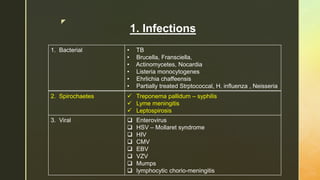
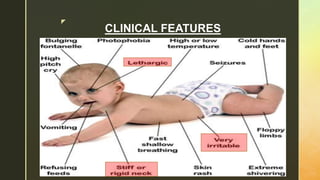
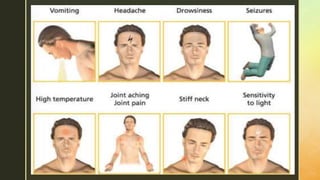
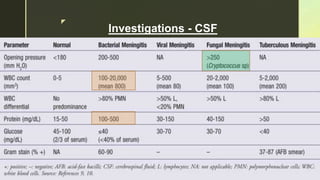
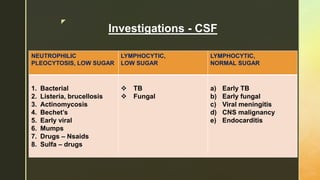
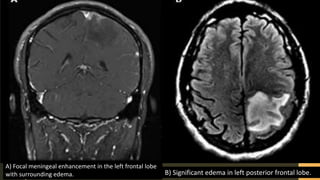
Chronic meningitis is defined as inflammation of the meninges lasting over 4 weeks, caused by infections (bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic), non-infectious inflammatory diseases, malignancies, or chemical factors. Symptoms can include hydrocephalus, cranial neuropathies, and cognitive decline, with a thorough patient history and examination needed for diagnosis. Treatment involves identifying the causative agent, with options including empirical therapy, anti-tubercular treatment, or antifungal medications, depending on the specific cause.