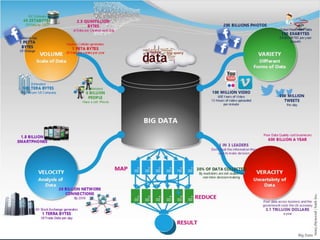
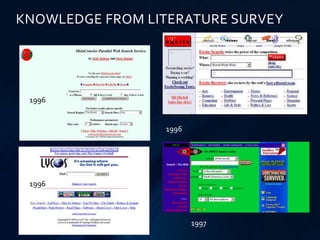
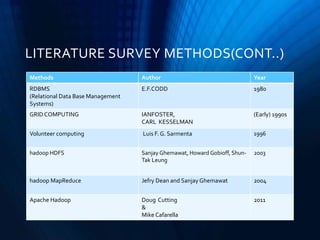
The document discusses big data analytics using Hadoop, highlighting its capability to analyze vast datasets for uncovering business insights and enhancing operational efficiency. It outlines challenges in data processing, such as data silos and the handling of unstructured data, and emphasizes the advantages of adopting technologies like MapReduce and HDFS. Additionally, it reviews the history of Hadoop's development and applications in various sectors, concluding that effective big data analytics can significantly improve business decisions and outcomes.