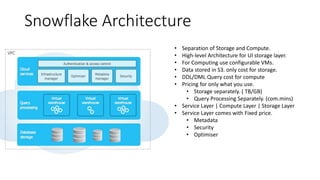
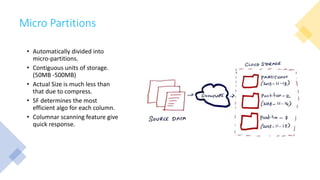
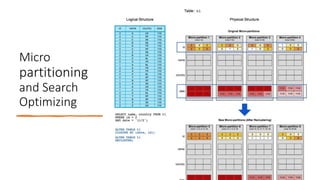
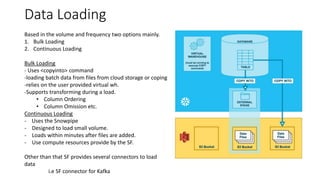
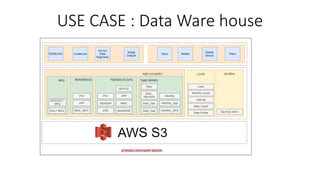
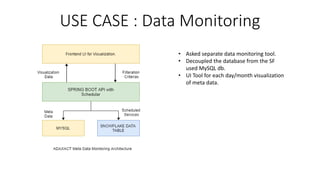
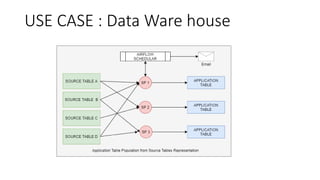
Snowflake is a SaaS data warehousing platform that operates on cloud infrastructure (AWS, Azure, GCP) without requiring hardware or software management from the user. Its architecture separates storage and compute, allowing for scalable and cost-efficient processing, while features like micro-partitioning and various data connectors enhance performance. Key use cases include data loading through bulk or continuous methods, and it offers a simplified approach compared to traditional databases.