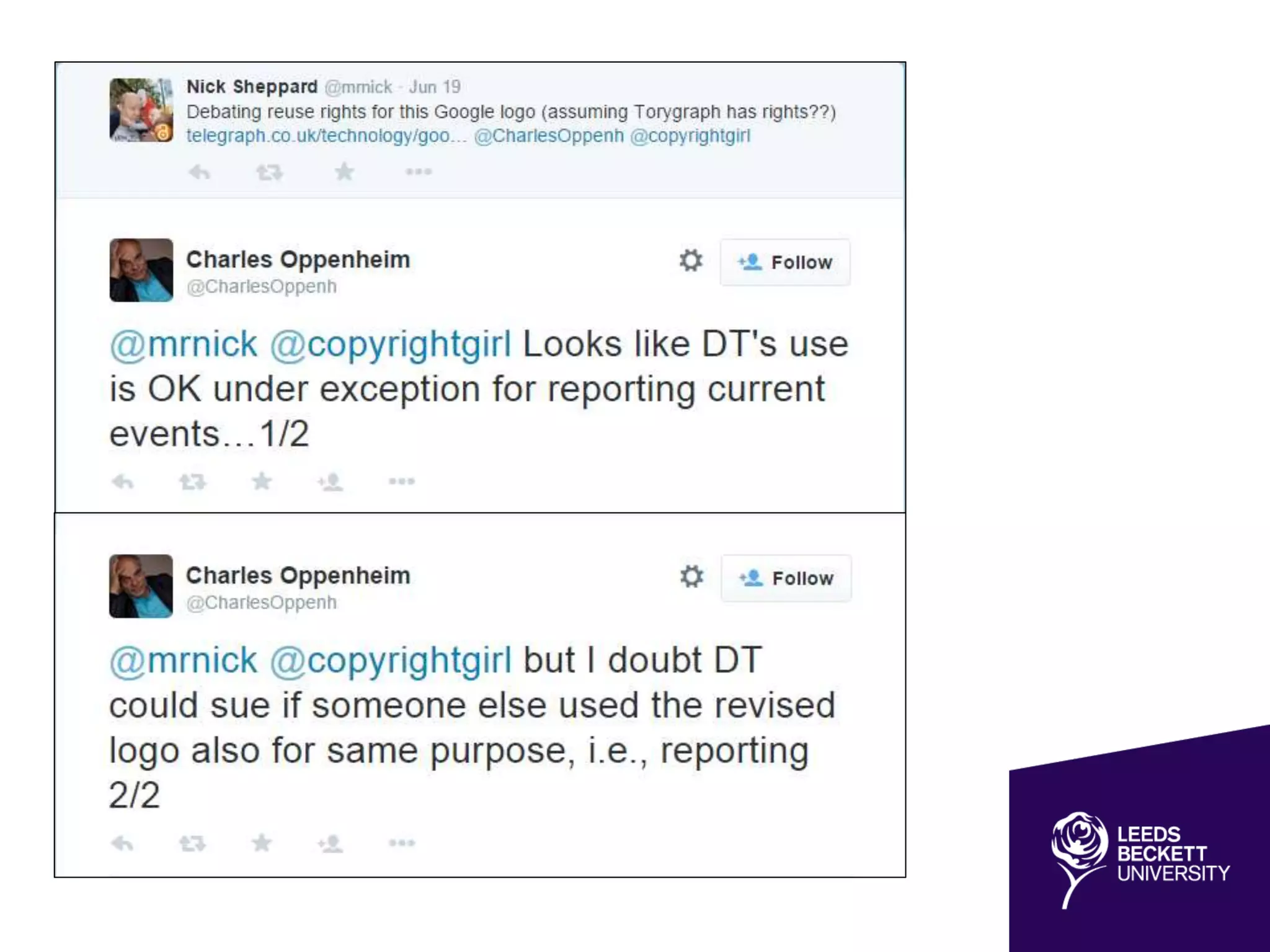
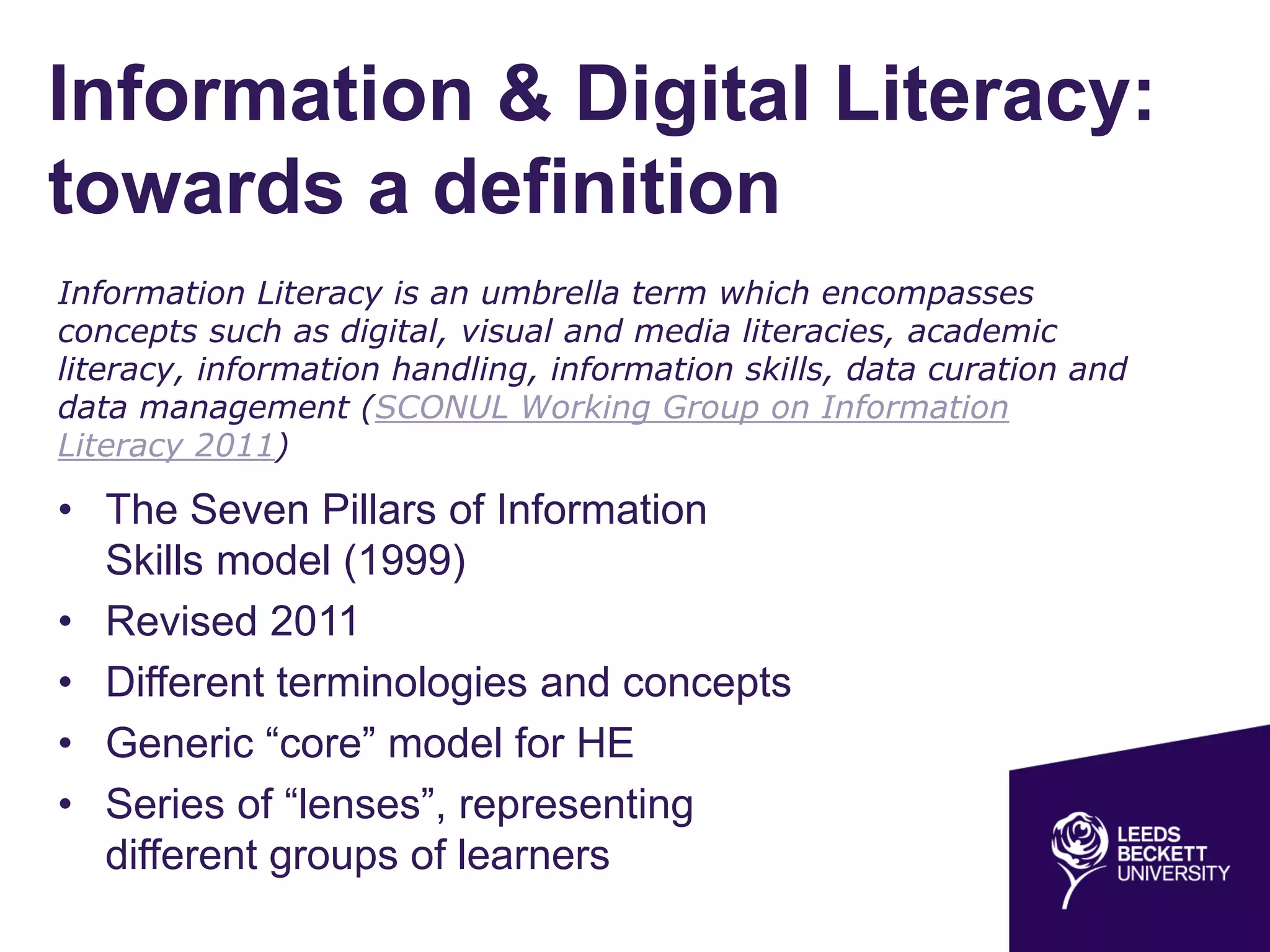
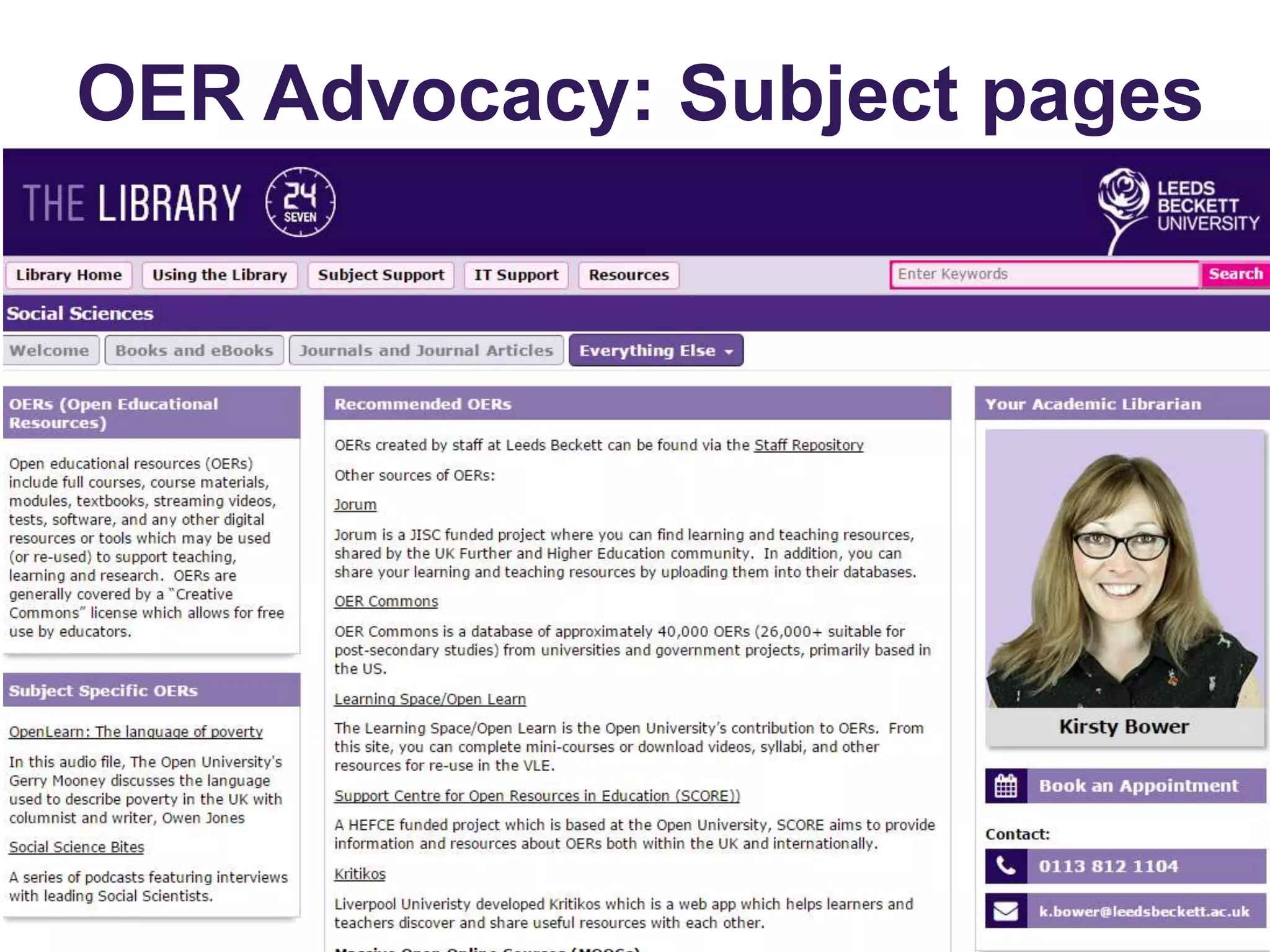
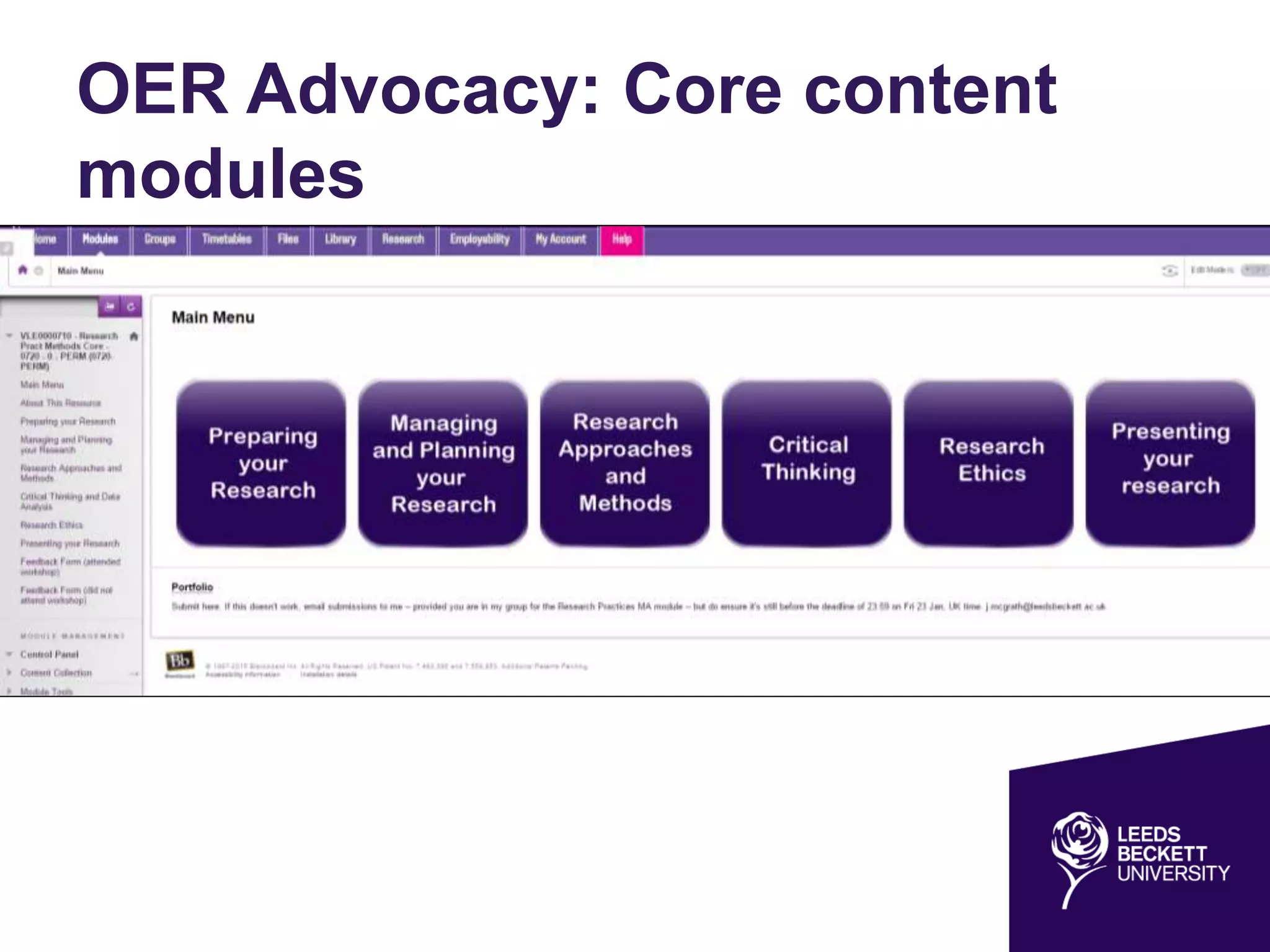
The document discusses the evolving landscape of information and digital literacy, emphasizing the importance of Open Educational Resources (OER) and institutional repositories in enhancing access to educational materials. It outlines the SCONUL Seven Pillars of Information Literacy and the role of tools like Xerte Online Toolkits in developing interactive learning resources. Additionally, it addresses copyright considerations, the integration of open access policies, and the synergies between open access and OER initiatives.