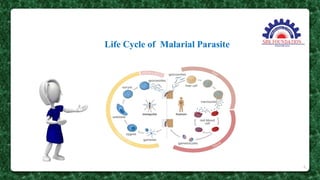
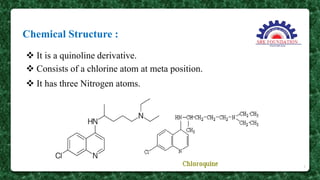
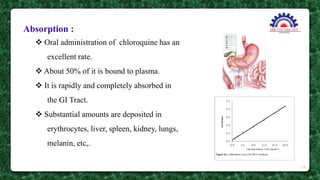
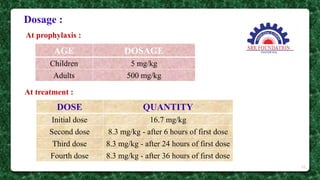
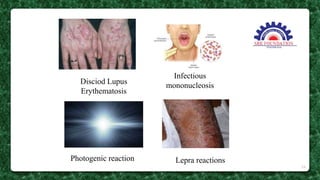
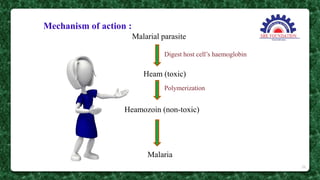
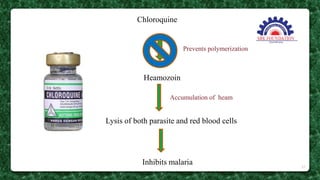
This document presents information on the drug chloroquine, an anti-malarial agent. It discusses chloroquine's introduction, chemical and physical properties, pharmacokinetics, mechanisms of action, indications, contraindications, interactions, and administration. Key points include that chloroquine is a quinoline derivative effective against malaria parasites, it has excellent oral absorption and distributes widely in tissues, and its primary mechanisms involve preventing heme detoxification and accumulating toxic levels of heme in parasites.