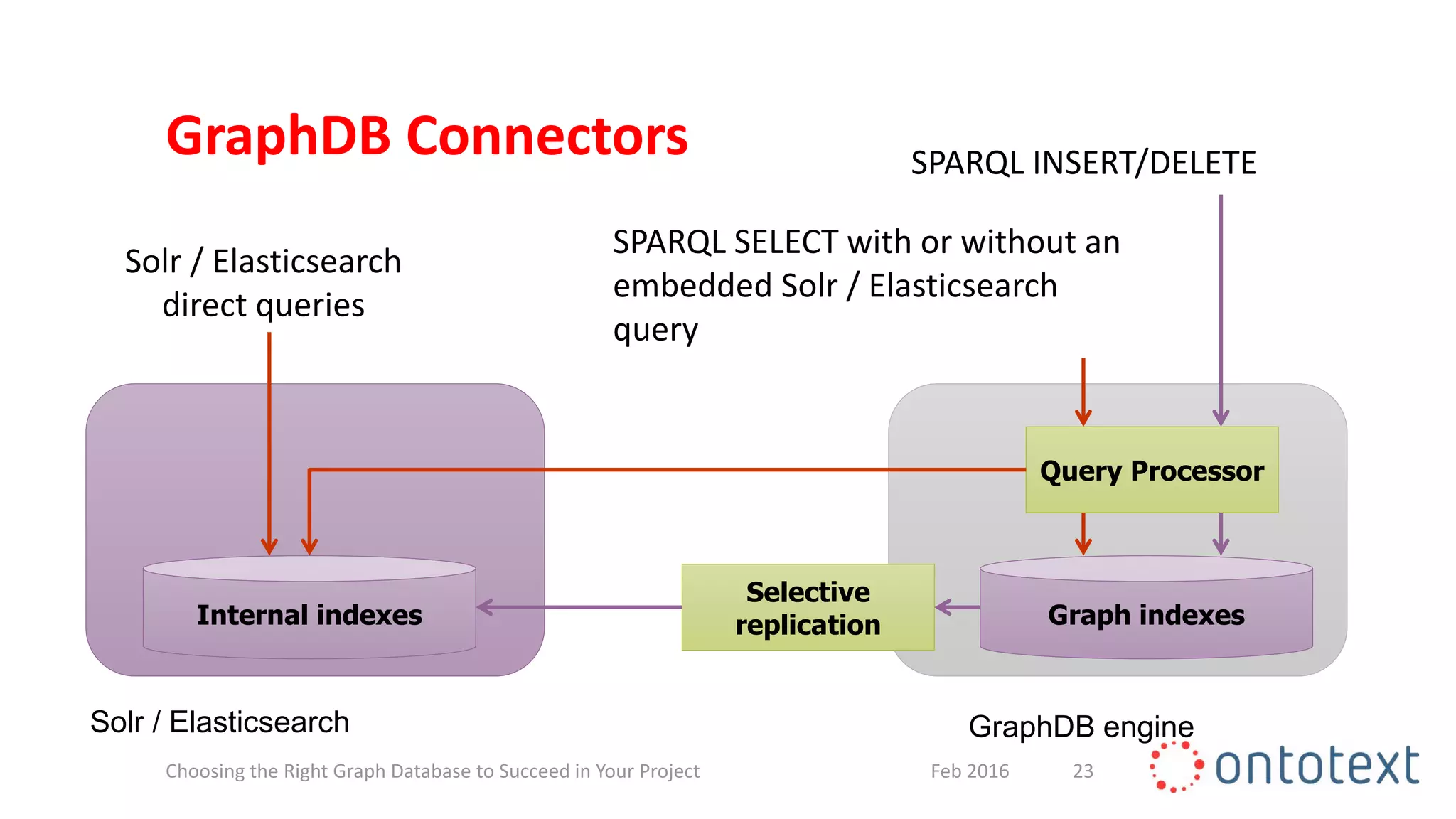
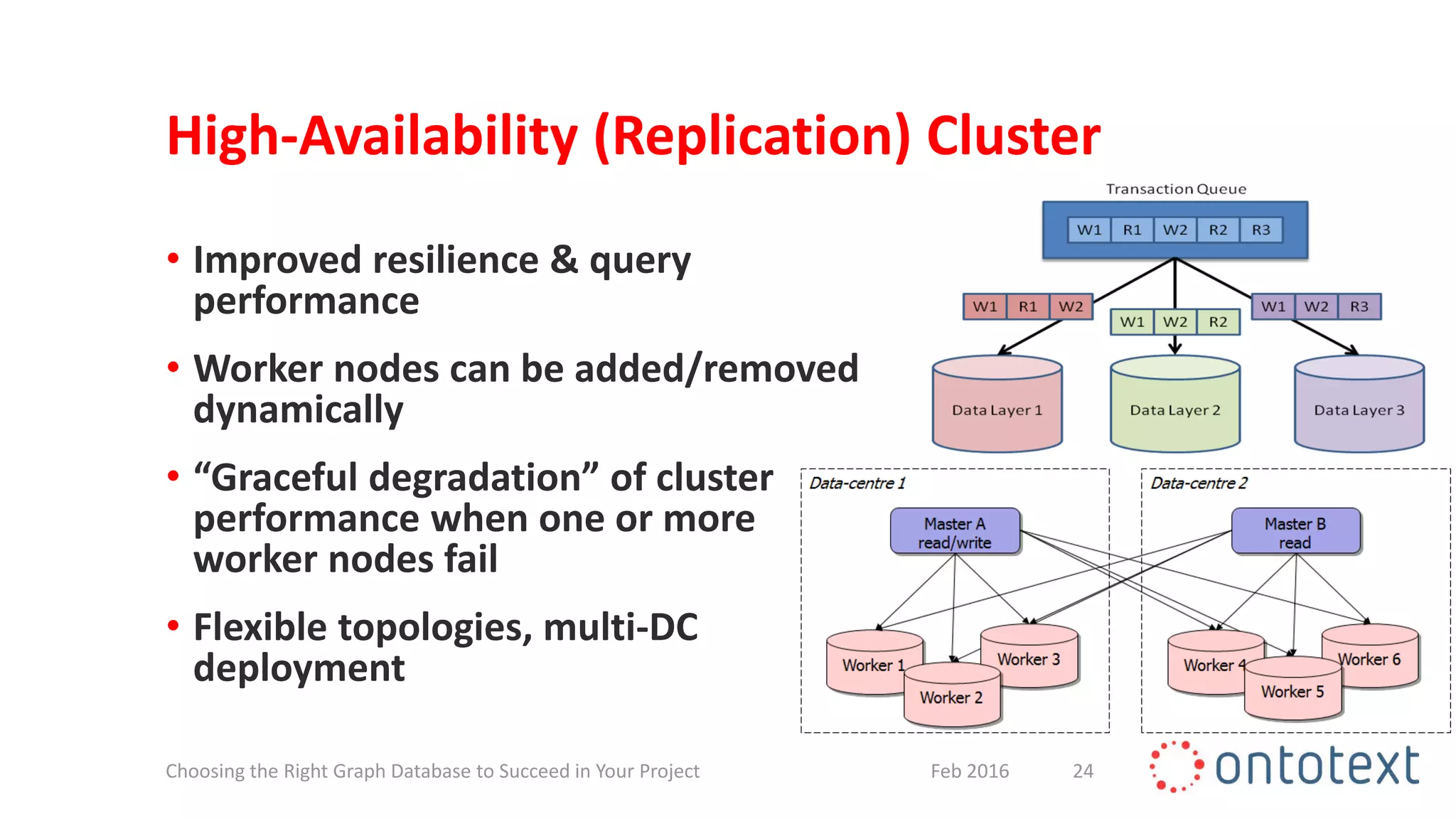
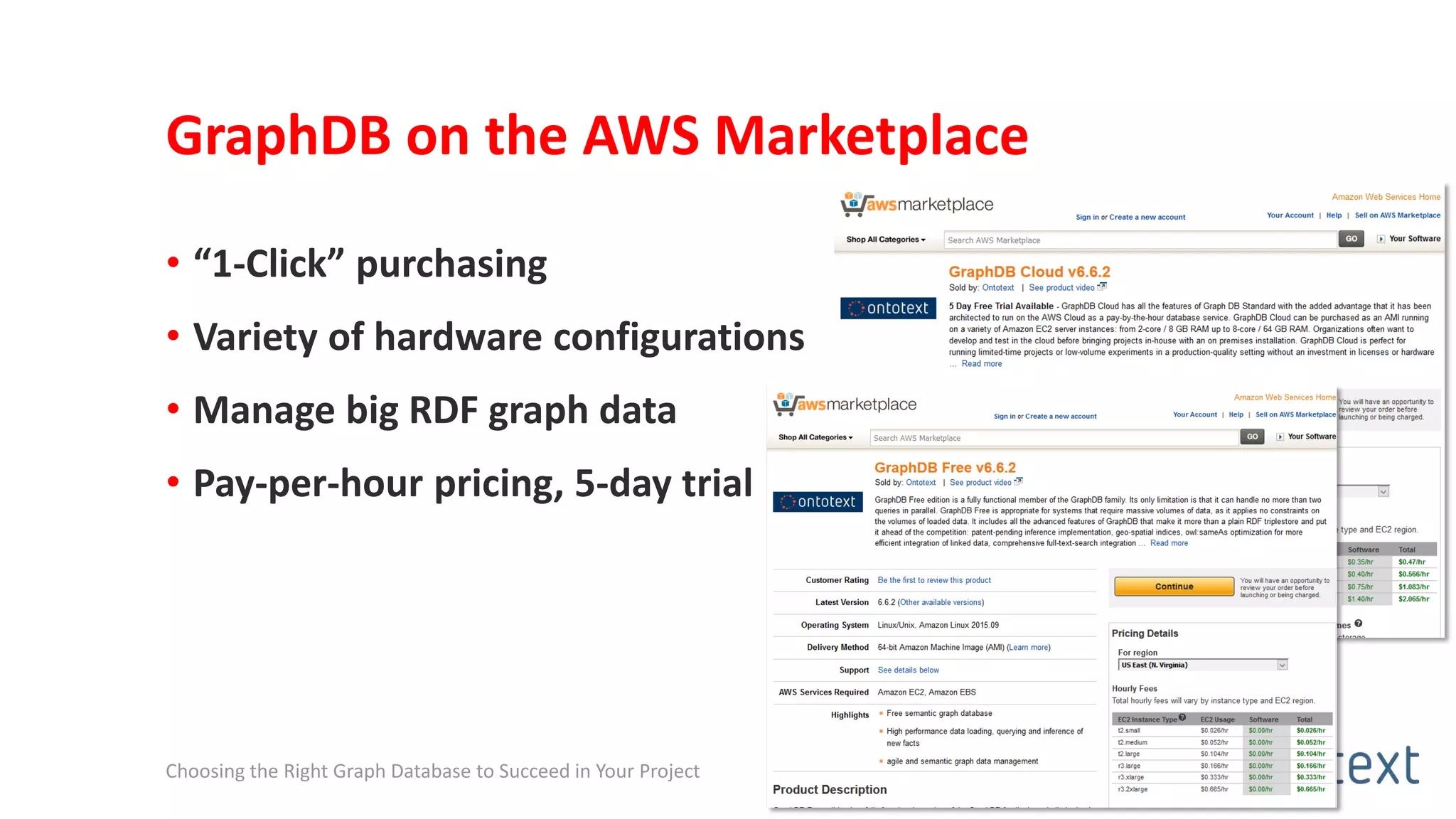
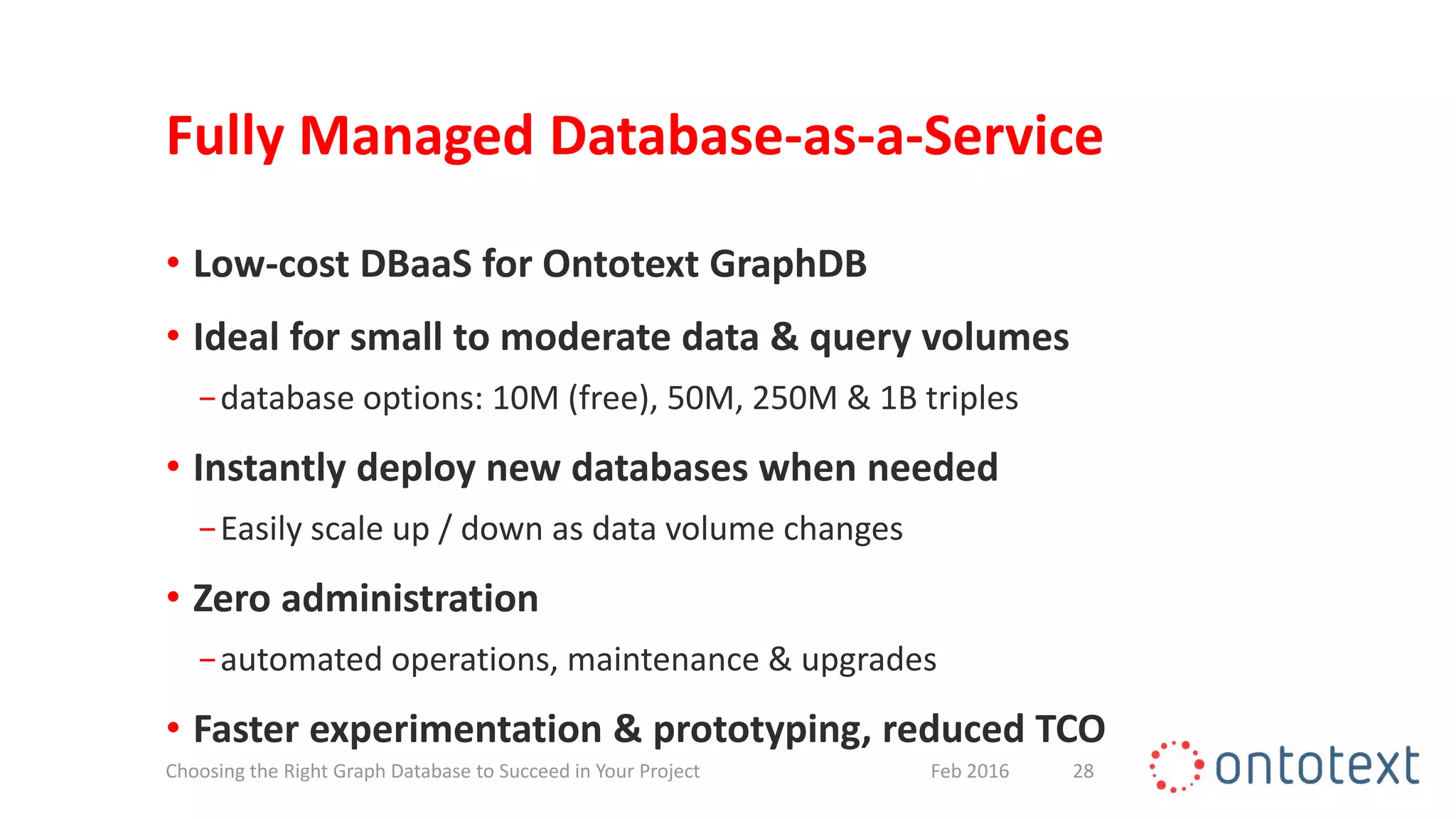
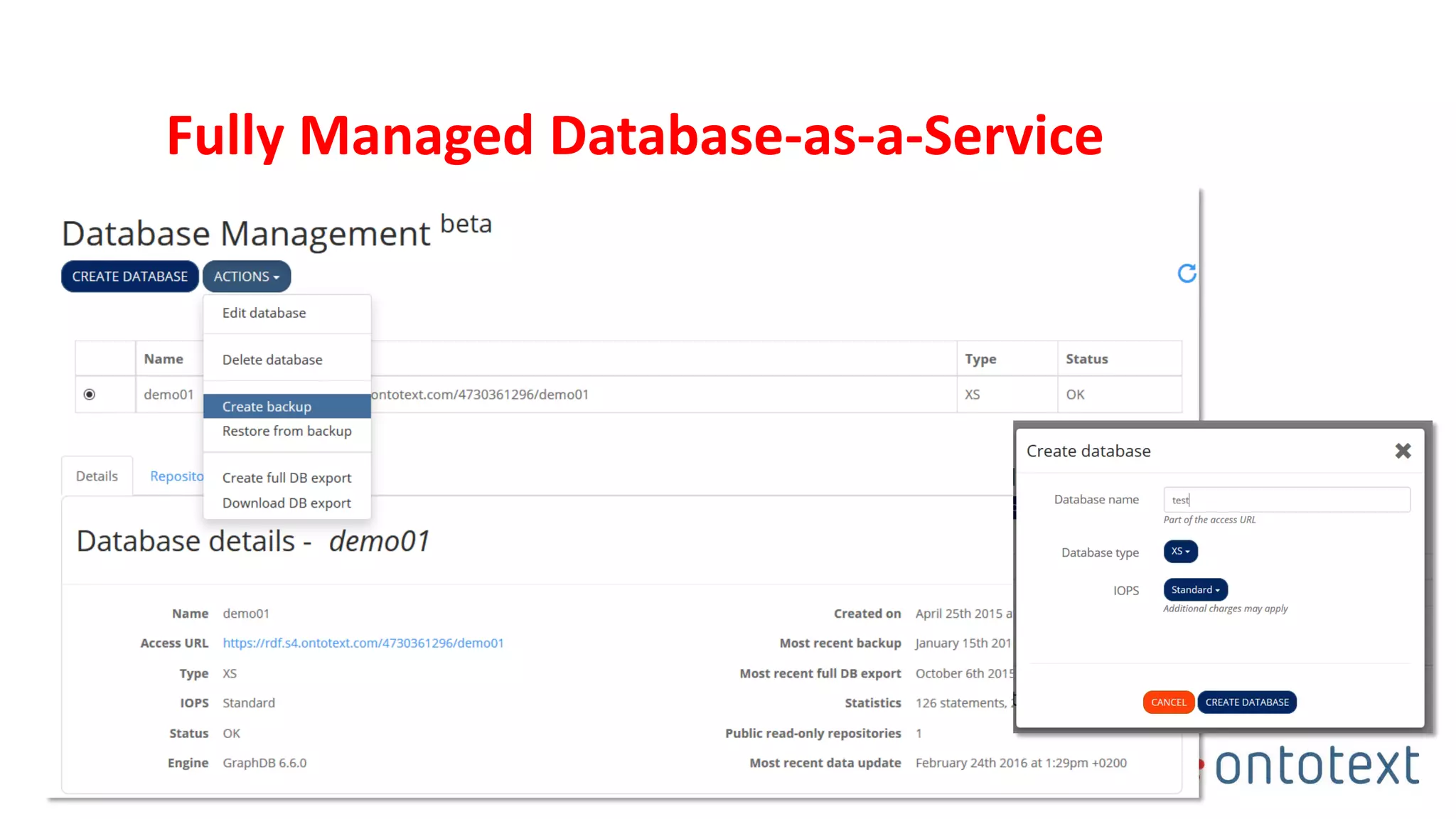
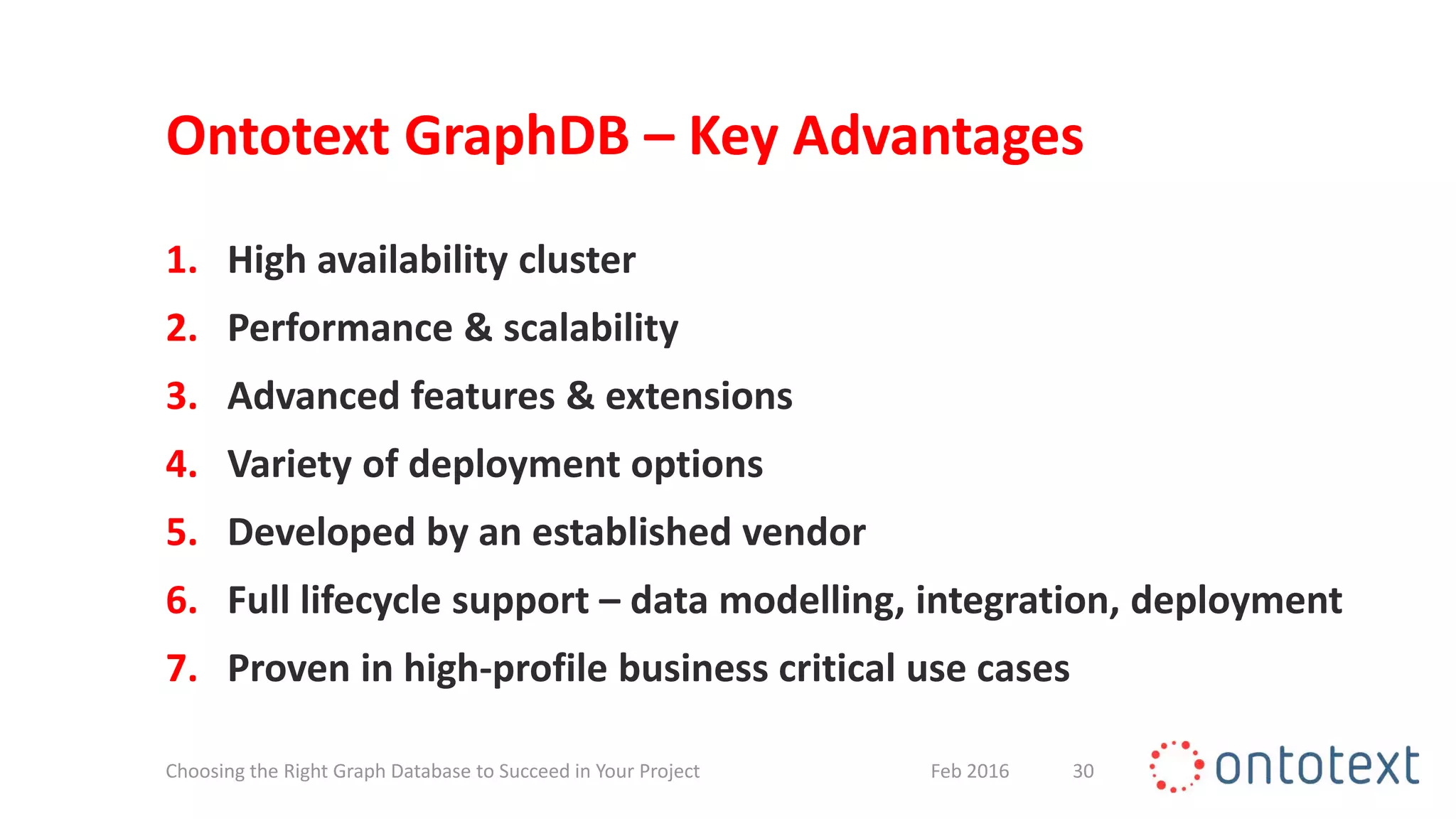
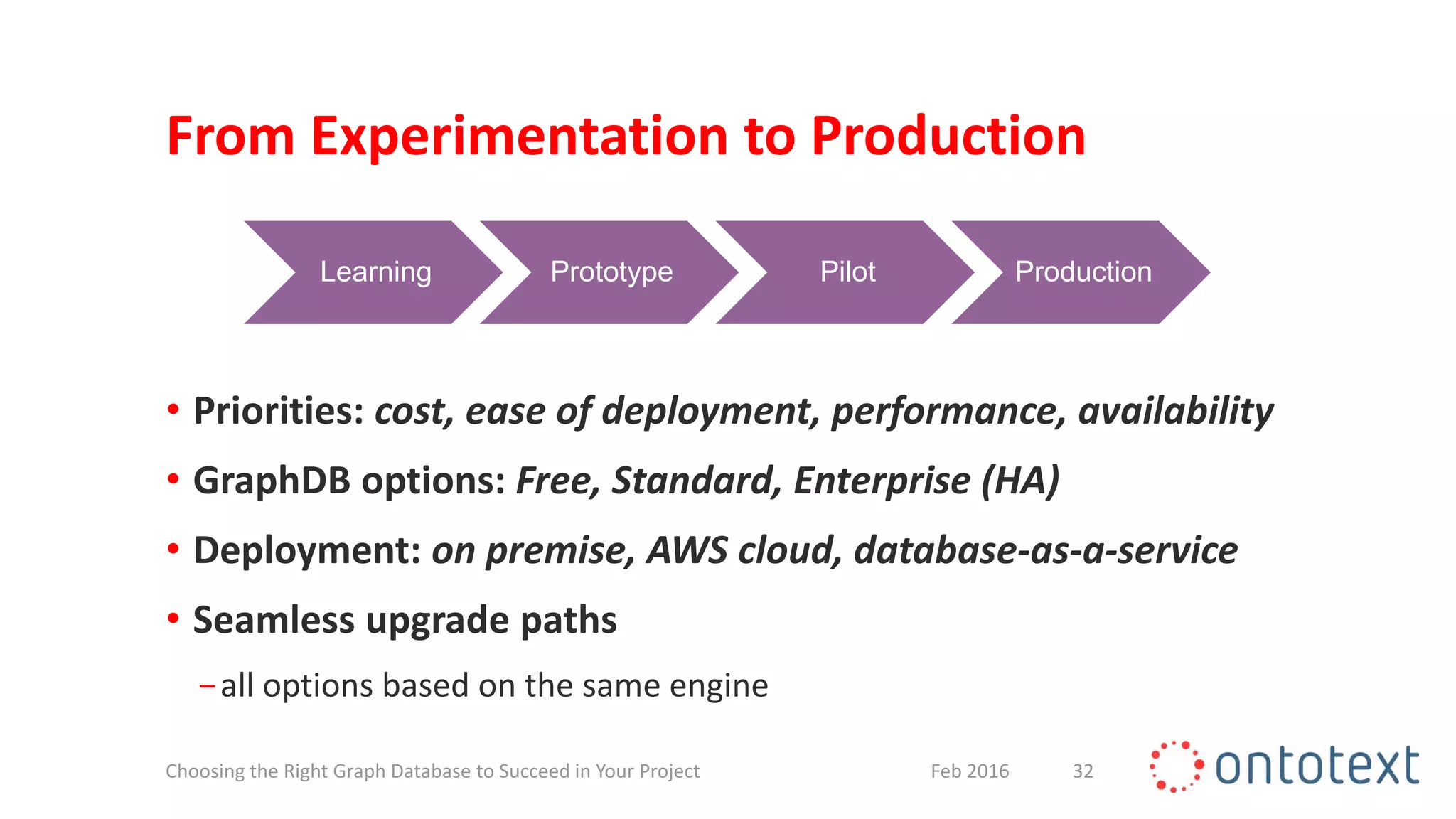
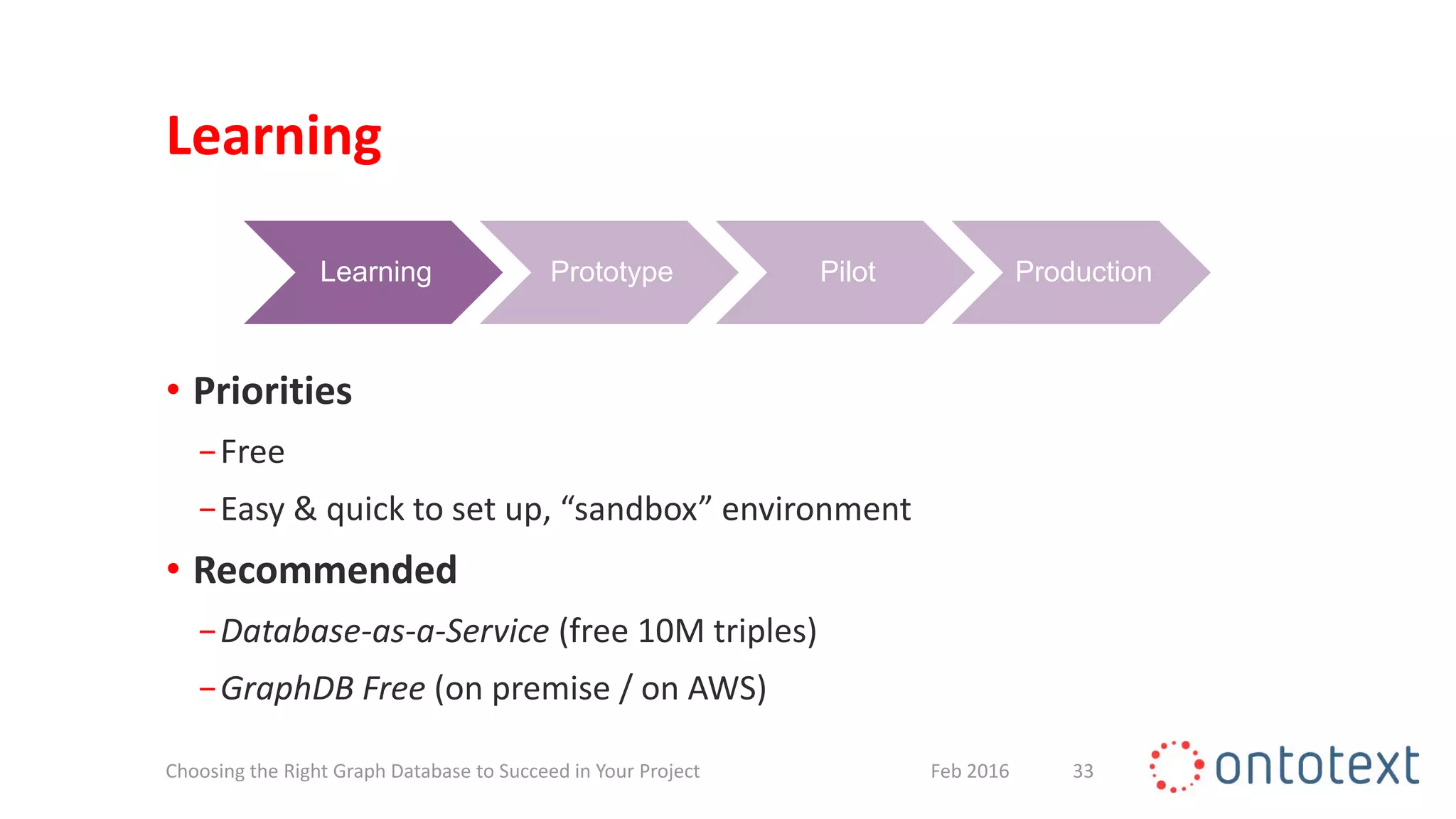
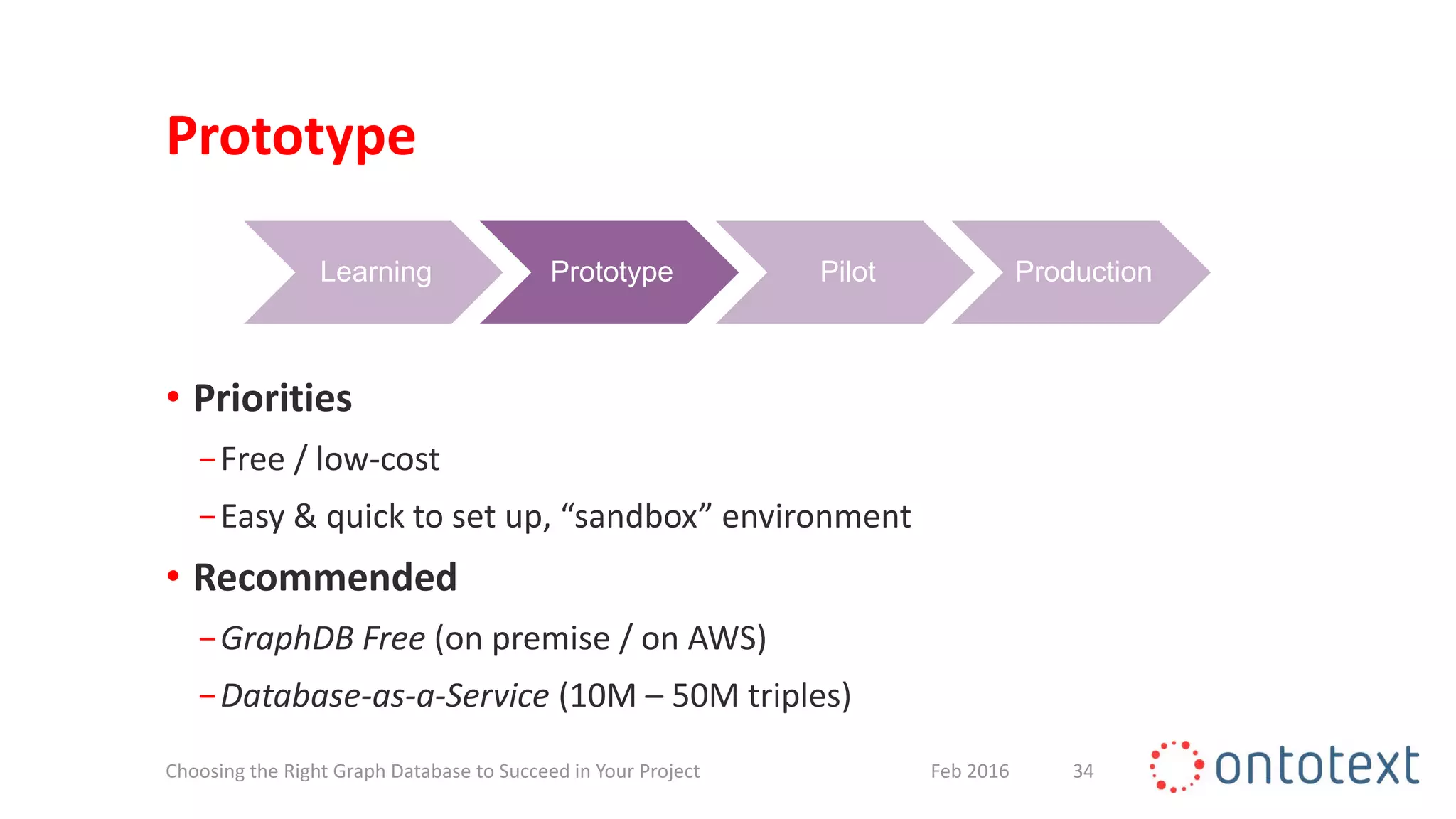
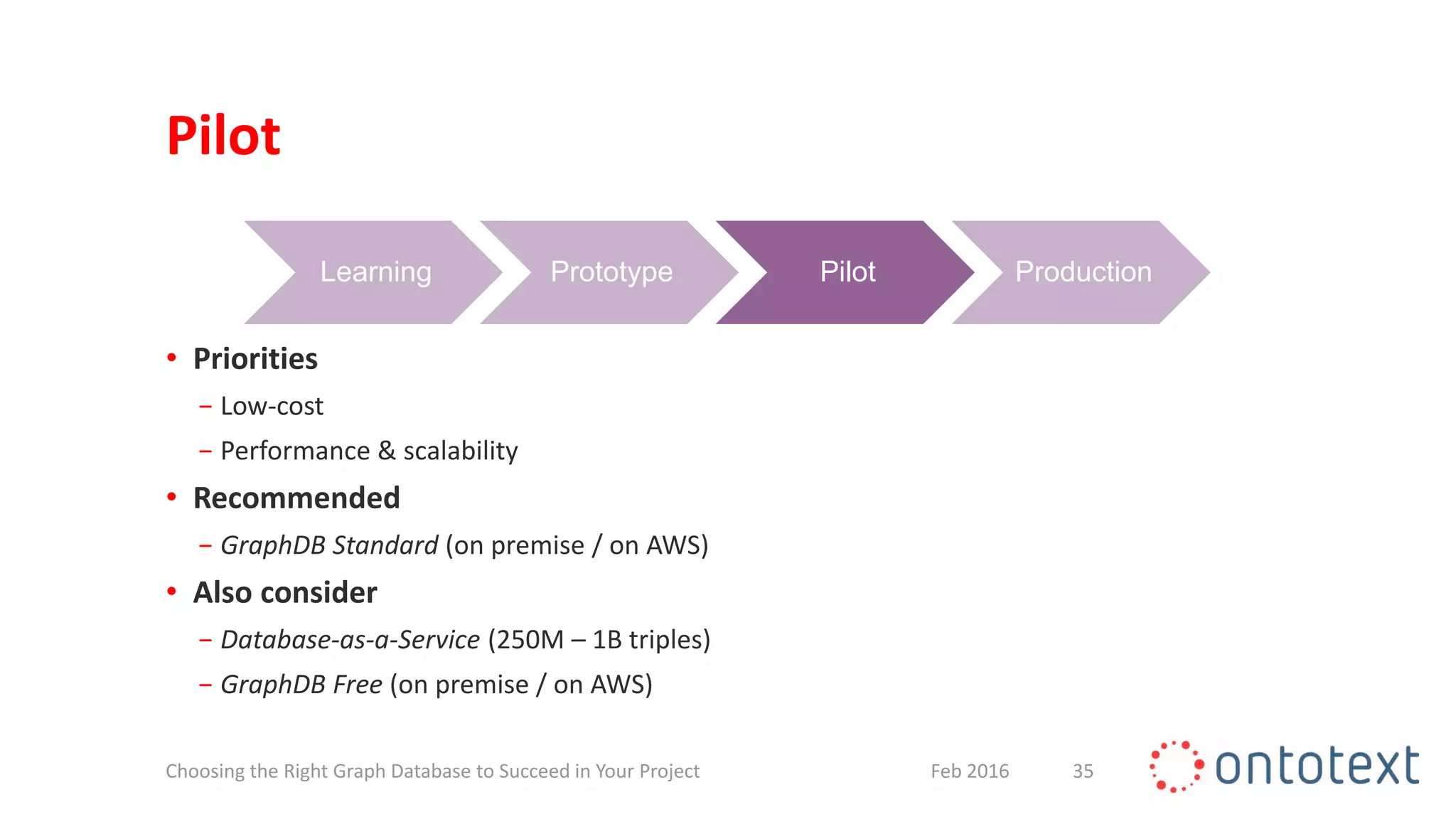
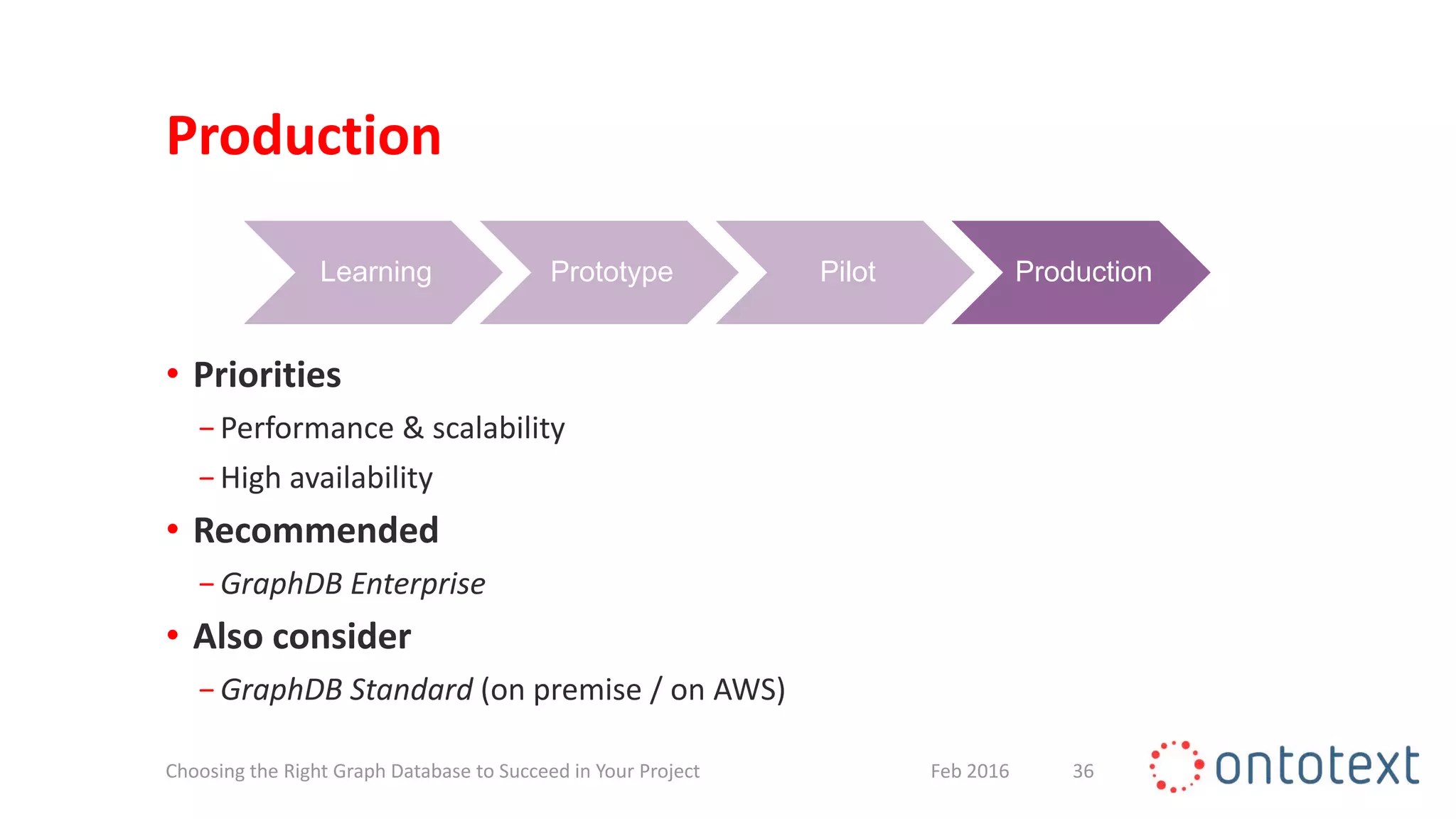
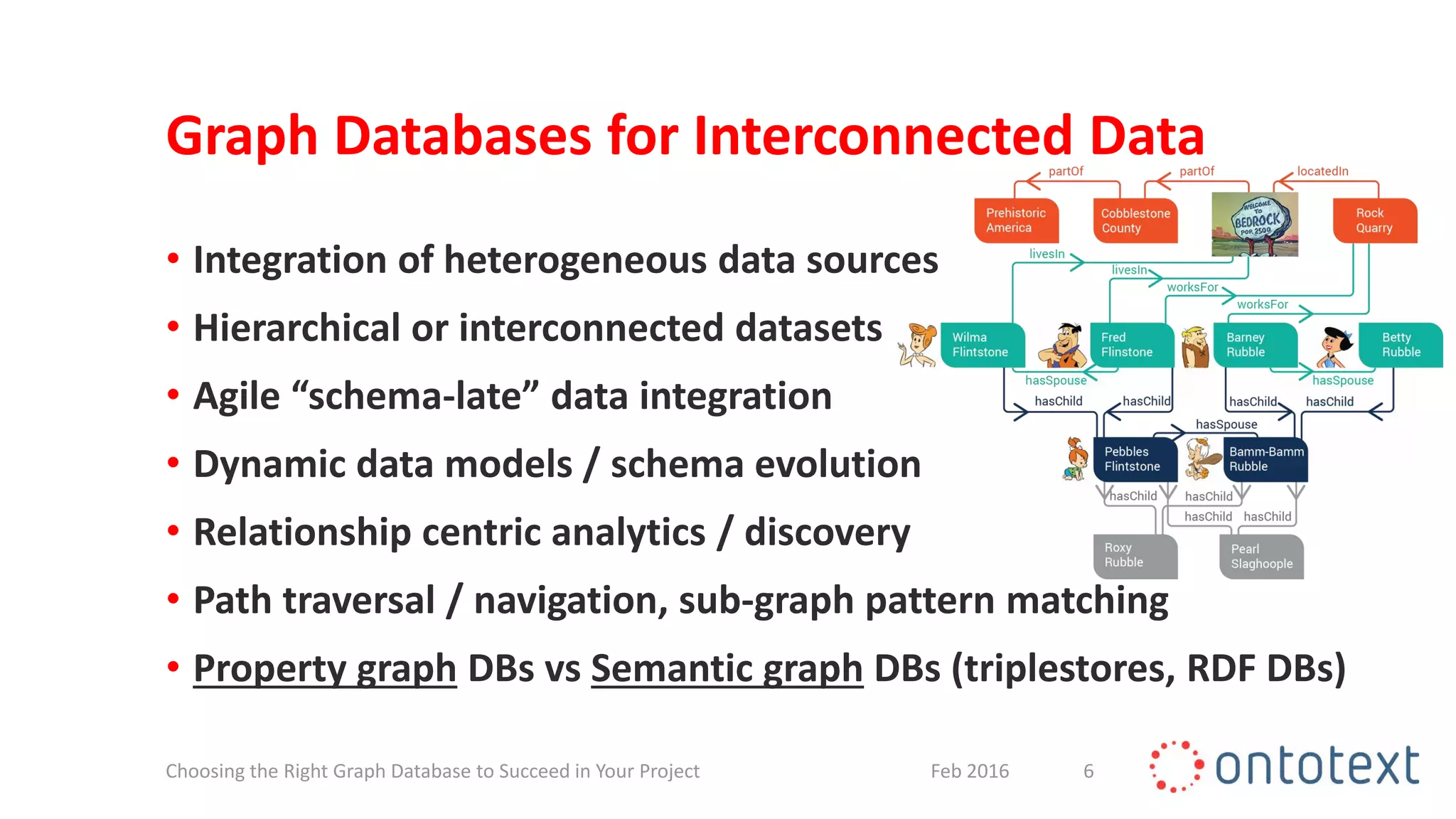
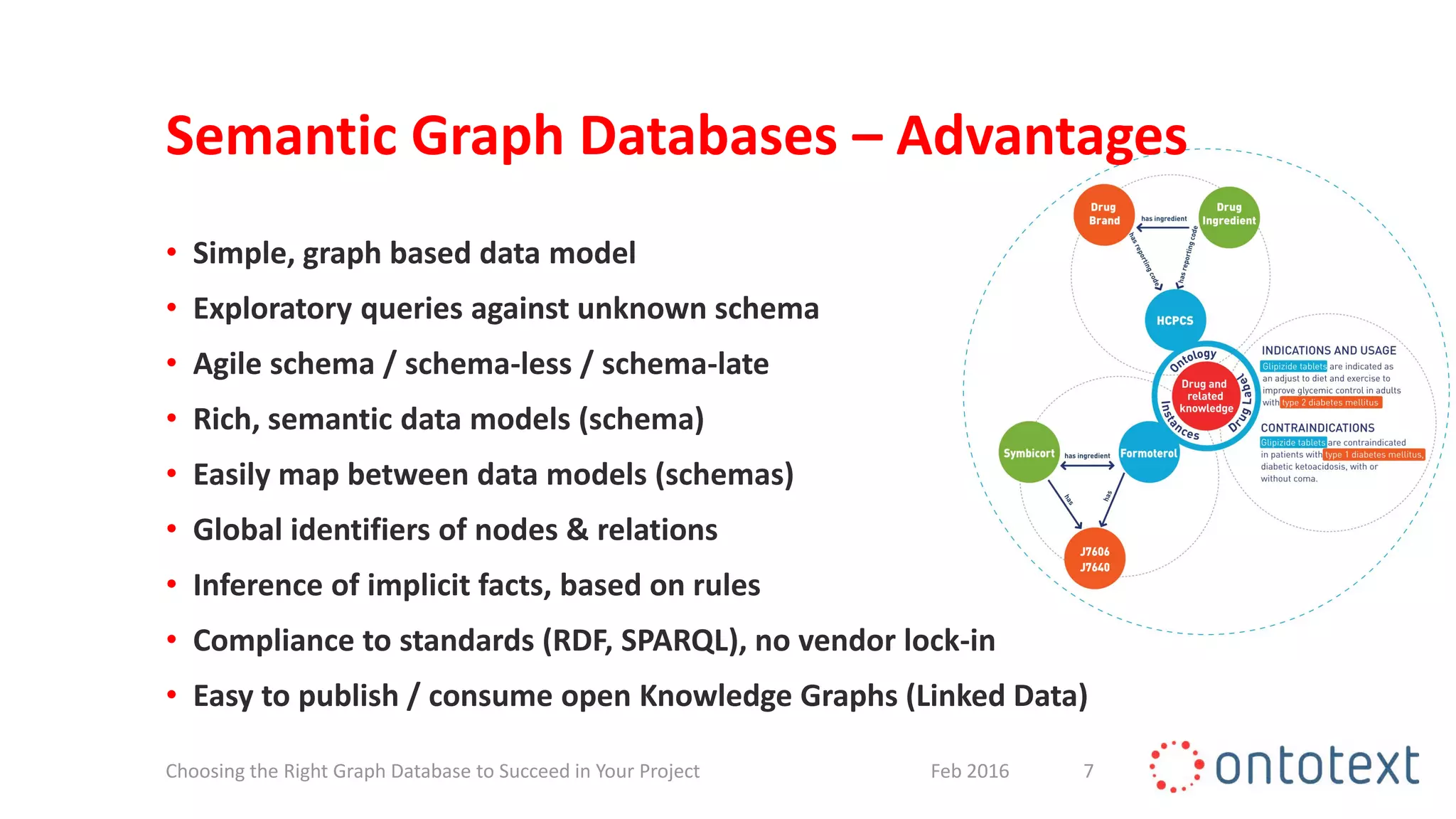
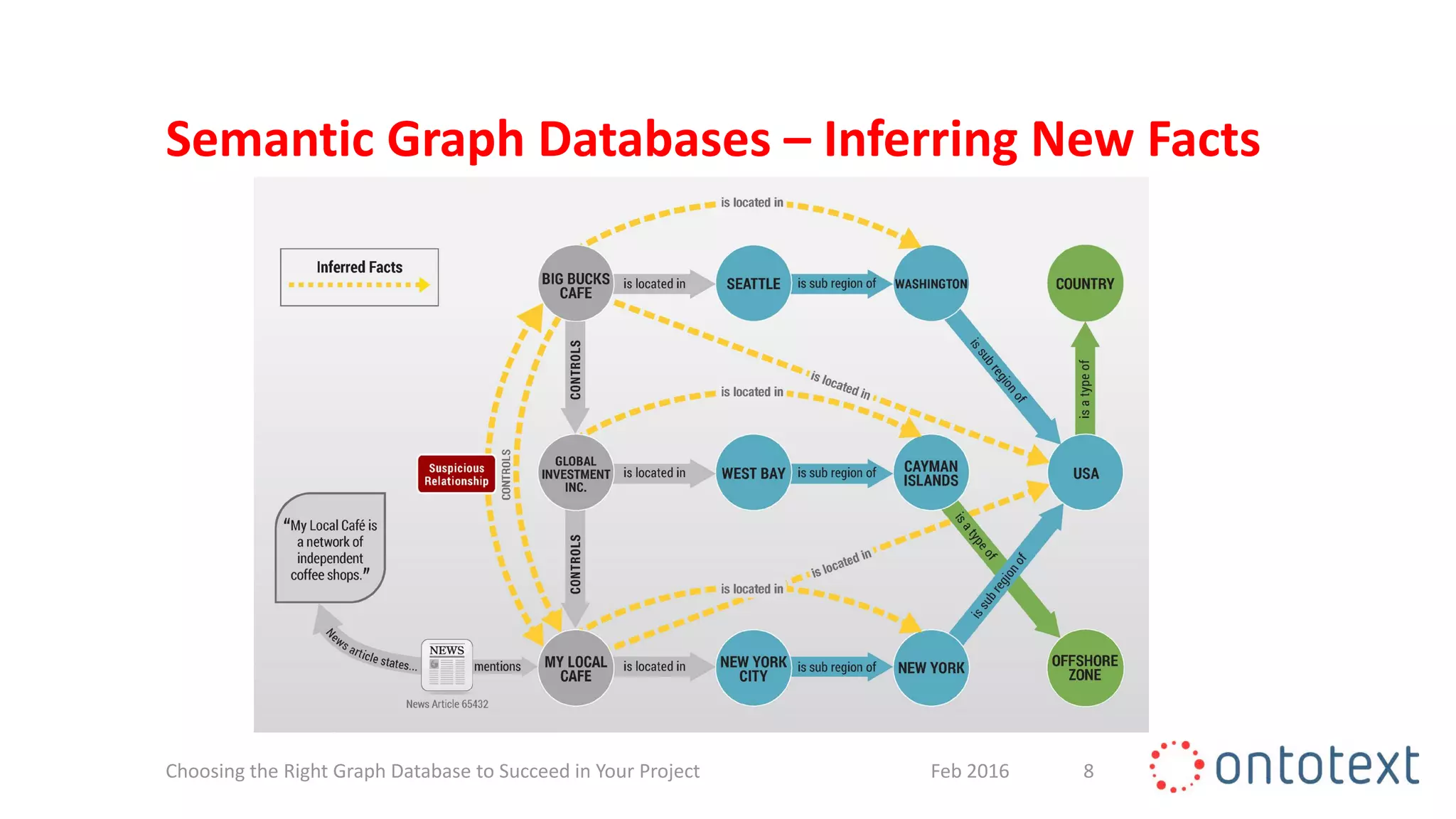
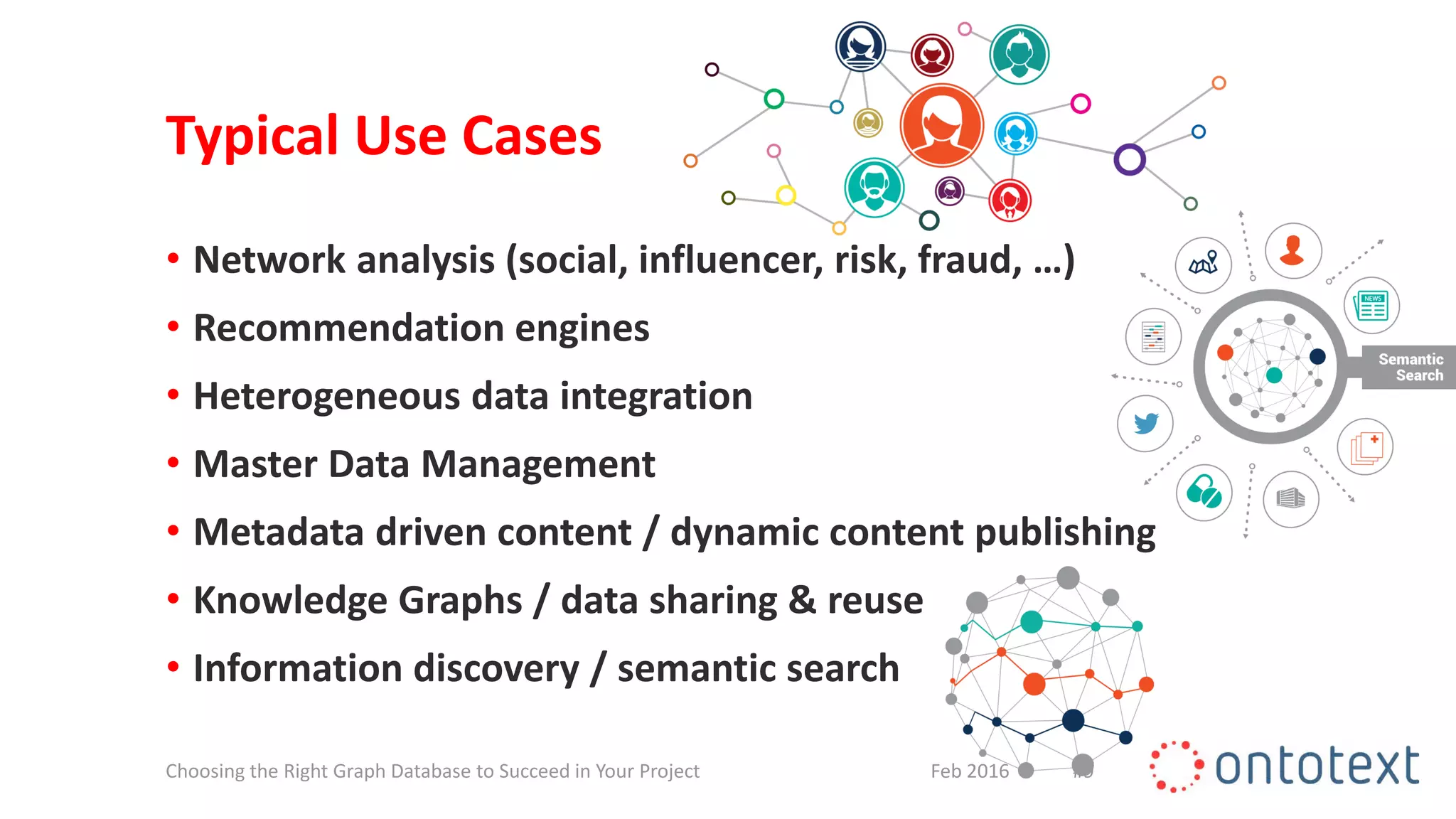
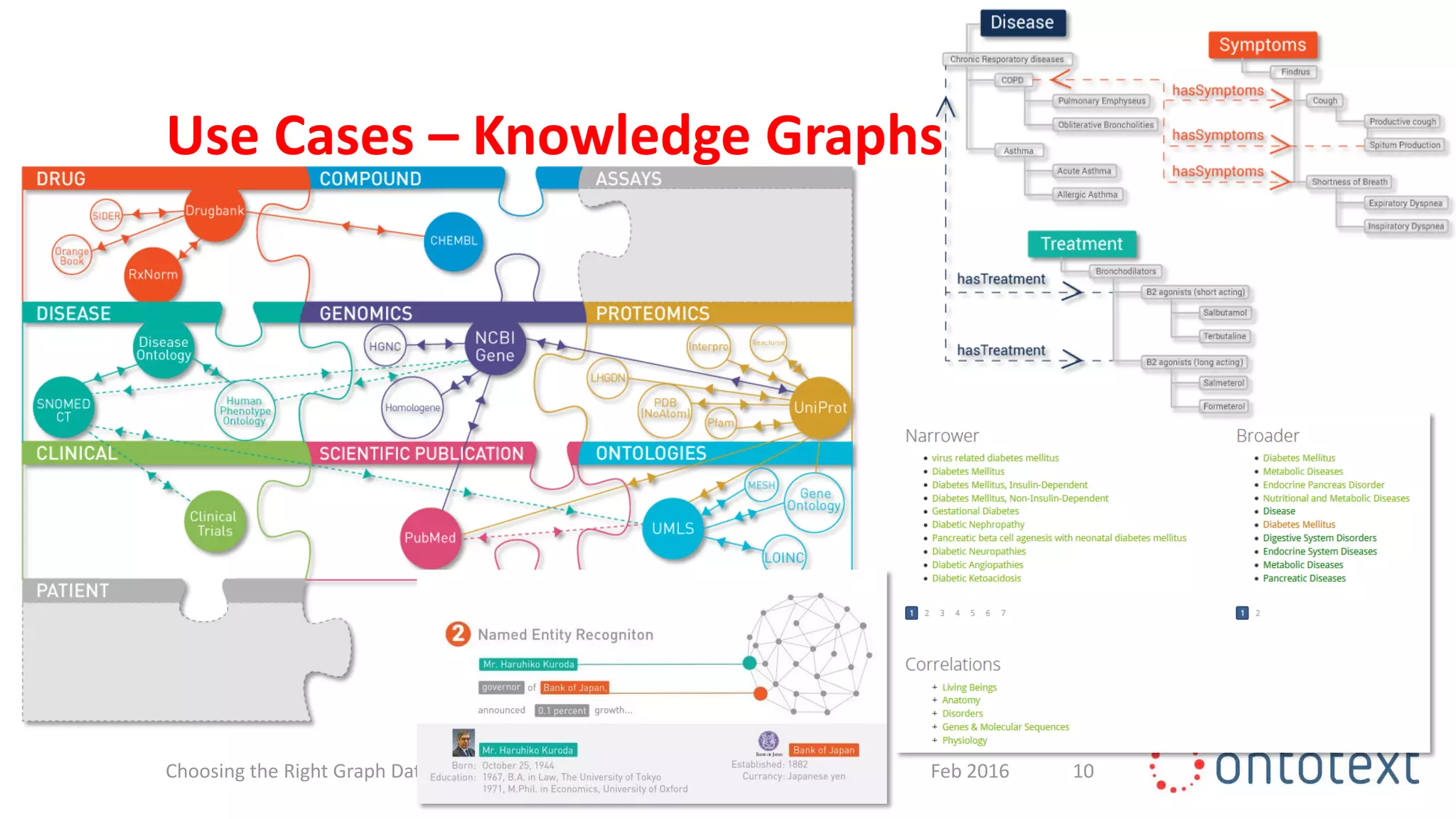
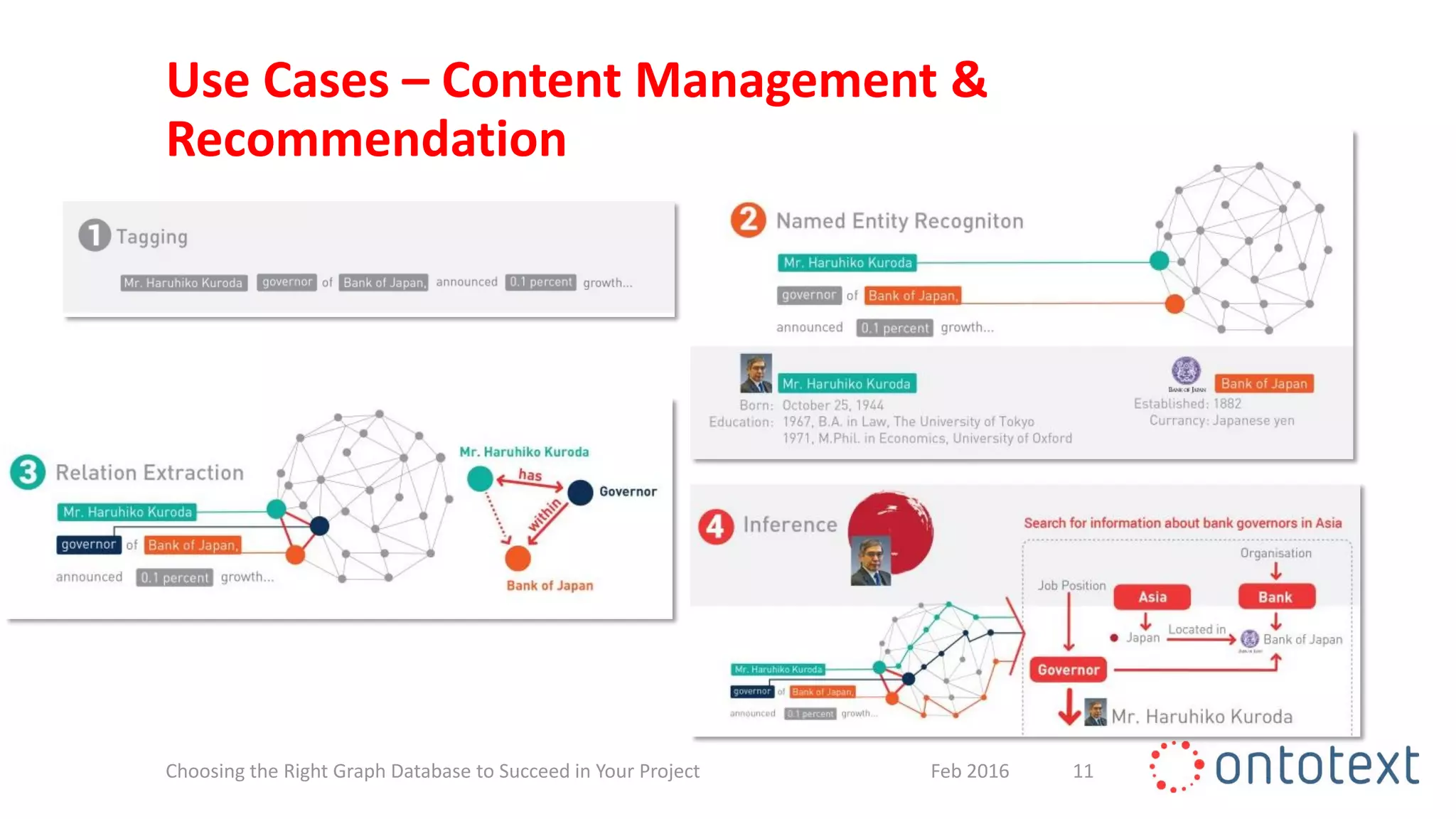
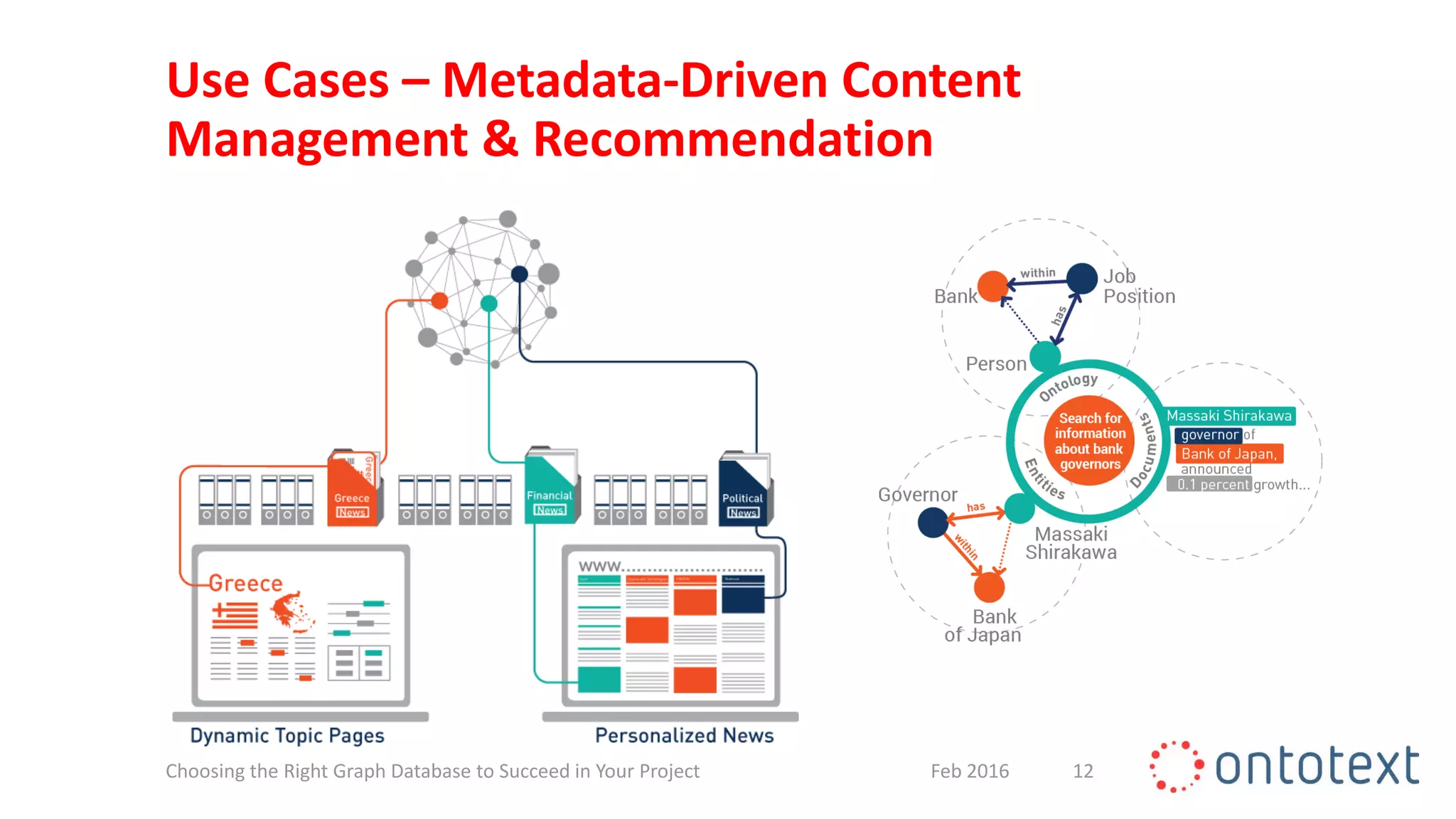
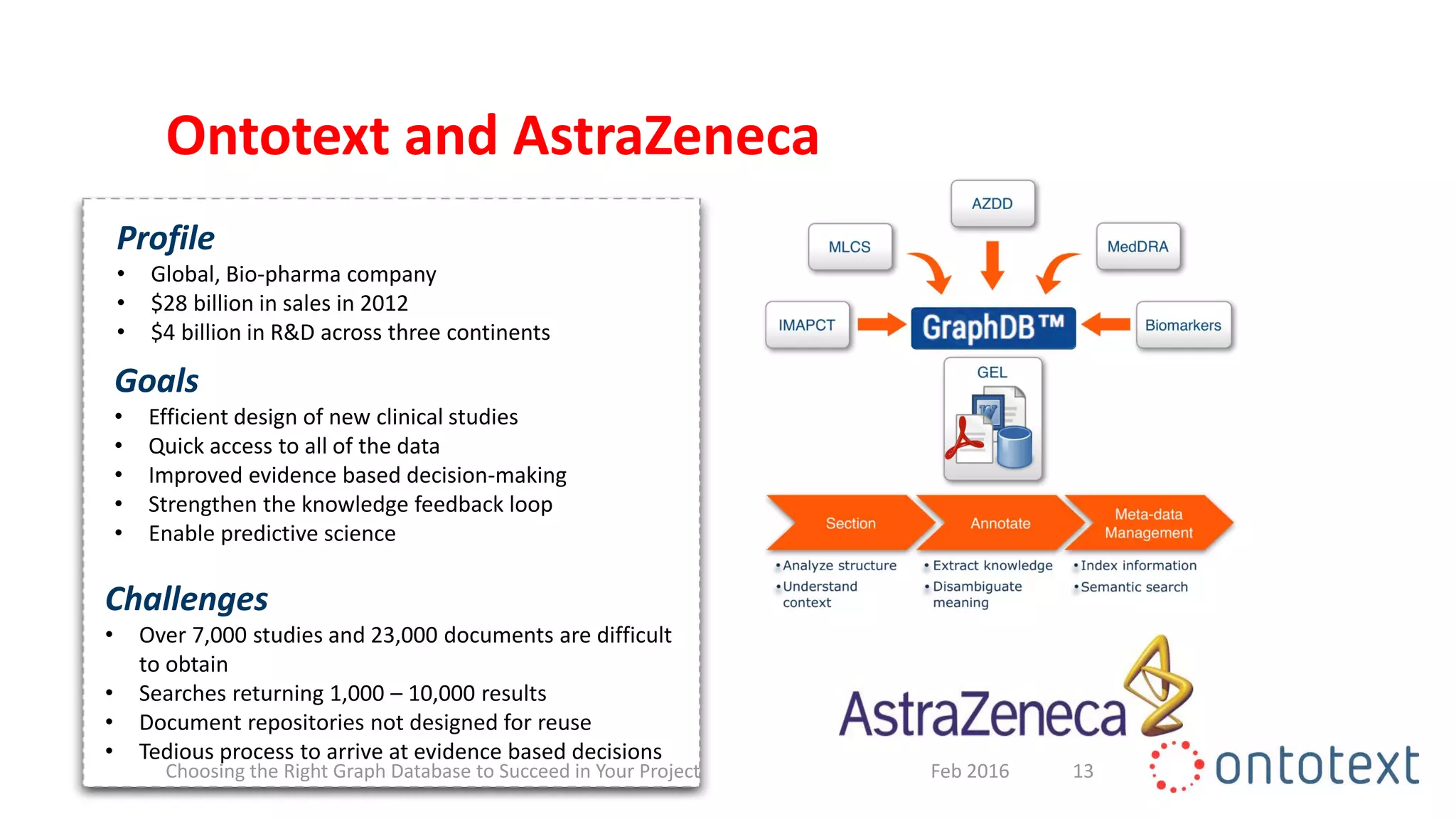
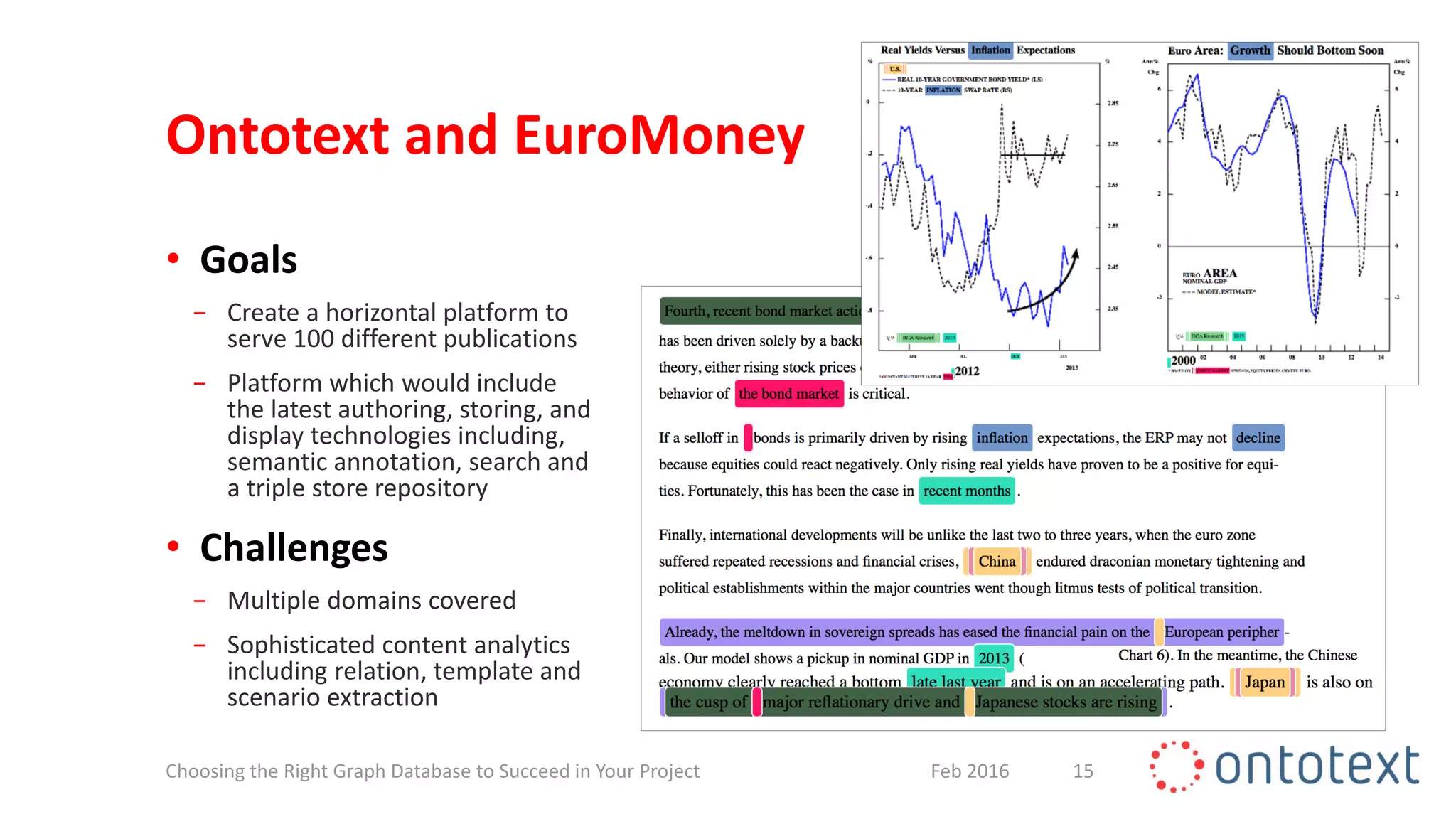
The document discusses choosing the right graph database for projects. It describes Ontotext, a provider of graph database and semantic technology products. It outlines use cases for graph databases in areas like knowledge graphs, content management, and recommendations. The document then examines Ontotext's GraphDB semantic graph database product and how it can address key use cases. It provides guidance on choosing a GraphDB option based on project stage from learning to production.



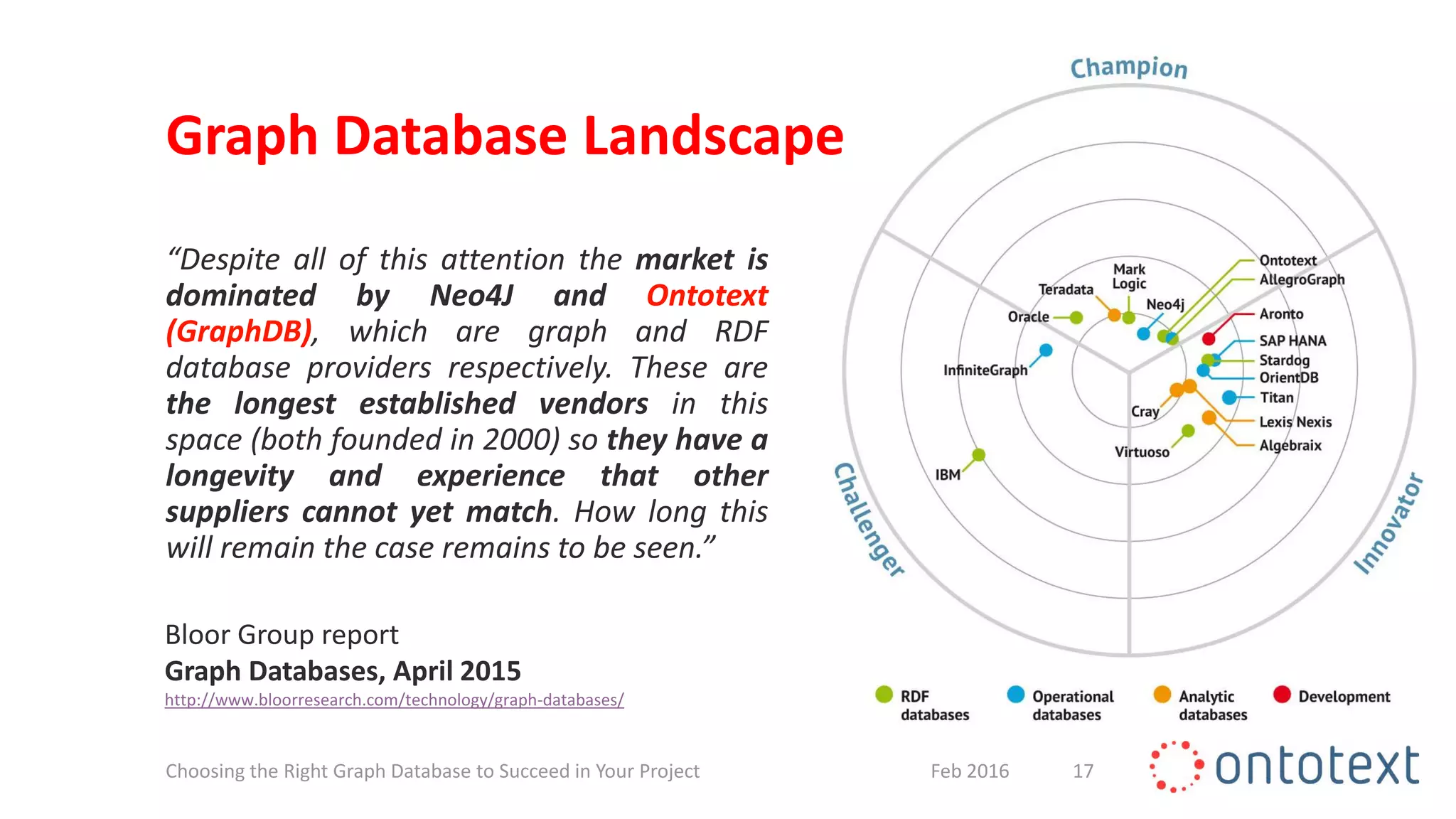
![Graph Database Landscape
“Linking a few data sources is often simple,
but to do so with significant amounts of
heterogeneous data requires a radically new
approach. Graph databases are a powerful
optimized technology that link billions of
pieces of connected data to help create new
sources of value for customers and increase
operational agility for customer service. […]
they are well-suited for scenarios in which
relationships are important.”
Forrester report
Market Overview: Graph Databases, May 2015
https://www.forrester.com/Market+Overview+Graph+Databases/fulltext/-/E-RES121473
18Feb 2016Choosing the Right Graph Database to Succeed in Your Project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/choosingtherightgraphdatabasewebinarslides-160229142025/75/Choosing-the-Right-Graph-Database-to-Succeed-in-Your-Project-18-2048.jpg)