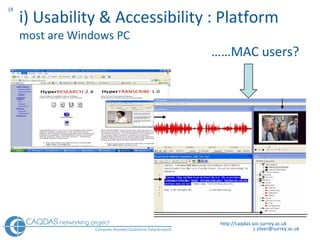
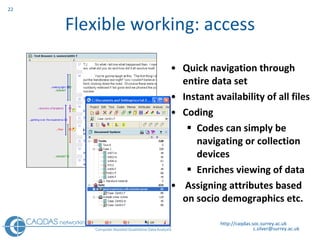
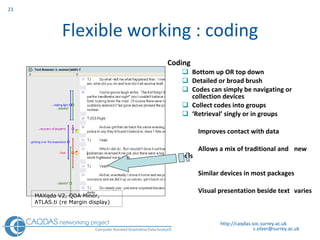
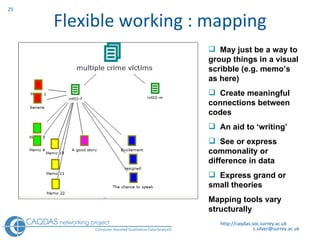
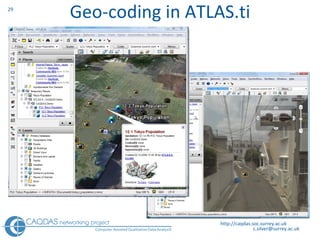
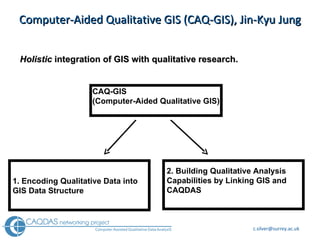
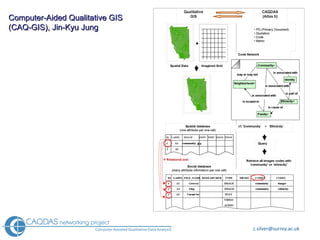
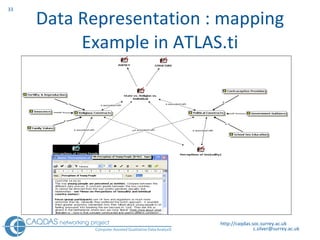
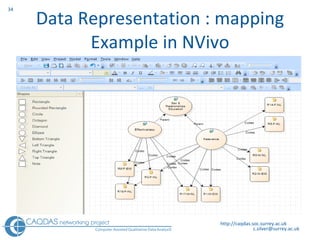
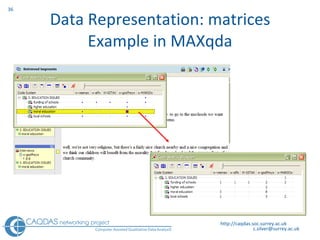
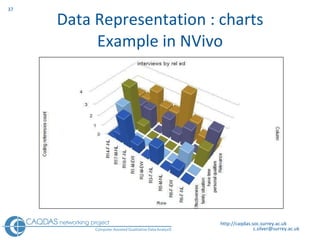
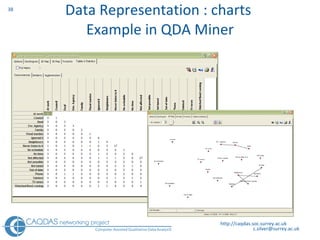
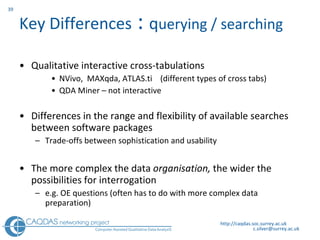
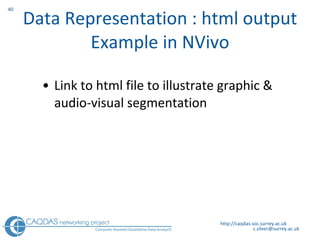
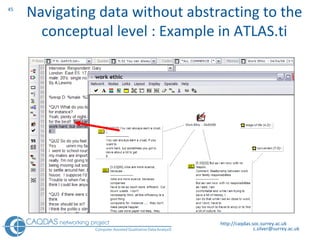
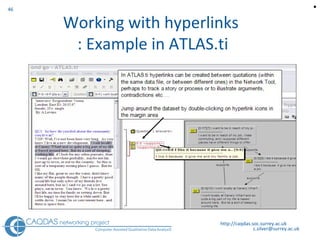
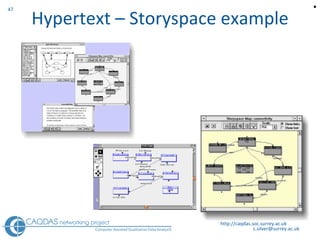
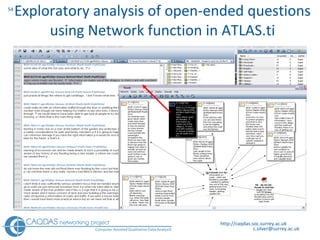
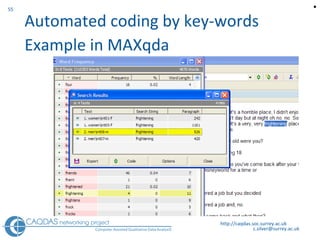
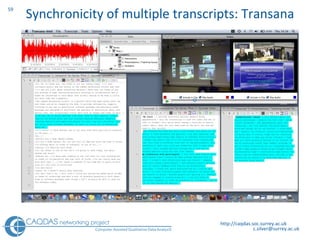
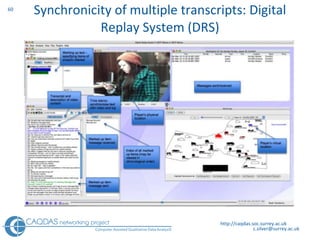
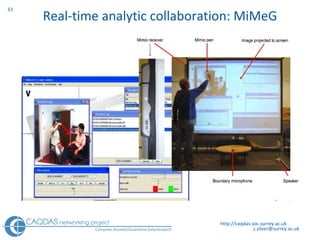
The document provides an overview of computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software (CAQDAS), including key functionalities, comparisons of leading packages, and their suitability for different research methodologies. It emphasizes the importance of critical evaluation in selecting software tools based on project requirements and offers guidance on budgeting and obtaining free or low-cost options. Additionally, it discusses the integration of qualitative and quantitative data, the evolving relationship between technology and methodology, and the representation of data through various tools.